Heat exchanger
Download as PPT, PDF3 likes2,427 views
This document discusses different types of heat exchangers. It describes shell and tube heat exchangers which consist of tubes that transfer heat between two fluids, one flowing inside the tubes and one outside. It also describes plate heat exchangers which use thin plates with large surface areas to transfer heat between fluids. Additionally, it mentions adiabatic wheel heat exchangers which use an intermediate solid or fluid to store heat and transfer it between two fluids, as well as plate fin and pillow plate heat exchangers.
1 of 8
Downloaded 69 times



Recommended
Heat exchangers



Heat exchangersRimjhim Raj singh Heat exchangers transfer heat between two or more fluids that are at different temperatures. They work by bringing the fluids into thermal contact through a conducting surface while preventing mixing. There are several types of heat exchangers classified by their heat exchange process, fluid flow direction, mechanical design, and physical state. A common type is the shell and tube heat exchanger, which consists of a shell with a bundle of tubes inside. One fluid flows through the tubes while another flows over the tubes to transfer heat between the fluids. Double pipe heat exchangers are a simpler design with one pipe inside a larger pipe, allowing fluids to flow within and between the pipes.
Condensors and evaporators



Condensors and evaporatorsMohammad Azam Khan Condensers and evaporators are basically heat exchangers in which the refrigerant undergoes a phase change. Next to compressors, proper design and selection of condensers and evaporators is very important for satisfactory performance of any refrigeration system.
evaporators



evaporatorsUmair hanif The document summarizes different types of evaporators used in industrial processes. It describes evaporators as equipment used to reduce volume, remove water, and improve storage life. It then provides details on various evaporator types including small scale methods using pans or stills, and large scale methods like calandria, climbing film, and horizontal film evaporators. Key factors affecting evaporation rates like temperature, surface area, and agitation are also summarized.
Heat Exchangers



Heat ExchangersSABIC Heat exchangers allow the transfer of heat between two fluids without direct contact. The main types are shell-and-tube, plate, air-cooled, and spiral. Shell-and-tube exchangers consist of tubes in a shell and are the most common, used across many industries. Plate exchangers use corrugated plates clamped together with gaskets to direct fluid flow. Spiral and air-cooled exchangers provide alternatives for applications where fouling is a problem.
Heat transfer by convection



Heat transfer by convectionbalkppt Convection is a mode of heat transfer between a solid surface and an adjacent moving fluid. There are two types of convection: forced convection, where an external force causes fluid motion, and natural convection, where fluid motion is caused by density differences due to temperature variations. The Nusselt, Reynolds, and Prandtl numbers are dimensionless numbers used to characterize convective heat transfer. The Nusselt number represents enhancement of heat transfer due to fluid motion. Flow can be laminar or turbulent depending on the Reynolds number. Boundary layers form near surfaces due to no-slip conditions.
Heat Exchangers



Heat ExchangersNAVEEN KUMAR This document provides an overview of different types of heat exchangers. It begins with an introduction to heat exchangers and their basic functions. It then describes several common types of heat exchangers including recuperators, regenerators, plate heat exchangers, shell and tube heat exchangers, and fin tube heat exchangers. It also discusses potential problems with heat exchangers such as fouling and corrosion and provides some precautions and considerations for heat exchanger design and cost.
Forced Convection Full-Technical Lab Report



Forced Convection Full-Technical Lab ReportAlfonso Figueroa • Consulted on the heat transfer coefficients on two different materials, concrete and aluminum.
• Generated plotted graphs of the temperature loss per time using two different methods, the Heisler Method and Newtonian Cooling Method, all while performing error analysis.
Refrigeration Basics



Refrigeration BasicsAlvin Bene Refrigeration works by removing heat from a space using a refrigerant in a closed loop system. As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it changes state from a liquid to a gas. It is then condensed back to a liquid, releasing the heat. The four main components are the compressor, condenser, metering device, and evaporator. Refrigerants have saturation temperatures where they change state based on pressure. Proper refrigerant charging can be done using pressure/temperature charts and measuring subcooling or superheat.
Heat exchangers



Heat exchangersAmmar Ashraf The document discusses heat transfer equipment and heat exchangers. It defines a heat exchanger as a device that transfers thermal energy between two or more fluids at different temperatures without mixing the fluids. Heat exchangers can be classified based on their transfer process, number of fluids, degree of surface compactness, construction, flow arrangement, and heat transfer mechanism. Common examples include shell-and-tube exchangers, radiators, condensers, evaporators, and cooling towers.
Heat exchanger



Heat exchangerAshutosh Heat exchangers are devices that transfer heat between two fluids to control the temperature of one fluid. There are various types of heat exchangers that differ based on their flow arrangement, surface compactness, construction technique, and whether they use direct or indirect contact between fluids. Common examples include shell and tube heat exchangers, which contain multiple tubes in a shell, and plate heat exchangers, which use metal plates to transfer heat. Coaxial heat exchangers consist of an inner corrugated tube within an outer tube to efficiently transfer heat between fluids flowing separately within the tubes.
Heat Exchanger recuperators 



Heat Exchanger recuperators Ali Abdullah Recuperators are heat exchangers that transfer heat from one fluid stream to another without mixing the fluids. They are commonly used to recover waste heat from exhaust gases to preheat intake air in applications like gas turbines, furnaces, and ventilation systems. This increases efficiency by reducing the amount of fuel or additional heat needed. Recuperators transfer heat through a solid barrier separating the fluid streams and come in designs like plate, tube, or rotary. They provide efficiency gains over alternatives but require maintenance to address deposits on heat transfer surfaces over time.
APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS 18ME42 Module 04 Question No 7a & 7b



APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS 18ME42 Module 04 Question No 7a & 7bTHANMAY JS Refrigeration and its Terminologies;
(i) Capacity or Units of refrigeration,
(ii) COP,
(iii) Types of Refrigerants
(iv) Refrigerants and their desirable properties,
Refrigeration Cycles:
(i) Vapor compression refrigeration system; description, analysis, refrigerating effect.
(ii) Vapor compression refrigeration system Special Case 1,2,3;
(iii) Deviation of the Actual Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle from the Ideal Cycle
Air cycle refrigeration;
a) reversed Carnot cycle,
b) reversed Brayton cycle,
c) Vapor absorption refrigeration system.
Previous Year Problems with Solution
Referigeration



ReferigerationAshish Khudaiwala Definations related to refrigeration like refrigerating effect,TON of refrigeration,COP,vapour compression refrigeration system and vapour absorption refrigeration system,types of refrigerants and properties of refrigerants.
Types of air preheaters and its advantages



