Meandering Rivers
Download as PPT, PDF25 likes25,524 views
Meandering rivers form sinuous patterns as they erode the outer banks of bends and deposit sediments inside bends. This process causes the river channel to migrate back and forth over time. Key features of meandering rivers include point bars, which are sediment deposits inside bends, and oxbow lakes, which form when meander loops are cut off from the main river channel. Meandering rivers have a single channel and flow in helical patterns that erode the outer bank and deposit sediments inside bends, causing the characteristic sinuous shape over time.
1 of 27
Downloaded 939 times










Recommended
Types of channel



Types of channelMs Geoflake There are three main types of channels: straight channels found in the upper zone on rock, braided channels in the middle zone on coarse alluvial material with several intersecting channels, and meandering channels in the lower zone on fine alluvial material that regularly change position across the floodplain. The long profile of a river shows it has a concave shape from the steeper upper reach to gentler lower reach, with an ideal graded long profile existing in a state of dynamic equilibrium between erosion and deposition rates.
Fluvial process



Fluvial processPRAMODA G Fluvial processes create distinct landforms over time as a river ages. In the youth stage, the river valley is narrow with steep sides. Meanders begin to form in the maturity stage as the river widens and deepens. In the old stage, the river flows across a flat floodplain as it approaches being a featureless plain. Distinct landforms are produced at each stage as the river's erosional and depositional activities change.
Fluvial processes and landforms



Fluvial processes and landformsProf. A.Balasubramanian Flowing water has the ability to dissolve the soluble mineral substances available on its way. The processes enacted by streams are called as fluvial processes. The word “fluvius” is derived from the latin word meaning “ river”. The world fluvial is used to denote the running water as streams or rivers. Fluvial processes entail the erosion, transportation, and deposition of earth materials by running water. Fluvial processes and fluvial landforms dominate land surfaces the world over, as opposed to the limited effects of glacial, coastal, and wind processes.
Meandering rivers



Meandering riversSrishti Aneja A meandering stream consists of successive bends called meanders that form through the erosion of sediments from the outside of bends and deposition on the inside. This process causes the stream channel to move back and forth across the landscape over time. Meanders are most prominent in the lower reaches of rivers as they slow over flatter land. Features that result from meandering include point bars of deposited sediment on the inside of bends, natural levees of sediment along river banks, and oxbow lakes that are formed when neck cuts off during floods.
River Landform



River Landformaikyatha Rivers have distinct features along their upper, middle, and lower courses. In the upper course, the river flows through a V-shaped valley with steep sides, eroding vertically. Meanders begin to form in the middle course as the river erodes more horizontally and widens the valley floor. In the lower course, the river flows through a wide, flat floodplain with features like oxbow lakes formed from abandoned meander loops.
Braided channels



Braided channelsmartina_mounir A braided channel consists of a network of smaller interconnected channels separated by small, temporary islands called eyots or braid bars. Braiding occurs when a river's sediment load and slope exceeds a threshold, causing deposition that divides the channel. This often happens after heavy rainfall, when discharge levels fluctuate. Braided channels are common where coarse sediments like sand and gravel are carried, such as in the wide, shallow valleys of rivers with little slope.
Aquifer Parameter Estimation



Aquifer Parameter EstimationC. P. Kumar 1) A pumping test was conducted where a well was pumped at 2500 m3/day and drawdowns were measured in an observation well 60 m away at various times.
2) The transmissivity and storativity of the confined aquifer were estimated using the Theis and Cooper-Jacob methods in AquiferTest software by analyzing the linear relationship between the logarithm of time and drawdown.
3) The accuracy of the aquifer parameter estimates depends on maintaining a constant pumping rate and measuring drawdowns at appropriate time intervals in multiple observation wells.
Chapter 3 Fetter Properties of Aquifers



Chapter 3 Fetter Properties of AquifersBakr Younis /Al-Azhar University – Gaza This document discusses key properties and concepts related to aquifers and groundwater flow. It defines terms like porosity, permeability, hydraulic conductivity, specific yield, and water table. It describes different types of aquifers such as unconfined, confined, and perched aquifers. Pumping from confined aquifers can create a cone of depression. Storativity describes how much water an aquifer can gain or lose from storage. Aquifer units can be homogeneous, heterogeneous, isotropic, or anisotropic depending on their properties.
Groundwater



Groundwater!SYOU co-designed sneakers The document discusses groundwater and the water cycle. It describes how (1) water moves among oceans, atmosphere, Earth and biosphere in the water cycle through processes like infiltration, transpiration and precipitation; (2) there is a balance in the water cycle as annual precipitation equals evaporation globally; and (3) groundwater is water located underground in the saturated zone below the water table, where it moves slowly through pores and fractures in rock and soil.
Aquifers



AquifersTarun kumar An aquifer is an underground layer of permeable rock or sediment that contains water. Aquifers can be confined or unconfined. A confined aquifer is separated from the surface by an impermeable layer, while an unconfined aquifer allows water to seep directly from the surface above. Natural recharge of unconfined aquifers occurs through downward percolation of excess water, while confined aquifers recharge where the aquifer reaches the surface. Infiltration galleries are underground tunnels constructed with holes to intercept groundwater flowing towards lakes or rivers and collect it for extraction.
Fluvial depositional landform geomorphology



