Contrast Media in Radiology
- 1. Contrast Media in Radiology what is used and why Introduced by Abdulrahman Alquait Medical imaging MSc student
- 2. -What is a contrast medium or contrast agent? It is a substance used to enhance the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging¹. ¹ contrast agent at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- 3. How can we achieve this? What type of imaging modality being used? What part of the body being investigated?
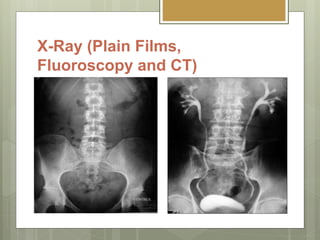
- 4. X-Ray (Plain Films, Fluoroscopy and CT) Beam attenuation.
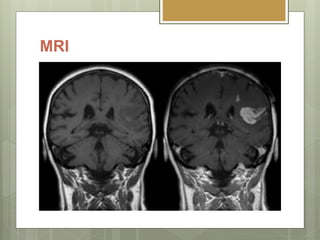
- 5. MRI T1 & T2 Relaxation times.
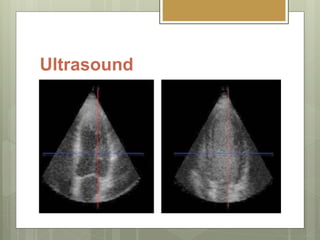
- 6. Ultrasound Decreasing reflection or increasing backscatter of echoes.
- 7. Types of contrast media in Radiography. Positive Contrast Agents. High atomic number. (e.g. iodine(53) and Barium(56)) Negative Contrast Agents. Low atomic number. (e.g. carbon dioxide (CO2) and air )
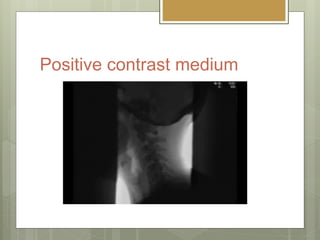
- 8. Positive contrast medium 1. Water insoluble. Barium sulphate. Barium meals and barium enemas to study the GI tract.
- 10. Positive contrast medium 2. Water soluble. Iodine compounds. Intravascular injections.
- 12. Safety Barium contrast media are generally safe if no GI perforation is present. Iodinated contrast media are relatively safe. Reactions probability²: o Minor reactions: 12.66% ICM, 3.13% NICM o Major reactions: 0.2% ICM, 0.04% NICM ²Katayama H, et al. Adverse reactions to ionic and nonionic contrast media. A report from the Japanese Committee on the Safety of Contrast Media. Radiology. Jun 1990;175(3):621-8