Types of air preheaters and its advantagesPreeti Agarwal A very basic word to word meaning is a device used to heat the air before further use is called as Air Preheater. They are also recognized as air heaters or air-heating pipe. It is designed to exchange heat energy with desuperheaters. Desuperheater is a Device which is been used to reduce the temperature of the steam in a high heat generation plants where large amount of heat energy or steam is released in the atmosphere.
Flash and fire point



Flash and fire pointphysics101 The document discusses flash point and fire point, which are measurements of the lowest temperatures at which lubricant vapors will ignite (flash point) or sustain combustion (fire point). The flash point indicates transportation and storage requirements, while a significantly lower flash point than normal may indicate contamination. The fire point is usually 8-10% higher than the flash point. The document also lists equipment needed to test flash point and fire point, including an open oil tester, thermometers, and oils of different weights.
Evaporator



Evaporatorrampal singh The evaporator is responsible for absorbing heat from the refrigerated space and removing both latent and sensible heat. There are several types of evaporators including bare tube, finned tube, plate, shell and tube, and shell and coil evaporators. Key factors that affect an evaporator's heat transfer capacity include its material, temperature difference, refrigerant velocity, thickness, and contact surface area. Evaporators also differ based on their construction, how refrigerant is fed, heat transfer mode, and operating conditions.
500 mw utility boiler ppt



500 mw utility boiler pptandyappan1 This document provides details on boiler types, components, and pressure parts. It discusses various classifications of boilers based on application, construction, fuel firing, number of drums, circulation, and other factors. Key boiler components and pressure parts are described in depth, including drums and drum internals. Performance parameters, design requirements, stress analysis needs, and arrangement considerations are covered for pressure parts. Specific features of 500MW utility boilers and recent changes are also summarized.
thermometric refrigeration system



thermometric refrigeration systemSaurabh Negi This document presents a thermoelectric refrigeration system project. It discusses the milestones, realization of the idea, introduction to thermoelectric refrigeration and the Peltier effect. It describes the materials used, working of the project including dimensions, advantages, drawbacks, applications, cost analysis, new opportunities, and concludes that the objective of long term cooling in power failures was achieved with a retention time of 57 minutes.
Refrigerant ppt



Refrigerant pptdineshucer This document discusses various types of refrigerants including halocarbon, azeotropic, zeotropic, inorganic, and hydrocarbon refrigerants. It provides examples of commonly used refrigerants for each type and notes their properties such as ozone depletion potential and global warming potential. Natural refrigerants like ammonia, hydrocarbons, and carbon dioxide are highlighted as having better environmental profiles than synthetic halocarbons or HFCs. The document advocates for increased use of natural refrigerants in refrigeration and air conditioning equipment to lower total environmental impact.
HEAT TRANSFER : Introduction 



HEAT TRANSFER : Introduction PRAMOD MAURYA 1. What is Heat Transfer?
2. APPLICATIONS OF HEAT TRANSFER
3. MODES OF HEAT TRANSFER
4. CONDUCTION
5. Fourier’s law of heat conduction
6. CONVECTION
7. Newton’s law of cooling
8. RADIATION
9. Stefan–Boltzmann law
Basic refrigeration cycle



Basic refrigeration cycleTherese Schutte The basic refrigeration cycle involves four main processes: 1) compression, where a refrigerant is compressed into a high-pressure gas, 2) condensation, where the high-pressure gas condenses into a liquid and releases heat, 3) expansion, where the high-pressure liquid passes through an expansion valve and decreases in pressure, and 4) evaporation, where the low-pressure liquid absorbs heat and evaporates back into a gas to be compressed and repeat the cycle. This cycle exploits how gases give off heat when condensed and liquids absorb heat when evaporated to provide cooling.
Cooling tower



Cooling towerSujeet TAMBE PRINCIPAL OF COOLING TOWER
TYPES OF COOLING TOWER
DIFFERENT TERMS USED IN COOLING TOWER SPECIFICATION
AIR PROPERTIES AND
SIZING OF COOLING TOWER HEIGHT
TYPICAL SPECIFICATION FORMAT / DATASHEET
Injection moulding process



Injection moulding processSmarty Dheeraj The document discusses the injection moulding process. It describes the key resources needed which include material, machines, moulds, and manpower. It explains the differences between thermoplastic and thermoset materials. The document outlines the injection moulding cycle and provides examples of common products made through this process. It also discusses important considerations for material, machines, moulds, and temperature ranges.
Basics of Vapor Compression.ppt



Basics of Vapor Compression.pptSyedZayanAli1 The document summarizes the vapor compression refrigeration cycle. It consists of four main processes: (1) evaporation of the refrigerant in the evaporator, (2) compression of the vapor in the compressor, (3) condensation of the vapor in the condenser, and (4) expansion of the liquid in the expansion valve back to the evaporator. The coefficient of performance (COP) measures the efficiency of the cycle and is affected by irreversibilities. Common refrigerants include CFCs, HCFCs, HFCs and natural refrigerants like CO2 and ammonia, with considerations for performance, safety, and environmental impact.
Refrigiration and air conditioning by abhishek singh



Refrigiration and air conditioning by abhishek singhAmiraj College Of Engineering And Technology deep details about the Refrigiration and air conditioning made by abhishek singh for the new comers engineers
Automotive air conditioning training manual



Automotive air conditioning training manualancaff This document is an automotive air conditioning training manual that covers various topics related to air conditioning systems. It discusses the four major functions of an automotive air conditioner which are to cool the air, circulate the air, purify the air, and dehumidify the air. It also covers the principles of heat transfer and measurement, different types of air conditioning systems, components of an air conditioning system, retrofitting air conditioning systems, equipment used for servicing AC systems, and procedures for servicing and troubleshooting AC systems.
Heat Exchanger and Its Types.pptx



Heat Exchanger and Its Types.pptxAtif Razi Heat exchangers are devices that facilitate the exchange of heat between two fluids that are at different temperatures while keeping them from mixing with each other.
The primary purpose of a heat exchanger is to either cool down or heat up a fluid, depending on the specific application.
Two fluids, a hot fluid and a cold fluid, flow through the heat exchanger in separate channels.
The hot fluid transfers heat to the cold fluid through the walls of the heat exchanger channels.
The hot fluid exits the heat exchanger at a lower temperature, and the cold fluid exits the heat exchanger at a higher temperature.
Parts :
Shell: The shell is the outer housing or casing of the heat exchanger.
Tubes: The tubes are the inner passages through which one of the fluids flows.
Tube sheet: The tube sheet is a flat plate that holds the tubes in place within the shell.
Baffles: Baffles are used to direct the flow of fluid through the tubes and to increase the heat transfer surface area.
Nozzles: Nozzles are the openings that allow the fluids to enter and exit the heat exchanger.
Applications of rac



