Digital Technology Merit Badge
- 2. Digital TechnologyDigital Technology Merit Badge CollegeMerit Badge College • Do you have completed Blue Cards?Do you have completed Blue Cards? • Are you in the right class?Are you in the right class? • Do you have Workbooks?Do you have Workbooks? 2
- 3. Before We Start… Read the Merit Badge Pamphlet Print out the Worksheet 1.Show your current, up-to-date Cyber Chip. 3
- 4. Tech Chip 4
- 5. Cyber Chip 5
- 6. History of Computers 2. Do the following: a. Give a brief history of the changes in digital technology over time. Discuss with your counselor how digital technology in your lifetime compares with that of your parent’s, grandparent’s, or other adult’s lifetime. b. Describe the kinds of computers or devices you imagine might be available when you are an adult. 6
- 7. History of Computers 7 1632 – Slide Rule 1100 BC – Abacus 1642 Pascaline 1617 – Logarithms
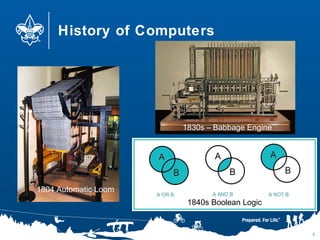
- 8. History of Computers 8 1804 Automatic Loom 1840s Boolean Logic 1830s – Babbage Engine
- 10. 1890 – Hollerith Machine 10 • Used electrical connections to trigger a counter, recording information • Data could be encoded by the locations of holes in a card • Hollerith determined that data punched on a card, could be counted or sorted mechanically
- 11. 1944 – Colossus Mark I 11 • 1st programmable digital computer • 5 tons, 500 miles of wire, 8 feet tall & 51 feet long • Ran non-stop for 15 years
- 12. 1945 – ENIAC 12 • Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer • 20 by 40 foot room • Weighed 30 tons • Used more than 18,000 vacuum tubes
- 13. 1959 – IBM Stretch 13 • The IBM 7030, or Stretch, was IBM's first transistorized supercomputer • Failed to meet aggressive performance estimates so price dropped from $13.5 million to only $7.78 million • It was the fastest computer in the world until 1964
- 14. 1970s – IBM Mainframes 14 • Standard dual-processor capability • “Monolithic main memory" based on integrated circuits • Full virtual memory through a new microcode floppy disk • 128-bit (hexadecimal) floating point arithmetic
- 15. 1975 – Altair 8800 15 • Name comes from Star Trek! • Mail order kit, assemble it yourself • No video output, LEDs instead • No keyboard, switches on the front
- 17. 17 The number of transistors per integrated circuit doubles about once every two years, while the price of the chip remains the same. In 1954, a transistor cost $5.52. By 2004, its price tag was a billionth of a dollar.
- 18. Moore’s Law 18
- 19. Computer Speak 19 “A” → 65 (ASCII) → 01000001 (Binary) →
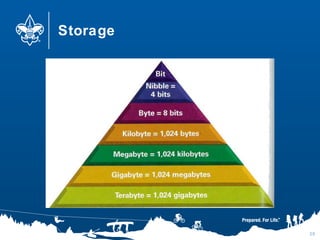
- 20. Storage 20
- 21. Storage 21
- 22. Storage 22
- 23. Merit Badge Fun Fact 23
- 24. Speed 24
- 26. The Future 26
- 27. Everywhere 27
- 28. The Future 28
- 29. The Future 29
- 30. Digital TechnologyDigital Technology 3. Do the following: a. Explain to your counselor how text, sound, pictures, and videos are digitized for storage. b. Describe the difference between lossy and lossless data compression, and give an example where each might be used. c. Describe two digital devices and how they are made more useful by their programming. d. Discuss the similarities and differences between computers, mobile devices, and gaming consoles. e. Explain what a computer network is and describe the network’s purpose. 30
- 31. File Formats Text (ASCII) txt, doc, docx, pdf Sound (waves) mp3, wma, aiff, au, raw, wav Pictures (pixels) jpg, gif, png, tiff, eps Videos (key frames + changes) avi, mpeg, flv, mov 31
- 32. Lossy vs. Lossless Compression Lossless allows the original to be recreated Lossy eliminates some data, can’t get it back 32
- 35. More Useful With Technology 35
- 36. More Useful With Technology 36
- 37. Computers, Mobile Devices & Gaming Consoles Similarities •Digital processing •Programs •Connectivity •Displays 37 Differences •Input – keyboard, screen, controller •Functionality •Versatility •Single Purpose •Proprietary software •Portability
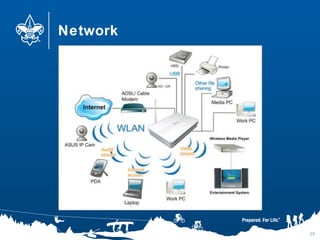
- 38. Network 38
- 39. Home Network 39
- 40. Network 40
- 41. Digital TechnologyDigital Technology 4. Do the following: a. Explain what a program or software application or “app” is and how it is created. b. Name four software programs or mobile apps you or your family use, and explain how each one helps you. c. Describe what malware is, and explain how to protect your digital devices and the information stored on them. 41