Fluvial depositional landform geomorphologyShivam Jain This document summarizes fluvial depositional landforms. It begins with an introduction to stream deposition and fluvial landforms. It then discusses reasons for sediment deposition including changes in slope, flow obstructions, and sediment supply. Major landforms are classified and explained, including alluvial fans/cones, braided streams, meandering belts, point bars, backswamps, floodplains, natural levees, and river deltas. Specific features of each landform like bar formation and channel abandonment are described. The document concludes by noting the geological significance of these landforms and their use for cultivation.
Introduction to Engineering Hydrology



Introduction to Engineering HydrologyMalla Reddy University Topics:
1. Hydrology & Hydrology Cycle
2. Rainfall Measurement
3. Analysis of Rainfall Records
4. Runoff Calculations
5. Abstraction from rainfall
6. Evaporation
7. Evapotranspiration
8. Infiltration
River Channel Processes & Landforms



River Channel Processes & LandformsMalia Damit The document discusses river channel processes and landforms, including:
1. River processes like erosion, transportation, and deposition shape landforms through sediment movement.
2. Velocity and discharge impact a river's ability to erode, transport, or deposit materials based on the Hjulström curve.
3. Meanders, floodplains, and deltas are examples of landforms formed by fluvial erosion and deposition that impact human settlements.
Presentation Hydrology



Presentation HydrologyMalia Damit Hydrology is the study of water on Earth. The key concepts discussed include:
1. The hydrological cycle which describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
2. Drainage basins which are areas of land where water from rain or snowmelt drains into a body of water.
3. Factors that influence storm hydrographs such as rock types, basin characteristics, precipitation levels, temperature, and vegetation cover.
Delta



DeltaM.T.H Group 1. Deltas form where rivers enter bodies of standing water, depositing large amounts of sediment. They are common features where large rivers meet the ocean.
2. Deltas consist of a delta plain, delta front, and prodelta. The delta plain is the subaerial region with distributary channels, the delta front is the shallow underwater region where mouth bars form, and the prodelta is the deepest region where fine sediments settle out.
3. Deltas are classified based on dominant hydrodynamic processes, including river-dominated, tide-dominated, and wave-dominated deltas which have characteristic morphologies and sedimentary structures.
origin, type and composition of ground water



origin, type and composition of ground waterDarshan Darji Groundwater originates from water that infiltrates through soil and rock below the earth's surface. It is found in aquifers, which are saturated geological formations that are capable of providing usable quantities of water. The main sources of groundwater are meteoric water from rainfall and snowmelt, connate water trapped in sediments when they were deposited, and magmatic water from volcanic activity. Groundwater composition varies depending on the geology, but common dissolved ions include bicarbonates, carbonates, chlorides, sulfates, fluorides, calcium, magnesium, sodium, and manganese.
Groundwater Data Requirement and Analysis



Groundwater Data Requirement and AnalysisC. P. Kumar The document discusses groundwater data requirements, acquisition, processing, and analysis. It outlines the types of physical and hydrological data needed for groundwater studies, including maps, cross-sections, and time-series data on water levels, quality, pumping, and other factors. Key points covered include establishing monitoring networks, validating data, preparing hydrographs, water table maps, and other tools to characterize the groundwater system and identify issues like contamination or over-pumping. Statistical methods for interpolating hydrological variables from point data across regions are also summarized.
Types of Aquifers



Types of AquifersAnanya21Mittal There are different types of underground formations that can store and transmit groundwater. An aquifer readily transmits significant quantities of water and can support water wells. It may be unconfined, with a water table, or confined under pressure between low-permeability layers. An aquitard has low permeability and does not yield much water to wells. Other formations may contain water but not transmit it (aquiclude) or contain no water (aquifuge). Perched aquifers occur above discontinuous low-permeability layers and are separated from the main groundwater body. The type of aquifer depends on its geology and subsurface position.
Floodplain presentation 2



Floodplain presentation 2samirpinal Floodplains are flat areas of land adjacent to rivers that experience occasional flooding when river discharge exceeds channel capacity. Floodplains hold excess water, allowing it to be slowly released and infiltrate while also providing time for sediment to settle. They support important wildlife habitats and are used for agriculture, recreation, and settlement due to fertile soil and access to transportation, though flooding must be controlled in urban areas through measures like levees. Floodplains form through erosion as rivers cut into channels and banks or through aggradation when sediment supply exceeds transport capacity, raising land elevation and water levels.
Aquifer



AquiferShah Naseer An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing rock. Water-bearing rocks are permeable, meaning that they have openings that liquids and gases can pass through. Sedimentary rock such as sandstone, as well as sand and gravel, are examples of water-bearing rock.
groundwater



groundwaterGladys Joy Bautista Groundwater is water located beneath the Earth's surface that infiltrates through soil and fills pores and cracks in rock. It is found within two main zones - the unsaturated zone above the water table where pores contain both air and water, and the saturated zone below where all pores are filled with water. Groundwater is recharged from precipitation and flows through the ground via gravity and pressure differences, discharging through springs, streams or being extracted by wells. Contamination can enter groundwater from various sources like spills, waste disposal or fertilizers, spreading through the subsurface over time. Treatment methods aim to filter out contaminants but remediating polluted groundwater is challenging.
Groundwater 1



Groundwater 1Usama Waly Groundwater is found underground in soil and rock pores and fractures. It is an important source of freshwater. Groundwater exists in three zones: the saturated zone where all pores are full of water, the capillary fringe just above it, and the aeration zone above that. The water table marks the top of the saturated zone. Groundwater interacts with streams, which can gain or lose water from interactions with the water table. Factors like porosity, permeability, and the slope of the water table influence groundwater storage and movement. Groundwater can emerge as springs, hot springs, or geysers, and be accessed via wells. Excessive pumping can cause problems like subsidence and saltwater contamination.
Introduction to River Engineering