Applications of racOmkar Bichkar RAC systems are used for various applications like refrigerators, water coolers, dairies, food preservation, and air conditioning. Refrigerators use insulation and thermostats to maintain temperatures between 0-4°C for food storage. Water coolers provide cool water at a constant temperature regardless of ambient conditions using thermostatic switches. Dairies use refrigeration for pasteurization and cooling of milk and cheese production. Cold storage facilities preserve processed foods at positive or sub-zero temperatures using insulated panels and temperature/humidity control. Large buildings use central air conditioning systems with ductwork while smaller spaces use packaged or split units.
Scada in hydropower plant



Scada in hydropower plantIndian Institute of Technology Delhi SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes. The document discusses the history and components of SCADA, including how it collects data from sensors using RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) and sends control signals. It also describes how SCADA is important for maintaining efficiency at power plants by remotely monitoring operations and automating processes to reduce costs. SCADA plays a key role in hydroelectric power plants by integrating maintenance systems and enabling remote monitoring and control to optimize maintenance scheduling.
Cadio munesh



Cadio muneshIndian Institute of Technology Delhi This document provides information about the cardiovascular system including its structure and function. It discusses the heart's location and layers, the four chambers and valves, blood flow pathways, intrinsic conduction system, cardiac cycle, and tests used to evaluate cardiovascular function like electrocardiograms, stress tests, and angiography. The cardiovascular system acts as a closed system to circulate blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients and removing waste via the heart, blood vessels, and blood flow.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Heat exchangers



Heat exchangersAmmar Ashraf The document discusses heat transfer equipment and heat exchangers. It defines a heat exchanger as a device that transfers thermal energy between two or more fluids at different temperatures without mixing the fluids. Heat exchangers can be classified based on their transfer process, number of fluids, degree of surface compactness, construction, flow arrangement, and heat transfer mechanism. Common examples include shell-and-tube exchangers, radiators, condensers, evaporators, and cooling towers.
Heat exchanger



Heat exchangerAshutosh Heat exchangers are devices that transfer heat between two fluids to control the temperature of one fluid. There are various types of heat exchangers that differ based on their flow arrangement, surface compactness, construction technique, and whether they use direct or indirect contact between fluids. Common examples include shell and tube heat exchangers, which contain multiple tubes in a shell, and plate heat exchangers, which use metal plates to transfer heat. Coaxial heat exchangers consist of an inner corrugated tube within an outer tube to efficiently transfer heat between fluids flowing separately within the tubes.
Heat Exchanger recuperators 



Heat Exchanger recuperators Ali Abdullah Recuperators are heat exchangers that transfer heat from one fluid stream to another without mixing the fluids. They are commonly used to recover waste heat from exhaust gases to preheat intake air in applications like gas turbines, furnaces, and ventilation systems. This increases efficiency by reducing the amount of fuel or additional heat needed. Recuperators transfer heat through a solid barrier separating the fluid streams and come in designs like plate, tube, or rotary. They provide efficiency gains over alternatives but require maintenance to address deposits on heat transfer surfaces over time.
APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS 18ME42 Module 04 Question No 7a & 7b



APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS 18ME42 Module 04 Question No 7a & 7bTHANMAY JS Refrigeration and its Terminologies;
(i) Capacity or Units of refrigeration,
(ii) COP,
(iii) Types of Refrigerants
(iv) Refrigerants and their desirable properties,
Refrigeration Cycles:
(i) Vapor compression refrigeration system; description, analysis, refrigerating effect.
(ii) Vapor compression refrigeration system Special Case 1,2,3;
(iii) Deviation of the Actual Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle from the Ideal Cycle
Air cycle refrigeration;
a) reversed Carnot cycle,
b) reversed Brayton cycle,
c) Vapor absorption refrigeration system.
Previous Year Problems with Solution
Referigeration



ReferigerationAshish Khudaiwala Definations related to refrigeration like refrigerating effect,TON of refrigeration,COP,vapour compression refrigeration system and vapour absorption refrigeration system,types of refrigerants and properties of refrigerants.
Types of air preheaters and its advantages



Types of air preheaters and its advantagesPreeti Agarwal A very basic word to word meaning is a device used to heat the air before further use is called as Air Preheater. They are also recognized as air heaters or air-heating pipe. It is designed to exchange heat energy with desuperheaters. Desuperheater is a Device which is been used to reduce the temperature of the steam in a high heat generation plants where large amount of heat energy or steam is released in the atmosphere.
Flash and fire point



Flash and fire pointphysics101 The document discusses flash point and fire point, which are measurements of the lowest temperatures at which lubricant vapors will ignite (flash point) or sustain combustion (fire point). The flash point indicates transportation and storage requirements, while a significantly lower flash point than normal may indicate contamination. The fire point is usually 8-10% higher than the flash point. The document also lists equipment needed to test flash point and fire point, including an open oil tester, thermometers, and oils of different weights.
Evaporator



Evaporatorrampal singh The evaporator is responsible for absorbing heat from the refrigerated space and removing both latent and sensible heat. There are several types of evaporators including bare tube, finned tube, plate, shell and tube, and shell and coil evaporators. Key factors that affect an evaporator's heat transfer capacity include its material, temperature difference, refrigerant velocity, thickness, and contact surface area. Evaporators also differ based on their construction, how refrigerant is fed, heat transfer mode, and operating conditions.
500 mw utility boiler ppt



500 mw utility boiler pptandyappan1 This document provides details on boiler types, components, and pressure parts. It discusses various classifications of boilers based on application, construction, fuel firing, number of drums, circulation, and other factors. Key boiler components and pressure parts are described in depth, including drums and drum internals. Performance parameters, design requirements, stress analysis needs, and arrangement considerations are covered for pressure parts. Specific features of 500MW utility boilers and recent changes are also summarized.
thermometric refrigeration system



thermometric refrigeration systemSaurabh Negi This document presents a thermoelectric refrigeration system project. It discusses the milestones, realization of the idea, introduction to thermoelectric refrigeration and the Peltier effect. It describes the materials used, working of the project including dimensions, advantages, drawbacks, applications, cost analysis, new opportunities, and concludes that the objective of long term cooling in power failures was achieved with a retention time of 57 minutes.
Refrigerant ppt



Refrigerant pptdineshucer This document discusses various types of refrigerants including halocarbon, azeotropic, zeotropic, inorganic, and hydrocarbon refrigerants. It provides examples of commonly used refrigerants for each type and notes their properties such as ozone depletion potential and global warming potential. Natural refrigerants like ammonia, hydrocarbons, and carbon dioxide are highlighted as having better environmental profiles than synthetic halocarbons or HFCs. The document advocates for increased use of natural refrigerants in refrigeration and air conditioning equipment to lower total environmental impact.
HEAT TRANSFER : Introduction 



