Solanaceae
Quick Summary:
Herbs, vines, shrubs, or trees.
- Flowers perfect, radially or bilaterally symmetrical. Sepals 5, fused. Petals 5, fused. Stamens 2, 4, or usually 5, epipetalous, sometimes with anthers connivent (converging or coming together but not fused). Pistil compound, ovary superior, carpels 2.
- Fruit a berry or capsule.
- Leaves simple or occasionally pinnately lobed to compound, alternate, without stipules.
- About 85 genera and more than 2200 species, primarily in tropical America.
The Solanaceae is not a significant family in the flora of B. C., but it is one of the most important in agriculture.
Representatives of this family provide food medicine, poison and ornamental plants. Important crops include Solanum (potato, eggplant), Lycopersicon (tomato), Physalis (tomatillo, ground cherry), Capsicum (red, yellow and green pepers), and Nicotiana (tobacco).
Alkaloids from Atropa (deadly nightshade or belladonna), Hyoscyamus (henbane), Datura, Mandragora (mandrake), and Brunfelsia are used as drugs, hallucinogens, or poisons. Petunia is the most important ornamental member of the Solanaceae in temperate region.
Petunia and Nicotiana
| Petunia: Petunias are a common garden plant. |
 Petunia plant |
 Petunia flower |
 Petunia flower, side view |
| Nicotiana: There are a number of Nicotiana plants grown horticulturally. Species of this genus are also grown for their leaves (tobacco). |
 Nicotiana plant |
| The flowers are long and the petals form a tube. |
 Nicotiana Flower |
| To the right is a longitudinal section through the flower. You should be able to identify all of the floral components. |
 Nicotiana flower, longitudinal section |
| This is the fruit (a capsule) of tobacco. |
 Fruit of tobacco, a capsule |
Solanum
| Solanum dulcamara (European Bittersweet): This is commonly found along roadsides and “waste lands”. Many of the members of the Solanaceae have large anthers which form a yellow cone in the centre of the flower. The stamens are attached to the purple petals. |
 Solanum flowers |
| The pollination mechanism of this type of flower is very interesting. The bee hangs upside down and buzzes, generating vibrations which cause the pollen to fall onto the body of the insect. The bees collect the pollen and take it back to the hive where it is fed to the developing larvae. Of course they cannot collect all of the pollen from their body and when they visit another flower the leftover pollen can be deposited on the stigma of the next flower. Notice the filament and stigma protruding from the cone of anthers in the picture below. |
 Solanum, flower arrangement |
| The fruits (berries) of this plant look delicious, but are very poisonous. |
 Solanum, berries |
| Solanum melongea (eggplant) – Flower |
 Flower of an eggplant |
| Solanum crispum (Chilean potato vine) |
 Chilean potato vine flower |
| Side view of the flower. |
 Close up, side view |
| You can see the pores terminating the anther (poricidal dehiscence). |
 Close up |
| Solanum lycopersicon = Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato). Not all buzz-pollinated flowers have purple flowers. Corollas come in other colours such as white and yellow. |
 Tomato flower |
| The petals have been removed to reveal the ovary and the sepals. |
 Ovary and sepals |
| Fruit (berry) cross-section: |
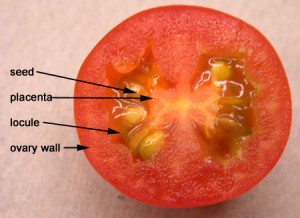 Tomato fruit, cross section |
Other members of the Solanaceae
| Atropa belledonna:Belladonna has a long history of use by people. It has links to witchcraft; it has chemicals which have been used for their hallucinogenic qualities. These chemicals have other very deadly side effects. We will explore the chemicals further in Unit 4. |
 Belladonna flower |
| Here you can see the flowers and fruit (berries). |
 Belladonna flower and fruit |
| Longitudinal section through a flower. |
 Belladonna flower, longitudinal section |
| A close-up of the fruit: |
 Belladonna fruit |
| Physalis ixocarpa (Tomatillo): The fruit of this plant is wrapped in the enlarged calyx. It is very popular in Mexican cuisine. |
 Tomatillo |
Back to Lab 3






