Introduction to River EngineeringManamnoBeza1 This document outlines the course content for a River Engineering course. It covers 5 main topics: 1) Introduction to River Engineering which discusses catchment areas, river classifications, and morphology; 2) River Hydraulics; 3) Sediment Transport; 4) River Training and Flood Control; and 5) Preliminary Design of Bridges. The objectives are for students to understand river behavior and morphology, sediment transport, river training structures, and bridge hydraulics. Evaluation includes assignments, exams, and presentations. References for further reading are also provided.
Geological Considerations - Dam



Geological Considerations - DamSouthern University Bangladesh The document discusses considerations for selecting dam and reservoir sites from a geological perspective. It defines different dam types including gravity, buttress, arch, and earth dams. Key factors for dam site selection include the underlying rock and soil composition and structure, with impermeable and stable foundations being important. Dams should avoid faults, fractures, and areas prone to erosion or earthquakes. The reservoir site selection process also aims to minimize land usage and sediment intake while ensuring adequate storage capacity.
River Rejuvination 



River Rejuvination NanaAsyi The document discusses several landforms that can result from river rejuvenation caused by a fall in sea level. Knick points form as steps where the river erodes downward to adjust to the new base level, and may create waterfalls. River terraces are abandoned floodplains left at higher levels after the river cuts down through deposits. Incised or enclosed meanders develop when the river maintains its meandering pattern while increasing vertical erosion.
Aquifer types



Aquifer typesProf. A.Balasubramanian This module explains about the water-bearing geological formations called as aquifers and their types.
Ground Water Hydrology



Ground Water HydrologyGAURAV. H .TANDON This document provides an overview of ground water hydrology. It defines key terms like aquifers, aquitards, the water table, porosity, permeability and discusses the movement and storage of groundwater. It explains that groundwater is an important source of water, especially in arid areas, and outlines the water balance concept and different zones of subsurface water like the saturated and aeration zones.
Geology of Dams & Reservoirs



Geology of Dams & ReservoirsHymavathi Jampani Types of dams, geological considerations in site selection, Competency of Rocks to offer stable dam foundation, effect of geological structures on dam, selection of dam site, Reservoir, purpose of reservoir, influence of water table, geological structures, life of reservoir, geophysical studies
Meander.ppt



Meander.pptCyprian Ozigbo This document discusses meandering river systems. It describes how meanders form through the erosion of the outer bank and deposition on the inner bank, creating sinuous bends in the channel over time. Key features of meandering rivers discussed include point bars, natural levees, crevasse splays, and oxbow lakes. The document also covers the helical flow processes responsible for erosion and deposition patterns in meander bends and defines the different facies deposits found in meandering river channels.
CAMBRIDGE AS GEOGRAPHY REVISION: HYDROLOGY AND FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY - 1.3 RI...



CAMBRIDGE AS GEOGRAPHY REVISION: HYDROLOGY AND FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY - 1.3 RI...George Dumitrache A presentation of the third subchapter (River Channel Processes) from the first chapter (Hydrology and Fluvial Geomorphology) of Revision for Geography AS Cambridge exam.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Groundwater



Groundwater!SYOU co-designed sneakers The document discusses groundwater and the water cycle. It describes how (1) water moves among oceans, atmosphere, Earth and biosphere in the water cycle through processes like infiltration, transpiration and precipitation; (2) there is a balance in the water cycle as annual precipitation equals evaporation globally; and (3) groundwater is water located underground in the saturated zone below the water table, where it moves slowly through pores and fractures in rock and soil.
Aquifers



AquifersTarun kumar An aquifer is an underground layer of permeable rock or sediment that contains water. Aquifers can be confined or unconfined. A confined aquifer is separated from the surface by an impermeable layer, while an unconfined aquifer allows water to seep directly from the surface above. Natural recharge of unconfined aquifers occurs through downward percolation of excess water, while confined aquifers recharge where the aquifer reaches the surface. Infiltration galleries are underground tunnels constructed with holes to intercept groundwater flowing towards lakes or rivers and collect it for extraction.
Fluvial depositional landform geomorphology



Fluvial depositional landform geomorphologyShivam Jain This document summarizes fluvial depositional landforms. It begins with an introduction to stream deposition and fluvial landforms. It then discusses reasons for sediment deposition including changes in slope, flow obstructions, and sediment supply. Major landforms are classified and explained, including alluvial fans/cones, braided streams, meandering belts, point bars, backswamps, floodplains, natural levees, and river deltas. Specific features of each landform like bar formation and channel abandonment are described. The document concludes by noting the geological significance of these landforms and their use for cultivation.
Introduction to Engineering Hydrology



Introduction to Engineering HydrologyMalla Reddy University Topics:
1. Hydrology & Hydrology Cycle
2. Rainfall Measurement
3. Analysis of Rainfall Records
4. Runoff Calculations
5. Abstraction from rainfall
6. Evaporation
7. Evapotranspiration
8. Infiltration
River Channel Processes & Landforms



River Channel Processes & LandformsMalia Damit The document discusses river channel processes and landforms, including:
1. River processes like erosion, transportation, and deposition shape landforms through sediment movement.
2. Velocity and discharge impact a river's ability to erode, transport, or deposit materials based on the Hjulström curve.
3. Meanders, floodplains, and deltas are examples of landforms formed by fluvial erosion and deposition that impact human settlements.
Presentation Hydrology