HEAT TRANSFER : Introduction PRAMOD MAURYA 1. What is Heat Transfer?
2. APPLICATIONS OF HEAT TRANSFER
3. MODES OF HEAT TRANSFER
4. CONDUCTION
5. Fourier’s law of heat conduction
6. CONVECTION
7. Newton’s law of cooling
8. RADIATION
9. Stefan–Boltzmann law
Basic refrigeration cycle



Basic refrigeration cycleTherese Schutte The basic refrigeration cycle involves four main processes: 1) compression, where a refrigerant is compressed into a high-pressure gas, 2) condensation, where the high-pressure gas condenses into a liquid and releases heat, 3) expansion, where the high-pressure liquid passes through an expansion valve and decreases in pressure, and 4) evaporation, where the low-pressure liquid absorbs heat and evaporates back into a gas to be compressed and repeat the cycle. This cycle exploits how gases give off heat when condensed and liquids absorb heat when evaporated to provide cooling.
Cooling tower



Cooling towerSujeet TAMBE PRINCIPAL OF COOLING TOWER
TYPES OF COOLING TOWER
DIFFERENT TERMS USED IN COOLING TOWER SPECIFICATION
AIR PROPERTIES AND
SIZING OF COOLING TOWER HEIGHT
TYPICAL SPECIFICATION FORMAT / DATASHEET
Injection moulding process



Injection moulding processSmarty Dheeraj The document discusses the injection moulding process. It describes the key resources needed which include material, machines, moulds, and manpower. It explains the differences between thermoplastic and thermoset materials. The document outlines the injection moulding cycle and provides examples of common products made through this process. It also discusses important considerations for material, machines, moulds, and temperature ranges.
Basics of Vapor Compression.ppt



Basics of Vapor Compression.pptSyedZayanAli1 The document summarizes the vapor compression refrigeration cycle. It consists of four main processes: (1) evaporation of the refrigerant in the evaporator, (2) compression of the vapor in the compressor, (3) condensation of the vapor in the condenser, and (4) expansion of the liquid in the expansion valve back to the evaporator. The coefficient of performance (COP) measures the efficiency of the cycle and is affected by irreversibilities. Common refrigerants include CFCs, HCFCs, HFCs and natural refrigerants like CO2 and ammonia, with considerations for performance, safety, and environmental impact.
Refrigiration and air conditioning by abhishek singh



Refrigiration and air conditioning by abhishek singhAmiraj College Of Engineering And Technology deep details about the Refrigiration and air conditioning made by abhishek singh for the new comers engineers
Automotive air conditioning training manual



Automotive air conditioning training manualancaff This document is an automotive air conditioning training manual that covers various topics related to air conditioning systems. It discusses the four major functions of an automotive air conditioner which are to cool the air, circulate the air, purify the air, and dehumidify the air. It also covers the principles of heat transfer and measurement, different types of air conditioning systems, components of an air conditioning system, retrofitting air conditioning systems, equipment used for servicing AC systems, and procedures for servicing and troubleshooting AC systems.
Heat Exchanger and Its Types.pptx



Heat Exchanger and Its Types.pptxAtif Razi Heat exchangers are devices that facilitate the exchange of heat between two fluids that are at different temperatures while keeping them from mixing with each other.
The primary purpose of a heat exchanger is to either cool down or heat up a fluid, depending on the specific application.
Two fluids, a hot fluid and a cold fluid, flow through the heat exchanger in separate channels.
The hot fluid transfers heat to the cold fluid through the walls of the heat exchanger channels.
The hot fluid exits the heat exchanger at a lower temperature, and the cold fluid exits the heat exchanger at a higher temperature.
Parts :
Shell: The shell is the outer housing or casing of the heat exchanger.
Tubes: The tubes are the inner passages through which one of the fluids flows.
Tube sheet: The tube sheet is a flat plate that holds the tubes in place within the shell.
Baffles: Baffles are used to direct the flow of fluid through the tubes and to increase the heat transfer surface area.
Nozzles: Nozzles are the openings that allow the fluids to enter and exit the heat exchanger.
Applications of rac



Applications of racOmkar Bichkar RAC systems are used for various applications like refrigerators, water coolers, dairies, food preservation, and air conditioning. Refrigerators use insulation and thermostats to maintain temperatures between 0-4°C for food storage. Water coolers provide cool water at a constant temperature regardless of ambient conditions using thermostatic switches. Dairies use refrigeration for pasteurization and cooling of milk and cheese production. Cold storage facilities preserve processed foods at positive or sub-zero temperatures using insulated panels and temperature/humidity control. Large buildings use central air conditioning systems with ductwork while smaller spaces use packaged or split units.
Viewers also liked (20)
Scada in hydropower plant



Scada in hydropower plantIndian Institute of Technology Delhi SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes. The document discusses the history and components of SCADA, including how it collects data from sensors using RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) and sends control signals. It also describes how SCADA is important for maintaining efficiency at power plants by remotely monitoring operations and automating processes to reduce costs. SCADA plays a key role in hydroelectric power plants by integrating maintenance systems and enabling remote monitoring and control to optimize maintenance scheduling.
Cadio munesh



Cadio muneshIndian Institute of Technology Delhi This document provides information about the cardiovascular system including its structure and function. It discusses the heart's location and layers, the four chambers and valves, blood flow pathways, intrinsic conduction system, cardiac cycle, and tests used to evaluate cardiovascular function like electrocardiograms, stress tests, and angiography. The cardiovascular system acts as a closed system to circulate blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients and removing waste via the heart, blood vessels, and blood flow.
To study of Shaded pole Induction motor



To study of Shaded pole Induction motorIndian Institute of Technology Delhi The shaded pole induction motor uses shaded poles to produce a rotating magnetic field and allow the motor to self-start on single phase power. The poles contain shading coils that cause the magnetic axis of the poles to shift between the shaded and unshaded parts of the poles during each half-cycle of input power. This shifting magnetic axis mimics the action of a rotating magnetic field and causes the squirrel cage rotor to turn. Shaded pole motors have low efficiency and starting torque but are very cheap and reliable, making them suitable for small appliances like fans, clocks, and hair dryers.
Npp



NppIndian Institute of Technology Delhi A brief idea of Nuclear Power Plant has been given by Mr. Anupam Singh, PG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Instrumentation. SLIET Longowal
Costumer focus12 06-2010



Costumer focus12 06-201013thidiot This document summarizes the key boiler auxiliaries and components involved in ash handling at a power plant. It describes the coal bunker, coal feeder, mills for pulverizing coal, primary air fans for heating air, air pre-heaters for preheating air, burners for burning coal with oil, forced draft fans for handling secondary air, and other components like the wind box, scanner fan, and soot blowers. It also provides brief explanations of heat exchangers, the draft system, chimney, and damper control systems.
Ash problems



