Raster Scan Display
- 1. Raster: A rectangular array of points or dots. Pixel (Pel): One dot or picture element of the raster. Scan Line: A row of pixels. Frame: The image to be scanned out on the CRT.
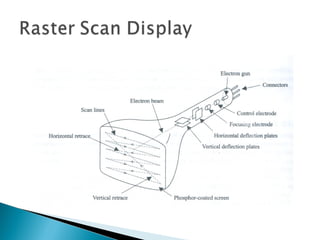
- 3. In raster scan approach, the viewing screen is divided into a large number of discrete phosphor picture elements, called pixels. In Raster scan display the electron beam is swept across the screen one row at a time from top to bottom.
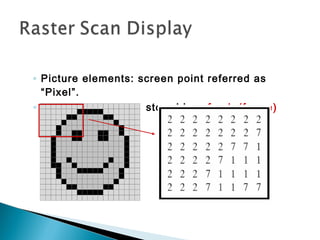
- 5. ◦ Picture elements: screen point referred as “Pixel”. ◦ Picture information stored in refresh (frame) buffer.
- 6. •Beam intensity is turned on and off to create a pattern. •Frame buffer or refresh buffer holds the set of all intensity values for all pixels. •Stored intensity values are then retrieved from the refresh buffer and painted on the screen one row at a time.
- 7. In simple black-and-white system, each pixel is either on or off, so only one bit per pixel is needed to control the intensity of screen positions. Buffer with 1 bit per pixel – Bitmap. Buffer with multiple bits per pixel – Pixmap.
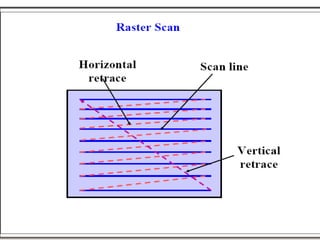
- 8. • Horizontal Retrace At the end of each scan line , the electron beam returns to the left side of the screen to begin displaying the next scan line. The return to the left of the screen , after refreshing each scan line is called horizontal retrace of electron beam. • Vertical retrace At the end of each frame the electron beam returns to the top left corner of the screen to begin the next frame. Refresing rate->60 to 80 frame per second.
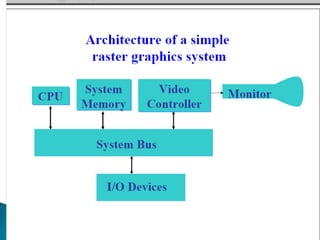
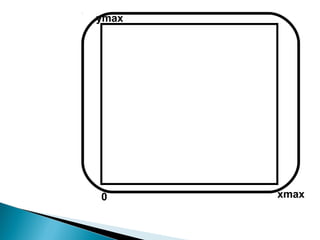
- 11. •A special purpose processor called video controller is used to control the operation of the display device. • Scan lines are labelled from ymax at the top of the screen to 0 at the bottom and screen pixel positions from 0 to xmax
- 12. 0 xmax ymax
- 13. • Advantages and Disadvantages of raster scan system. • Advantages – Refresh rate independent of image complexity. – Can handle colour and filled areas. • Disadvantages – Uses more memory
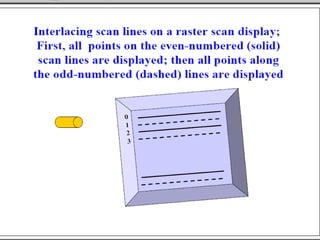
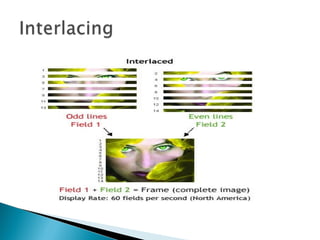
- 14. Interlacing is a method of encoding a bitmap image such that a person who has partially received it sees a degraded copy of the entire image. To reduce flicker, divide frame into two fields— one consisting of the even scan lines and the other of the odd scan lines. Even and odd fields are scanned out alternately to produce an interlaced image.