Presentation HydrologyMalia Damit Hydrology is the study of water on Earth. The key concepts discussed include:
1. The hydrological cycle which describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
2. Drainage basins which are areas of land where water from rain or snowmelt drains into a body of water.
3. Factors that influence storm hydrographs such as rock types, basin characteristics, precipitation levels, temperature, and vegetation cover.
Delta



DeltaM.T.H Group 1. Deltas form where rivers enter bodies of standing water, depositing large amounts of sediment. They are common features where large rivers meet the ocean.
2. Deltas consist of a delta plain, delta front, and prodelta. The delta plain is the subaerial region with distributary channels, the delta front is the shallow underwater region where mouth bars form, and the prodelta is the deepest region where fine sediments settle out.
3. Deltas are classified based on dominant hydrodynamic processes, including river-dominated, tide-dominated, and wave-dominated deltas which have characteristic morphologies and sedimentary structures.
origin, type and composition of ground water



origin, type and composition of ground waterDarshan Darji Groundwater originates from water that infiltrates through soil and rock below the earth's surface. It is found in aquifers, which are saturated geological formations that are capable of providing usable quantities of water. The main sources of groundwater are meteoric water from rainfall and snowmelt, connate water trapped in sediments when they were deposited, and magmatic water from volcanic activity. Groundwater composition varies depending on the geology, but common dissolved ions include bicarbonates, carbonates, chlorides, sulfates, fluorides, calcium, magnesium, sodium, and manganese.
Groundwater Data Requirement and Analysis



Groundwater Data Requirement and AnalysisC. P. Kumar The document discusses groundwater data requirements, acquisition, processing, and analysis. It outlines the types of physical and hydrological data needed for groundwater studies, including maps, cross-sections, and time-series data on water levels, quality, pumping, and other factors. Key points covered include establishing monitoring networks, validating data, preparing hydrographs, water table maps, and other tools to characterize the groundwater system and identify issues like contamination or over-pumping. Statistical methods for interpolating hydrological variables from point data across regions are also summarized.
Types of Aquifers



Types of AquifersAnanya21Mittal There are different types of underground formations that can store and transmit groundwater. An aquifer readily transmits significant quantities of water and can support water wells. It may be unconfined, with a water table, or confined under pressure between low-permeability layers. An aquitard has low permeability and does not yield much water to wells. Other formations may contain water but not transmit it (aquiclude) or contain no water (aquifuge). Perched aquifers occur above discontinuous low-permeability layers and are separated from the main groundwater body. The type of aquifer depends on its geology and subsurface position.
Floodplain presentation 2



Floodplain presentation 2samirpinal Floodplains are flat areas of land adjacent to rivers that experience occasional flooding when river discharge exceeds channel capacity. Floodplains hold excess water, allowing it to be slowly released and infiltrate while also providing time for sediment to settle. They support important wildlife habitats and are used for agriculture, recreation, and settlement due to fertile soil and access to transportation, though flooding must be controlled in urban areas through measures like levees. Floodplains form through erosion as rivers cut into channels and banks or through aggradation when sediment supply exceeds transport capacity, raising land elevation and water levels.
Aquifer



AquiferShah Naseer An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing rock. Water-bearing rocks are permeable, meaning that they have openings that liquids and gases can pass through. Sedimentary rock such as sandstone, as well as sand and gravel, are examples of water-bearing rock.
groundwater



groundwaterGladys Joy Bautista Groundwater is water located beneath the Earth's surface that infiltrates through soil and fills pores and cracks in rock. It is found within two main zones - the unsaturated zone above the water table where pores contain both air and water, and the saturated zone below where all pores are filled with water. Groundwater is recharged from precipitation and flows through the ground via gravity and pressure differences, discharging through springs, streams or being extracted by wells. Contamination can enter groundwater from various sources like spills, waste disposal or fertilizers, spreading through the subsurface over time. Treatment methods aim to filter out contaminants but remediating polluted groundwater is challenging.
Groundwater 1



Groundwater 1Usama Waly Groundwater is found underground in soil and rock pores and fractures. It is an important source of freshwater. Groundwater exists in three zones: the saturated zone where all pores are full of water, the capillary fringe just above it, and the aeration zone above that. The water table marks the top of the saturated zone. Groundwater interacts with streams, which can gain or lose water from interactions with the water table. Factors like porosity, permeability, and the slope of the water table influence groundwater storage and movement. Groundwater can emerge as springs, hot springs, or geysers, and be accessed via wells. Excessive pumping can cause problems like subsidence and saltwater contamination.
Introduction to River Engineering



Introduction to River EngineeringManamnoBeza1 This document outlines the course content for a River Engineering course. It covers 5 main topics: 1) Introduction to River Engineering which discusses catchment areas, river classifications, and morphology; 2) River Hydraulics; 3) Sediment Transport; 4) River Training and Flood Control; and 5) Preliminary Design of Bridges. The objectives are for students to understand river behavior and morphology, sediment transport, river training structures, and bridge hydraulics. Evaluation includes assignments, exams, and presentations. References for further reading are also provided.
Geological Considerations - Dam



Geological Considerations - DamSouthern University Bangladesh The document discusses considerations for selecting dam and reservoir sites from a geological perspective. It defines different dam types including gravity, buttress, arch, and earth dams. Key factors for dam site selection include the underlying rock and soil composition and structure, with impermeable and stable foundations being important. Dams should avoid faults, fractures, and areas prone to erosion or earthquakes. The reservoir site selection process also aims to minimize land usage and sediment intake while ensuring adequate storage capacity.
River Rejuvination 