Ash problems13thidiot The document summarizes several problems with an ash handling plant and provides suggestions for improvements. It discusses issues such as excessive coal pile dust, poor coal quality, unexpected costs of coal burning, high maintenance costs, and an old piping system. Suggestions are provided such as installing sprinklers on the coal pile, conducting coal quality tests, reworking the coal handling philosophy, implementing predictive maintenance, and repairing the aging piping system.
Ppt on boilers



Ppt on boilersIndian Institute of Technology Delhi This presentation provides an overview of boilers. It defines a boiler as a vessel that heats water to produce hot water or steam. The presentation describes the basic principle of operation where hot gases produced from burning fuel transfer heat to water inside the boiler vessel. It then discusses the main types of boilers, including fire tube and water tube boilers, and describes their key characteristics and differences. Examples are given of commonly used boiler designs like Babcock and Wilcox, pulverized fuel, and fluidized bed boilers. Factors for selecting an appropriate boiler type are also summarized.
Power plant chemistry corrosion theory and its prevention



Power plant chemistry corrosion theory and its preventionumar farooq The document provides information about corrosion theory and prevention in power plants. It defines corrosion and discusses corrosion mechanisms such as the corrosion cell and various corrosion reactions. It also covers different types of corrosion like general corrosion, pitting, galvanic corrosion and stress corrosion cracking. Additionally, it lists factors that affect corrosion rates like dissolved gases, solids, temperature and acidity. Finally, it discusses methods of corrosion control like using corrosion inhibitors and promoting protective scales to change the corrosive environment. The document is a technical report on corrosion prepared by Umar Farooq, a chemist at SEC in Saudi Arabia.
Pollution & control



Pollution & controlAjaykumar Asodariya Thermal power plants produce various air, water, and solid pollutants that harm both the environment and human health. The main air pollutants are SO2, NOx, CO2, and particulate matter which can cause respiratory issues. Water used for cooling is discharged at high temperatures, reducing oxygen levels and disturbing ecosystems. Ash and other wastes contaminate water and soil. Various methods can control these pollutants, such as scrubbers for SO2 removal, low-temperature combustion to reduce NOx, and wastewater treatment before discharge. If uncontrolled, pollution from thermal plants poses serious risks.
Scada in hydropower plant



Scada in hydropower plantIndian Institute of Technology Delhi SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes. The document discusses the history and components of SCADA, including how it collects data from sensors using RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) and sends control signals. It also describes how SCADA is important for maintaining efficiency in power plants by remotely monitoring operations and reducing maintenance costs. SCADA plays a key role in hydroelectric power plants by integrating maintenance workstations, communicating alarm signals, and supporting future maintenance strategies through its database of equipment information.
Ahp presentation



Ahp presentationIndian Institute of Technology Delhi This presentation discusses ash handling in power plants. It describes the two main types of ash handling - dry ash handling and bottom ash handling. For dry ash handling, the main parts of the system are the electrostatic precipitator, buffer hopper, transport air compressor, and dry fly ash storage silo. For bottom ash handling, the key components are the bottom ash hopper, scrapper chain conveyor, clinker grinder, slurry sump, and hydrobin. Fly ash has various applications including use in cement production, road construction, soil stabilization, and mine reclamation.
Coal handling plant



Coal handling plantRohit Khatri This document provides information about a coal handling plant (CHP) at a thermal power station. It discusses the general working of a CHP, including receiving coal via various transportation methods, crushing and sizing the coal, storing it in bunkers, and sending it to coal mills. It also addresses common problems faced at CHPs, such as design issues, rainy season challenges, and equipment failures. Additionally, the document proposes designs for managing dust at different stages of the CHP process, such as adding moisture, using wind breaks, compacting coal piles, and installing a wet dust collector to reduce water consumption and dust levels.
Ash handling system



Ash handling systemVvs Pradeep Ash handling systems in power plants have three main types: hydraulic, pneumatic, and mechanical. The hydraulic system uses high pressure water jets to carry hot ash through channels from the furnace to an ash sump, where it is separated from water and transported for disposal. The pneumatic system uses high velocity air or steam to move crushed ash through pipes to a collection point, with filters to remove dust from exhaust air. The mechanical system conveys cooled ash on belt conveyors from the furnace to an ash bunker, from which trucks transport it to the dumping site. Proper site selection for power plants considers factors like available water, distance from load centers and populated areas, accessibility, and space for waste disposal.
Automatic speed control of DC motor



Automatic speed control of DC motorIndian Institute of Technology Delhi In this presentation, basic study of Control of DC motor , study of MATLAB/Simulink, Simulation of entitled project and problem associate with dc motor.
This presentation has been submitted to Mr.Anurag Agrawal and submitted by Munesh Singh, Anitya Shukla, Devendra Kumar and Aditya Vikram Singh in May 2012 to Kanpur institute of Technology,Kanpur India.
Power plant chemistry ( External Water Treatment )



Power plant chemistry ( External Water Treatment )umar farooq The document provides an overview of power plant chemistry and related topics. It discusses basic chemistry concepts, heat transfer, water chemistry, types of hardness in water, and marine ecology surveys. The document is presented in multiple parts that cover fundamental concepts, water treatment processes, steam water cycle systems, boiler operations, and course objectives for participants.
Chp in presentation



Chp in presentationrajkumar_sm The document describes the processes involved in a typical coal handling plant. The key processes are: [1] Unloading coal via wagon tipplers or bottom-opening wagons; [2] Feeding the coal using various feeders like belt, apron or vibrating feeders; [3] Screening to size the coal using screens or rollers; [4] Crushing oversized coal using impact, attrition or compression crushers; [5] Stacking and reclaiming coal using stacker-reclaimers; [6] Bunkering coal into storage bins using trippers. Magnetic separators are used to remove tramp iron from the coal flow. The diagram shows the typical flow of coal from
Coal and ash handling systems



Coal and ash handling systemsAjaykumar Asodariya This document discusses coal handling and storage methods at power plants. It describes dead storage or outdoor storage where coal is piled directly on the ground, which can lead to spontaneous combustion from oxidation. It then discusses live storage in vertical bunkers or silos. The document also covers different types of stoker firing systems used to burn coal, including travelling grate stokers and spreader stokers. Finally, it summarizes pulverized coal firing and the unit and central systems used to grind, dry and feed pulverized coal to boiler furnaces.
POWER PLANT CHEMISTRY



POWER PLANT CHEMISTRYDilip Kumar This document discusses the role of chemistry in power plants. It covers various aspects of feedwater treatment including removal of insoluble and soluble impurities. It discusses parameters for boiler water quality at different plant capacities. Methods for physical and chemical deaeration of feedwater like use of hydrazine are explained. Boiler water chemistry including use of volatile alkalis like ammonia for pH control is covered. Methods for detecting and addressing condenser leaks are summarized. Quality guidelines for steam and requirements for monitoring systems are provided.
Power plant chemistry internal water treatment



Power plant chemistry internal water treatmentumar farooq This document provides an overview of internal water treatment in power plants. It was authored by Umar Farooq, a senior chemist working for NOMAC in Saudi Arabia. The document covers basic chemistry concepts, properties of water, types of hardness, and various internal water treatment methods including phosphate and oxygen scavenger treatment. The goal of internal water treatment is to prevent scale and corrosion in boiler systems by maintaining proper water chemistry conditions. Phosphate treatment works by precipitating hardness minerals to form a protective sludge layer, while oxygen scavengers like sodium sulfite and hydrazine remove dissolved oxygen to inhibit corrosion.
Similar to Heat exchanger (20)
Heat exchangers



Heat exchangersLeji Latheef Heat exchangers are devices used to transfer heat between fluids. They transfer heat from outgoing vapors and liquids to incoming fluids to reduce fuel consumption. Common applications include heating, cooling, power generation, and industrial processes. The main types are double pipe, shell and tube, plate, plate and shell, and spiral heat exchangers. Double pipe exchangers have one pipe inside another but low efficiency. Shell and tube exchangers use bundles of tubes in a shell and are robust for high pressures. Plate exchangers use parallel plates for compactness while spiral exchangers use coiled tubes. Selection depends on parameters like pressure, temperature, and space.
Heat Exchangers, Its types and classifications. functioning of each type



Heat Exchangers, Its types and classifications. functioning of each typejeevanprasad8 Heat Exchangers, Its types and classification of heat exchangers. functioning of each type of heat exchangers. counter flow, cross flow, Multiple cross flow heat exchangers. Regenerative and recupurative heat exchangers. Tubular and plate type heat exchangers.
Module 4.2 Heat Exchangers.pptx



Module 4.2 Heat Exchangers.pptxPrabhatHambire A heat exchanger transfers heat between two or more fluids. There are several types including double pipe, shell and tube, plate, and spiral heat exchangers. Double pipe heat exchangers consist of one fluid passing through an inner tube while the other fluid passes in the outer tube. Shell and tube heat exchangers have one fluid passing through tubes inside a shell while the other fluid passes over the tubes. Plate heat exchangers use thin plates with precision cut channels to efficiently transfer heat between fluids. Spiral heat exchangers coil one tube around another in a counter-flow arrangement to optimize heat transfer in a compact design. Heat exchangers are widely used in industries like manufacturing, power plants, and buildings.
chapter6 heat exchangers.pptx



chapter6 heat exchangers.pptxMalik Mustafa Mohammed A heat exchanger transfers heat between two or more fluids. There are four main types classified by fluid flow: countercurrent, cocurrent, crossflow, and hybrids. Heat exchangers are also classified by construction: recuperative have separate fluid paths while regenerative use a single path. Common construction types include shell and tube, plate, and pipe in pipe. Shell and tube designs use a bundle of tubes to efficiently transfer heat. Plate heat exchangers use corrugated plates to maximize surface area. Pipe in pipe is a simple double pipe design.
TYPES OF HEAT EXCHANGERS-HEAT TRANSFER -CO-CURRENT



TYPES OF HEAT EXCHANGERS-HEAT TRANSFER -CO-CURRENTNITIN ASNANI A heat exchanger transfers heat between two or more fluids. There are four main types classified by fluid flow: countercurrent, cocurrent, crossflow, and hybrids. Heat exchangers are also classified by construction: recuperative have separate fluid paths while regenerative use a single path. Common construction types include shell and tube, plate, and pipe in pipe. Shell and tube designs use a bundle of tubes to efficiently transfer heat. Plate heat exchangers use corrugated plates to maximize surface area. Pipe in pipe is a simple double pipe design.
classes of hech.pptx



classes of hech.pptxBekeleSerbessa 1. A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat between two or more fluids (liquid or gas), which are at different temperatures. Common types are shell and tube, plate, and double pipe (or hairpin) heat exchangers.
2. Heat exchangers can be classified based on their flow configuration (countercurrent, cocurrent, crossflow) or construction (recuperative, regenerative). Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of tubes bundled inside a shell. Plate heat exchangers use corrugated plates to create flow paths.
3. Heat is transferred between fluids via conduction, convection, and thermal radiation. The rate of conductive heat transfer depends on surface area,
Heat exchanger ppt



Heat exchanger pptSiddharthSiddu5 This document discusses different types of heat exchangers. It introduces heat exchangers as equipment that transfers heat between two fluids without mixing them. It then describes several common types of heat exchangers: shell and tube, plate, adiabatic wheel, plate fin, and pillow plate. It provides brief explanations of how each type functions and materials used. Applications mentioned include use in industries like oil, gas, chemicals as well as vehicles, air conditioning and heating systems.
presentation on heat exchanger



presentation on heat exchangerAyush Upadhyay The document discusses heat exchangers, which transfer heat from one medium to another. It classifies heat exchangers based on their processes, fluid motion direction, mechanical design, and physical state of fluids. It then describes several common types of heat exchangers - shell and tube, plate, adiabatic wheel, plate fin, and pillow plate. It notes that shell and tube exchangers use tubes to transfer heat between two fluids, while plate exchangers use thin stacked plates. Heat exchangers have applications in engines, industries like oil/gas and chemicals, power generation, and HVAC systems like air conditioners and furnaces.
Heat exchangers 



Heat exchangers Effah Effervescence HEAT EXCHANGERS. Heat exchangers are devices that facilitate the exchange of heat between two fluids that are at different temperature while keeping them from mixing with each other.
2. Double Pipe Heat Exchangers
3. A typical double pipe heat exchanger basically consists of a tube or pipe fixed concentrically inside a larger pipe or tube They are used when flow rates of the fluids and the heat duty are small (less than 5 kW) These are simple to construct, but may require a lot of physical space to achieve the desired heat transfer area.
4. Double-pipe exchangers is the generic term covering a range of jacketed 'U' tube exchangers normally operating in countercurrent flow of two types which is true double pipes and multitubular hairpins. One fluid flows through the smaller pipe while the other fluid flows through the annular space between the two pipes. Two types of flow arrangement: Parallel flow Counter flow
5. • The fluids may be separated by a plane wall but more commonly by a concentric tube (double pipe) arrangement shown in fig. If both the fluids move in the same direction, the arrangement is called a parallel flow type. In the counter flow arrangement the fluids move in parallel but opposite directions. In a double pipe heat exchanger, either the hot or cold fluid occupies the annular space and the other fluid moves through the inner pipe. The method of solving the problem using logarithmic mean temperature difference is typical and more iteration must be done. So it takes more time for the problem to solve. Therefore another method is practiced for solving this type of problems. This method is known as Effectiveness and Number of Transfer Units or simply ε-NTU method.“Effectiveness of heat exchangers is defined as actual heat transfer rate by maximum possible heat transfer rate”.The LMTD method may be applied to design problems for which the fluid flow rates and inlet temperatures, as well as a desired outlet temperature, are prescribed.
6. Application of Double Pipe Heat Exchanger Pasteurization or sterilization of food and bioproducts Condensers and evaporators of air conditioners Radiators for internal combustion engines Charge air coolers and intercoolers for cooling supercharged engine intake air of diesel engines.
Fertilizer international heat-exchanger