River Rejuvination NanaAsyi The document discusses several landforms that can result from river rejuvenation caused by a fall in sea level. Knick points form as steps where the river erodes downward to adjust to the new base level, and may create waterfalls. River terraces are abandoned floodplains left at higher levels after the river cuts down through deposits. Incised or enclosed meanders develop when the river maintains its meandering pattern while increasing vertical erosion.
Aquifer types



Aquifer typesProf. A.Balasubramanian This module explains about the water-bearing geological formations called as aquifers and their types.
Ground Water Hydrology



Ground Water HydrologyGAURAV. H .TANDON This document provides an overview of ground water hydrology. It defines key terms like aquifers, aquitards, the water table, porosity, permeability and discusses the movement and storage of groundwater. It explains that groundwater is an important source of water, especially in arid areas, and outlines the water balance concept and different zones of subsurface water like the saturated and aeration zones.
Geology of Dams & Reservoirs



Geology of Dams & ReservoirsHymavathi Jampani Types of dams, geological considerations in site selection, Competency of Rocks to offer stable dam foundation, effect of geological structures on dam, selection of dam site, Reservoir, purpose of reservoir, influence of water table, geological structures, life of reservoir, geophysical studies
Similar to Meandering Rivers (20)
Meander.ppt



Meander.pptCyprian Ozigbo This document discusses meandering river systems. It describes how meanders form through the erosion of the outer bank and deposition on the inner bank, creating sinuous bends in the channel over time. Key features of meandering rivers discussed include point bars, natural levees, crevasse splays, and oxbow lakes. The document also covers the helical flow processes responsible for erosion and deposition patterns in meander bends and defines the different facies deposits found in meandering river channels.
CAMBRIDGE AS GEOGRAPHY REVISION: HYDROLOGY AND FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY - 1.3 RI...



CAMBRIDGE AS GEOGRAPHY REVISION: HYDROLOGY AND FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY - 1.3 RI...George Dumitrache A presentation of the third subchapter (River Channel Processes) from the first chapter (Hydrology and Fluvial Geomorphology) of Revision for Geography AS Cambridge exam.
floodplain presentation



floodplain presentationrupankar456 This document provides an overview of fluvial geomorphology and floodplains. It discusses how rivers erode, transport, and deposit sediment, forming various fluvial landforms like alluvial fans, floodplains, and deltas. Floodplains are formed through vertical accretion, lateral accretion, and channel abandonment. They support rich ecosystems but also experience flooding that interacts with human settlements. India has several major flood-prone river basins, and floods annually cause billions in damage, affected millions of hectares and thousands of lives.
Humid geomorphic environment



Humid geomorphic environmentMd. Nazir Hossain Running water and streams are formed from net precipitation. Streams are classified as perennial or intermittent depending on continuous flow. A river is a large natural channel that flows into another body of water. Streams have sources, mouths, confluences and basins. Rivers originate based on factors like water availability and slope. They evolve through youthful, mature and old stages. Rivers erode the land through processes like hydraulic action and transport sediment in solution, suspension, saltation and traction. This forms erosional landforms like valleys, gorges, waterfalls and meanders as well as depositional landforms like floodplains, deltas and alluvial fans.
Natural Disasters Topic 8 (Drainage Basins & Rivers)



Natural Disasters Topic 8 (Drainage Basins & Rivers)William W. Little The document summarizes key aspects of river systems and their transport of sediment. It describes how rivers transition from steep mountain headwaters to flatter plains, carrying sediment in various modes of transport. It also discusses characteristics of meandering and braided rivers, and how river channels migrate and deposit sediment in point bars and during floods. The document concludes by outlining features that form as rivers enter standing bodies of water, such as deltas, alluvial fans, and fan-deltas.
Unit 12 River training work.pdf



Unit 12 River training work.pdfBittuRajkumar Rivers carry large amounts of water and sediment. They can be classified based on their topography into upper reach rivers flowing through hills, lower reach rivers flowing through flood plains, and tidal rivers. River training works are constructed to guide and confine river flows, control river beds, and ensure safe flood passage. Methods for river training include embankments/levees, guide banks, groynes, cutoffs, and pitched islands. Guide banks are constructed in pairs to create a waterway and prevent structures from being outflanked by the river.
River Development.ppt



River Development.pptManamnoBeza1 Rivers naturally carry large amounts of water and sediment from mountains to plains and eventually to seas. They can be classified based on factors like flow patterns and location. As rivers flow from their origin, they typically pass through rocky, boulder, alluvial, and deltaic stages. In the alluvial stage, rivers can be aggrading, degrading, stable, or deltaic depending on sediment load and erosion patterns. Alluvial rivers tend to form straight reaches, bends, and eventually meandering patterns as centrifugal forces cause erosion on outer banks and deposition on inner banks of curves over time.
introduction.ppt



introduction.pptManamnoBeza1 Rivers naturally meander through plains, eroding outer banks and depositing sediment on inner banks. This forms alternating curves known as meanders. As meanders develop, the neck between curves narrows until the river cuts through and abandons the old channel, shortening its path. Rivers are classified based on flow patterns, including perennial, non-perennial, flashy, and more. They pass through different stages from mountains to deltas, including rocky, boulder, alluvial and deltaic. Alluvial rivers can be aggrading, degrading, stable or deltaic depending on sediment load and erosion/deposition.
Grade 12 notes (Geomorphology) .pdf



Grade 12 notes (Geomorphology) .pdfBRYAN SHINGANGE This document provides a summary of key concepts in geomorphology. It defines important terms like drainage basin, catchment area, river types and features. It describes different drainage patterns that form based on geology and topography. Factors that influence river discharge and landforms created by fluvial processes like meanders and waterfalls are also outlined. The document also discusses concepts like river grading, rejuvenation, and capture - how rivers gain or lose energy over time.
Channel dynamics of meandering, straight and braided rivers.pdf



Channel dynamics of meandering, straight and braided rivers.pdfShakib Rayhan Channel dynamics is a field of fluvial geomorphology that studies the patterns, behaviors, and processes governing river channels as they transport water and sediment across landscapes. In this extended analysis, we will explore the principles and types of channel dynamics, factors influencing them, and the ecological and socio-economic implications of river channel changes. River channel dynamics are critical to understanding landscape evolution, sediment transport, and the management of water resources, as they impact both natural ecosystems and human infrastructure.
1. Fundamental Principles of Channel Dynamics
Rivers are natural conveyors of water and sediment, shaped by the forces of erosion and deposition. Channel dynamics refers to the various ways rivers adjust their width, depth, and direction in response to changes in flow and sediment load. Rivers constantly evolve by eroding banks, depositing sediment, and altering their course through processes such as meandering, braiding, and avulsion (rapid channel shift). These changes occur across different spatial and temporal scales, from small sediment movements within hours to large-scale shifts that shape valleys over centuries.
Channel dynamics are fundamentally driven by the balance between sediment load (amount and size of sediment) and the river's energy (flow velocity and discharge). This balance governs whether a river will deposit sediment and form bars, or erode banks and deepen its channel. The type of material in a river’s bed and banks, the vegetation present, and external factors like tectonic activity, glaciation, and human interference also play roles in determining a river's dynamic behaviors.
2. Types of Channel Patterns and Their Dynamics
Rivers are classified into different channel types based on their morphology and dynamic behavior:
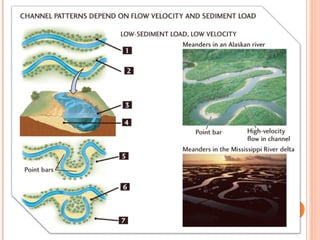
Meandering Rivers: These rivers have sinuous channels that curve back and forth across their floodplain. Meandering occurs due to erosion on the outer banks and deposition on the inner banks, creating a looping pattern. Meanders tend to migrate over time, which can lead to the formation of oxbow lakes when loops are cut off from the main channel. Factors like sediment size, bank material, and vegetation influence the rate of meander migration.
Braided Rivers: Braided rivers have multiple interwoven channels separated by bars or islands. Braiding occurs when rivers carry large amounts of coarse sediment that is deposited in bars within the channel, which forces the flow to split and reform around these obstructions. Braided channels are common in rivers with highly variable flow rates and sediment loads, such as glacial meltwater streams.
Anastomosing Rivers: These rivers consist of multiple interconnected channels, but unlike braided rivers, their channels are more stable and separated by vegetated islands rather than bare bars. Anastomosing rivers usually form in regions with low gradients, and high sediment loads.
River Changes And Landforms



River Changes And Landformswhiskeyhj The document provides information about river characteristics and landforms. It describes key features of drainage basins such as tributaries, watersheds and confluences. It explains the changes that occur along a river's long profile from upper to middle to lower course, including differences in gradient, erosion processes and landforms. Specific features of the upper course like interlocking spurs and waterfalls are also outlined. The formation of meanders and oxbow lakes in the middle course through erosion and deposition is detailed.
River Profiles



River ProfilesJohn Lanser This document discusses river profiles, fluvial landforms, and river capture/stream piracy. It begins by outlining the learning objectives, which are processes of river transportation, river profiles (long and cross), fluvial landforms, and river abstraction/stream piracy. It then provides details on longitudinal and cross river profiles, including typical shapes and features. A number of fluvial landforms are described, such as meanders, waterfalls, levees, and deltas. The document concludes by explaining river capture/stream piracy, how watershed boundaries can shift due to unequal erosion rates on either side of a drainage divide.
Geography fluvial landforms



Geography fluvial landformsvusumuzingwane1 Stream capture, also known as river capture or stream piracy, is the process where a river or stream redirects its flow and starts flowing into another river's drainage basin instead of continuing into its own basin. This can occur where two drainage basins are separated by an erosion-resistant divide that is breached by headward erosion of one of the streams. Once the divide is breached, the stream will capture the tributaries of the neighboring basin and divert its entire flow into the new course. Stream capture events can result in changes to drainage patterns over time.
Fluvial processes and_land_forms



Fluvial processes and_land_formsZeeshan Khan Streams shape the land through erosion and deposition via fluvial processes. A stream system typically has three courses - upper, middle, and lower. The upper course has steep valleys and gorges due to erosion. The middle course features meandering streams and floodplains. The lower course is dominated by depositional landforms like deltas. A stream erodes until it reaches its base level, which can be an ocean, lake, or resistant rock layer.
1.3 river channel processes



1.3 river channel processesKylie Kemp 1. The document defines key terms related to river channel processes including abrasion, attrition, capacity, competence, deltas, discharge, gorges, helicoidal flow, hydraulic action, laminar flow, levees, load, point bars, pools, riffles, river cliffs, solution, turbulent flow, waterfalls, and rapids.
2. It discusses factors that affect rates of erosion in river channels including load, velocity, gradient, geology, pH, and human impact.
3. The main types of river channel flow are laminar, turbulent, and helicoidal flow while channel types include straight, meandering, and braided channels. Meanders have asymmetric cross-sections
River erosion