Fertilizer international heat-exchangerrajeshkumar elango Heat exchangers transfer heat from one medium to another and come in many designs. Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of tubes bundled together within a shell and are commonly used for high pressure and temperature applications. Plate heat exchangers use thin, stacked plates to transfer heat efficiently in a compact space. Selection of the appropriate heat exchanger design considers factors like pressure limits, thermal performance, materials, and cost. Heat exchangers play an important role in many industrial processes like ammonia production.
heat exchangers of bioprocess industries



heat exchangers of bioprocess industriesshalinikaushik different types of heat exchangers are used in the bioprocess industries ...there are brief knowledge offew heat exchangers used in such industries.
Chapter1



Chapter1Ram Kumar A tube heat exchanger consists of a shell containing a bundle of tubes, with one fluid flowing through the tubes and another fluid flowing over the tubes to facilitate heat transfer. There are several types of heat exchangers that vary in their design and construction, but all aim to efficiently transfer heat from one fluid to another.
heat exchanger (2).pdf



heat exchanger (2).pdfAnandPandey888127 Heat exchangers transfer heat between two or more fluids and are widely used in applications like refrigeration, air conditioning, and chemical processing. There are various types of heat exchangers including shell and tube, which consists of tubes bundled together inside a cylindrical shell. Heat is transferred as fluids flow through the tubes and over the tubes in the shell. Selection of a heat exchanger depends on factors like process requirements, operating conditions, maintenance needs, and cost effectiveness.
Type of heat exchanger



Type of heat exchangerMayank Soni Type of heat exchanger. Which is mainly used in food industries, like dairy plant, for the pasturization, heat treatment of the beavrages or liquid raw material.
دراسات خاصه.pptxhfkfvjfscjfvckvsibdubfxjydvkxejvyvdi



دراسات خاصه.pptxhfkfvjfscjfvckvsibdubfxjydvkxejvyvdiimae4 https://youtube.com/watch?v=RbmhsyYsEuk&si=vFEHLXbKnV-VFURDhttps://youtu.be/gtxryoHbBrM?si=oCr9_KxMfHwQtvILhttps://youtu.be/kXUeBTvpa94?si=SL5Qyp1cfFLoTI1Udefine about prediction in simulationsPrediction in simulations refers to the process of estimating or forecasting the future behavior or outcomes of a system based on its current state and known dynamics. Simulations are often used to model complex systems, such as physical phenomena, economic systems, or social interactions, and prediction is a crucial aspect of understanding and analyzing these systems.
In simulation-based prediction, the behavior of the system is simulated over time using mathematical models, algorithms, or computer programs. The initial conditions of the system are defined, and the simulation progresses by iteratively updating the state of the system according to the specified rules and dynamics. By observing the simulated behavior, researchers can gain insights into how the system might evolve under different conditions or scenarios.
Predictions in simulations can take various forms depending on the nature of the system being modeled. They can involve estimating the future values of specific variables, such as the position of a particle in a physical simulation or the price of a stock in an economic model. Alternatively, predictions can involve forecasting the overall behavior or trends of the system, such as predicting the spread of a disease in an epidemiological simulation or the performance of a new product in a market simulation.
It's important to note that predictions in simulations are based on assumptions and simplifications made in the models. The accuracy of the predictions depends on the quality of the model, the accuracy of the input data, and the validity of the underlying assumptions. Simulations can be used to explore different scenarios and test the sensitivity of predictions to changes in parameters or initial conditions, helping to identify potential risks, optimize strategies, or guide decision-making.define about prediction in simulationDescribe the main elements of different reservoir dynamic simulation models.
Reservoir simulation models are often referred to by types of models:
· Black-oil
A black-oil simulator does not consider changes in composition of the hydrocarbons as the field is produced, beyond the solution or evolution of dissolved gas in oil, or vaporization or dropout of condensate from gas.
· Compositional
A compositional reservoir simulator calculates the PVT properties of oil and gas phases once they have been fitted to an equation of state (EOS), as a mixture of components. The simulator then uses the fitted EOS equation to dynamically track the movement of both phases and components in field. This is accomplished at increased cost in setup time, compute time, and computer memory.
· Thermal
Thermal simulators (most commonly used for heavy crude oil applications) add conservation of energy to this list, allowing temperatures t
HEAT_EXCHANGER_Final.pptx



HEAT_EXCHANGER_Final.pptxSashwatkumarsingh Heat exchangers are devices that transfer thermal energy between two or more fluids at different temperatures. The document discusses several types of heat exchangers including shell and tube, plate, air cooled, and spiral. It covers their basic designs, components, functions, applications, maintenance requirements, and classifications such as counterflow or parallel flow configurations. Selection of heat exchangers depends on factors like pressure limits, temperature ranges, cost, and materials.
HEAT_EXCHANGER_Final.ppt



HEAT_EXCHANGER_Final.pptPrashantKuwar Heat exchangers are devices that transfer thermal energy between two or more fluids at different temperatures. The document discusses several types of heat exchangers including shell and tube, plate, air cooled, and spiral. It covers their basic designs, components, functions, applications, maintenance requirements, and classifications such as counterflow or parallel flow configurations. Selection of heat exchangers depends on factors like temperature ranges, pressure limits, flow capacities, and materials required.
heat exchangers 



heat exchangers Mandla handirisi This document provides information on different types of heat exchangers:
- Multiple pass heat exchangers allow fluids to pass each other more than once using U-bend tubes or shell-side baffles, improving heat transfer.
- Plate heat exchangers use corrugated metal plates separated by gaskets to transfer heat between fluids in alternating channels. They are compact and efficient.
- Scraped surface heat exchangers have an internal rotating cylinder fitted with blades that continuously scrape the heating surface, used for viscous fluids.
- Double pipe heat exchangers consist of two concentric pipes for countercurrent flow, used in boilers, coolers, condensers and evaporators.
Shell and tube heat exchanger



Shell and tube heat exchangerPaul singh This presentation deals with the definition of shell and tube heat exchanger, the Theory, its Applications and its Design
Recently uploaded (20)
Soil Properties and Methods of Determination



Soil Properties and Methods of DeterminationRajani Vyawahare This PPT covers the index and engineering properties of soil. It includes details on index properties, along with their methods of determination. Various important terms related to soil behavior are explained in detail. The presentation also outlines the experimental procedures for determining soil properties such as water content, specific gravity, plastic limit, and liquid limit, along with the necessary calculations and graph plotting. Additionally, it provides insights to understand the importance of these properties in geotechnical engineering applications.
ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-2 and Unit-3



ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-2 and Unit-3prasadmutkule1 ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-2 and Unit-3
IoT-based-Electrical-Motor-Fault-Detection-System.pptx



IoT-based-Electrical-Motor-Fault-Detection-System.pptxatharvapardeshi03 IoT-based-Electrical-Motor-Fault-Detection-System.pptx
GE 6B GT Ratcheting Animation- Hemananda Chinara.ppsx



GE 6B GT Ratcheting Animation- Hemananda Chinara.ppsxHemananda Chinara GE 6B Gas Turbine Ratcheting Mechanism Animation made by Hemananda Chinara, SIC, CPP, HPL.
Machine Vision lecture notes for Unit 3.ppt



Machine Vision lecture notes for Unit 3.pptSATHISHKUMARSD1 This is the document related to machine vision subject for final year mechatronics students.
Data recovery and Digital evidence controls in digital frensics.pdf



Data recovery and Digital evidence controls in digital frensics.pdfAbhijit Bodhe This topic contain information about Data recovery and Digital evidence controls in cyber and digital awareness
Biases, our brain and software development



Biases, our brain and software developmentMatias Iacono Quick presentation about cognitive biases, classic psychological researches and quite new papers that displays how those biases might be impacting software developers.
ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-1 and Unit-2



ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-1 and Unit-2prasadmutkule1 ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-1 and Unit-2
ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3



ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3prasadmutkule1 ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3
Indian Soil Classification System in Geotechnical Engineering



Indian Soil Classification System in Geotechnical EngineeringRajani Vyawahare This PowerPoint presentation provides a comprehensive overview of the Indian Soil Classification System, widely used in geotechnical engineering for identifying and categorizing soils based on their properties. It covers essential aspects such as particle size distribution, sieve analysis, and Atterberg consistency limits, which play a crucial role in determining soil behavior for construction and foundation design. The presentation explains the classification of soil based on particle size, including gravel, sand, silt, and clay, and details the sieve analysis experiment used to determine grain size distribution. Additionally, it explores the Atterberg consistency limits, such as the liquid limit, plastic limit, and shrinkage limit, along with a plasticity chart to assess soil plasticity and its impact on engineering applications. Furthermore, it discusses the Indian Standard Soil Classification (IS 1498:1970) and its significance in construction, along with a comparison to the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS). With detailed explanations, graphs, charts, and practical applications, this presentation serves as a valuable resource for students, civil engineers, and researchers in the field of geotechnical engineering.
Environmental Product Declaration - Uni Bell



Environmental Product Declaration - Uni BellManishPatel169454 The Uni-Bell PVC Pipe Association (PVCPA) has published the first North American industry-wide environmental product declaration (EPD) for water and sewer piping, and it has been verified by NSF Sustainability, a division of global public health organization NSF International.
Von karman Equation full derivation .pdf



Von karman Equation full derivation .pdfEr. Gurmeet Singh Von karman Equation full derivation
By Er. GURMEET SINGH
G.C.E.T JAMMU
Contact: [email protected]
M.tech Transportation Engineering
Heat exchanger
- 1. TTyyppeess ooff HHeeaatt EExxcchhaannggeerrss Presented By:- Ajay Asodariya (130043119003) Department of Mechanical Engineering
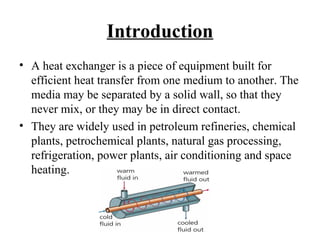
- 2. Introduction • A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The media may be separated by a solid wall, so that they never mix, or they may be in direct contact. • They are widely used in petroleum refineries, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, natural gas processing, refrigeration, power plants, air conditioning and space heating.
- 3. Types of Heat Exchangers. •Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger. •Plate Heat Exchanger. •Adiabatic Wheel Heat Exchanger. •Plate Fin Heat Exchanger. •Pillow Plate Heat Exchanger.
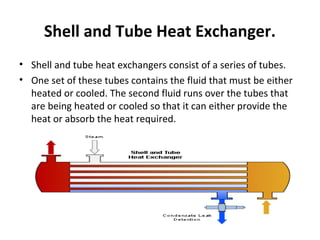
- 4. Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger. • Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of a series of tubes. • One set of these tubes contains the fluid that must be either heated or cooled. The second fluid runs over the tubes that are being heated or cooled so that it can either provide the heat or absorb the heat required.
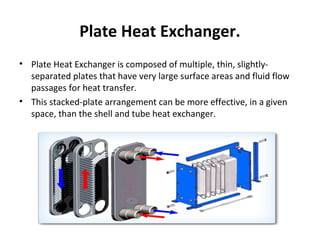
- 5. Plate Heat Exchanger. • Plate Heat Exchanger is composed of multiple, thin, slightly-separated plates that have very large surface areas and fluid flow passages for heat transfer. • This stacked-plate arrangement can be more effective, in a given space, than the shell and tube heat exchanger.
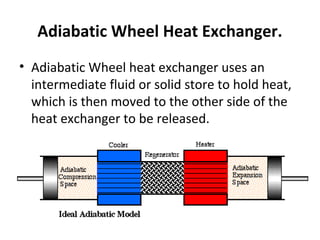
- 6. Adiabatic Wheel Heat Exchanger. • Adiabatic Wheel heat exchanger uses an intermediate fluid or solid store to hold heat, which is then moved to the other side of the heat exchanger to be released.
- 7. Plate Fin Heat Exchanger. • Plate Fin heat exchanger uses "sandwiched" passages containing fins to increase the affectivity of the unit. • The designs include cross flow and counter flow coupled with various fin configurations such as straight fins, offset fins and wavy fins.
- 8. Pillow Plate Heat Exchanger. • A pillow plate exchanger is commonly used in the dairy industry for cooling milk in large direct-expansion stainless steel bulk tanks. • The pillow plate allows for cooling across nearly the entire surface area of the tank, without gaps that would occur between pipes welded to the exterior of the tank.