River erosionVasu Goel This document outlines key features of river erosion and river systems. It begins with a longitudinal profile diagram showing how a river's gradient is steepest at the headwaters and gentlest near the base level. It then discusses drainage patterns like dendritic and trellis. Common river features like meanders and waterfalls are also explained. The document covers the erosional work of rivers through processes like abrasion and hydraulic action. Methods of sediment transportation like suspension and traction are outlined. Stages in river development from youthful to mature to old age are also summarized.
River Landforms



River LandformsLeonardo Felipe This document discusses rivers and associated landforms. It describes how rivers shape the landscape through erosion and deposition. A river system is divided into three subsystems: the collecting system of tributaries, the transporting trunk stream, and the dispersing distributary network at the river's mouth or delta. Common landforms created by rivers include alluvial fans at mountain bases where sediment is deposited, braided channels in steep areas, meandering patterns on floodplains, and deltas where rivers enter standing bodies of water.
sedimentary environment (fluvial channel)



sedimentary environment (fluvial channel)Cyprian Ozigbo This document outlines the key aspects of fluvial channels and deposits. It discusses the origin and stages of river development from mountainous sources. The main forms of fluvial channels are straight, anastomosing, braided, and meandering, with braided bars and point bars being the main deposits. Fluvial deposits have economic importance as aquifers, reservoirs, and hosts for minerals like gold. In conclusion, the presentation covered the origin, forms, deposits, and economic value of fluvial systems.
River_Landform.ppt



River_Landform.pptPapuKumarNaik1 This document discusses rivers and associated landforms. It describes how rivers gradually shape the land through erosion and deposition. A river system consists of a collecting system of tributaries, a transporting trunk stream, and a dispersing system of distributaries that spread water and sediment into oceans or lakes. Common landforms created by rivers include deltas, meanders, braided channels, and alluvial fans.
River and landforms by rivers



River and landforms by riversAnasZafar8 This document discusses river landforms and processes. It begins by defining a river and explaining fluvial processes. It then discusses key aspects of river systems such as tributaries, floodplains, and meanders. Different drainage patterns like dendritic, parallel and trellis are described. The document also covers stream discharge, perennial and non-perennial streams, erosion types, sediment load and transportation methods. Finally, it summarizes the landforms created by upper, middle and lower course rivers such as V-shaped valleys, waterfalls, meanders, ox-bow lakes and deltas.
Recently uploaded (20)
Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHat
Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?



Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?MIPLM Presentation of the CEIPI DU IPBA oral exam of Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publication, UGC-MMTTC, MANUU, 25/02/2025, Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria, University of Delhi, [email protected]
ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat



ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatScholarhat ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat
Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar Slides



Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar SlidesPooky Knightsmith For more information about my speaking and training work, visit: https://www.pookyknightsmith.com/speaking/
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat
Odoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 Slides



Odoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 SlidesCeline George In this slide, we’ll discuss on accounting access rights in odoo 18. To ensure data security and maintain confidentiality, Odoo provides a robust access rights system that allows administrators to control who can access and modify accounting data.
Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation.
How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.
Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptx



Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptxSamruddhi Khonde 📢 Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
🔬 Antibiotics have revolutionized medicine, playing a crucial role in combating bacterial infections. Among them, Beta-Lactam antibiotics remain the most widely used class due to their effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This guide provides a detailed overview of their history, classification, chemical structures, mode of action, resistance mechanisms, SAR, and clinical applications.
📌 What You’ll Learn in This Presentation
✅ History & Evolution of Antibiotics
✅ Cell Wall Structure of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria
✅ Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: Classification & Subtypes
✅ Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems & Monobactams
✅ Mode of Action (MOA) & Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
✅ Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors & Resistance Mechanisms
✅ Clinical Applications & Challenges.
🚀 Why You Should Check This Out?
Essential for pharmacy, medical & life sciences students.
Provides insights into antibiotic resistance & pharmaceutical trends.
Useful for healthcare professionals & researchers in drug discovery.
👉 Swipe through & explore the world of antibiotics today!
🔔 Like, Share & Follow for more in-depth pharma insights!
Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.
Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George In this slide we’ll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH
Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute NAPD Annual Symposium
“Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?”
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Meandering Rivers
- 1. MEANDERING RIVERS UMER KHAYAM FINAL YEAR (Eve)
- 2. MEANDERING STREAM A stream consisting of successive Meanders A meander in general is a bend in a sinous watercourse.
- 3. FORMATION A meander is formed when the moving water in a river erodes the outer banks and widens its valley. A stream of any volume may assume a meandering course, alternatively eroding sediments from the outside of a bend and depositing them on the inside. The result is a snaking pattern as the stream meanders back and forth across its down-valley axis.
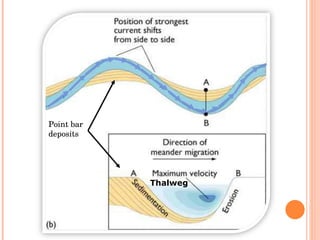
- 4. Point bar deposits Thalweg
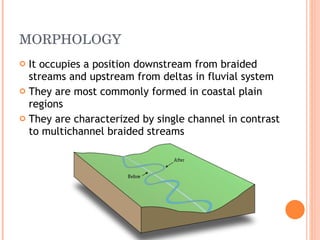
- 5. MORPHOLOGY It occupies a position downstream from braided streams and upstream from deltas in fluvial system They are most commonly formed in coastal plain regions They are characterized by single channel in contrast to multichannel braided streams
- 6. MORPHOLOGY Meander develops as a result of disruption in uniform flow across the channel Caused by variation in; Sediments Slope or Gradient Bed roughness etc... The channel profile comprises of a steep side & a gently sloping side relative to stream bed The steep side experiences lateral erosion and gently sloping side is characterised by sedimentation
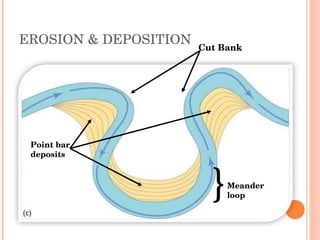
- 7. EROSION & DEPOSITION Point bar deposits } Meander loop Cut Bank
- 8. PROCESSES They are characterized by turbulent flow; velocity varies both horizontaly & vertically across the channel It transport the material both as bed load and wash load Unlike braided streams, meandering streams provides a regular pattern of flow There is a consensus about the flow in meanders which may be ellaborated as;
- 9. FLOW IN MEANDERS Helical Flow It is the major flow in the meander bends. This flow causes an elevation of water level on the outside of meander This helical flow produces a component of flow which is normal to stream bank; towards the eroding bank near the surface and towards the accreting bank near the bottom This has the net effect of producing a circulation cell which interects with the bed to carry sediments upslope along the accretion surface
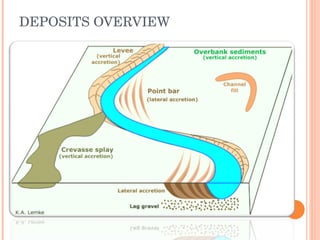
- 11. FEATURES There are numerous environments & subenvironments related to meandering streams; each having characterstic deposits These include; Channel Lag Point Bar Overbank Deposits Natural Levees Crevasse-splays Flood Basin Deposits
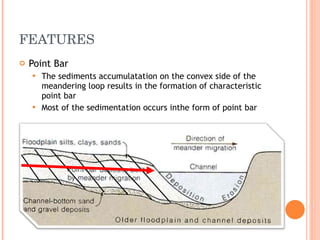
- 13. FEATURES Point Bar The sediments accumulatation on the convex side of the meandering loop results in the formation of characteristic point bar Most of the sedimentation occurs inthe form of point bar
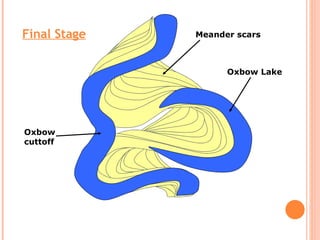
- 14. FEATURES OxBow Lake Oxbow lakes are created when growing meanders intersect each other and cut off a meander loop, leaving it without an active cutting stream. Over a period of time, these oxbow lakes tend to dry out or fill in with sediments
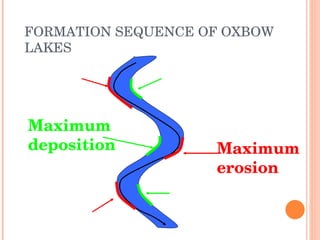
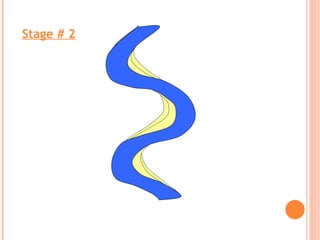
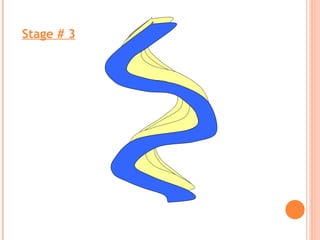
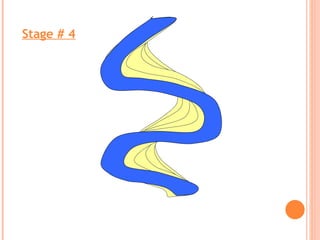
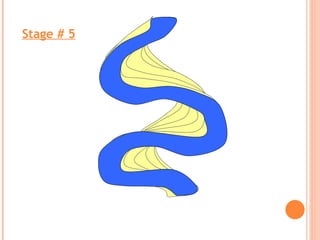
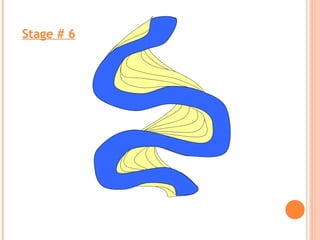
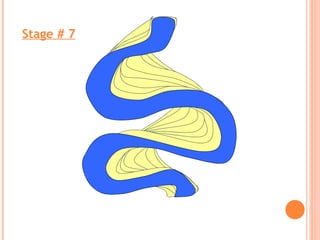
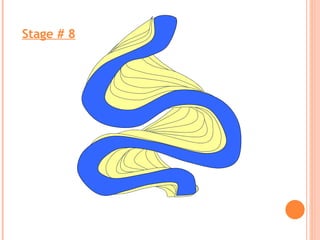
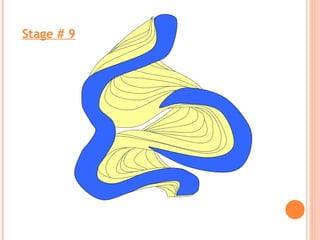
- 16. Maximum erosion Maximum deposition FORMATION SEQUENCE OF OXBOW LAKES
- 17. Stage # 1
- 18. Stage # 2
- 19. Stage # 3
- 20. Stage # 4
- 21. Stage # 5
- 22. Stage # 6
- 23. Stage # 7
- 24. Stage # 8
- 25. Stage # 9
- 26. Oxbow Lake Oxbow cuttoff Meander scars Final Stage
- 27. QUESTIONS & ANSWERS From Professor M.Haneef The honourable Chairman!