- 42. Programs or “Apps” Series of commands or set of instructions for a processor to complete a task – Word Processing – Games – Utilities (calendar, calculator) – Photo/Video Editor Coded or scripted with a special language 42
- 44. Games 44
- 45. Utilities 45
- 48. Video Editors 48
- 49. Video Editors 49
- 50. Malware • Malicious code in the form of viruses, worms, Trojan horses, spyware, adware, scareware, or ransomware • Any software used to disrupt computer operation, gather sensitive information, or gain access to private computer systems • Defined by its malicious intent, acting for the interests of the malware owner, rather than the user 50
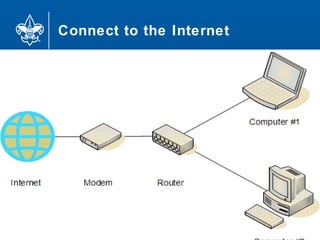
- 52. Digital TechnologyDigital Technology 5. Do the following: a. Describe how digital devices are connected to the Internet. b. Using an Internet search engine (with your parent's permission), find ideas about how to conduct a troop court of honor or campfire program. Print out a copy of the ideas from at least three different websites. Share what you found with your counselor, and explain how you used the search engine to find this information. c. Use a Web browser to connect to an HTTPS (secure) website (with your parent's permission). Explain to your counselor how to tell whether the site's security certificate can be trusted, and what it means to use this kind of connection. 52
- 53. Connect to the Internet 53
- 54. Connect to the Internet 54
- 55. Connect to the Internet 55
- 56. Connect to the Internet 56
- 57. Campfire or Court of Honor 57
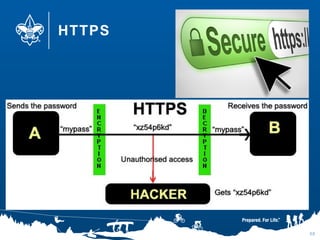
- 58. HTTPS 58
- 59. HTTPS 59
- 60. HTTPS 60
- 61. Security 61
- 62. Security 62
- 63. Digital TechnologyDigital Technology 6. Do THREE of the following. Provide me with a copy. a. Food budget OR roster spreadsheet for campout. b. Letter to troop’s parents, inviting them to a troop event. c. Campsite plan for your troop OR create a flier for an upcoming troop event, incorporating text and photographs. d. Five slide presentation, with photographs. e. Photos of a troop activity. f. Record your voice and transfer the file to a different device. g. Blog 5 of your scouting activities. h. Create a web page for your troop, patrol, school, or church. 63
- 64. Digital TechnologyDigital Technology 7. Do the following: a. Explain to your counselor each of these protections and why they exist: copyright, patents, trademarks, trade secrets. b. Explain when it is permissible to accept a free copy of a program from a friend. c. Discuss with your counselor an article or a news report about a recent legal case involving an intellectual property dispute. 64
- 65. Copyrights Legal right created by the law of a country, that grants the creator of an original work exclusive rights to its use and distribution, usually for a limited time, with the intention of enabling the creator to receive compensation for their intellectual effort. 65
- 66. Trademarks A recognizable sign, design or expression which identifies products or services of a particular source from those of others. The trademark owner can be an individual, business organization, or any legal entity. A trademark may be located on a package, a label, a voucher or on the product itself. 66
- 67. Patents A set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for detailed public disclosure of an invention. An invention is a solution to a specific technological problem and is a product or a process. 67
- 68. Trade Secrets An invented formula, practice, process, design, instrument, pattern, commercial method, or compilation of information which is not generally known or reasonably ascertainable by others, and by which a business can obtain an economic advantage over competitors or customers. 68
- 69. Piracy 69
- 70. Give Software to Friend 70
- 71. Give Software to Friend 71
- 72. Give Software to Friend 72
- 73. Give Software to Friend 73
- 74. Digital TechnologyDigital Technology 8. Do TWO of the following: a. Why proper disposal of digital technology is important. List at least three dangerous chemicals that could be used to create digital devices or used inside a digital device. b. What is a certified recycler of digital technology hardware. c. Research an organization that collects discarded digital technology hardware for repurposing or recycling. d. Visit a recycling center that disposes of digital technology hardware. e. Find a battery recycling center near you and find out what it does to recycle batteries. 74
- 75. Proper Disposal 75 Electronic devices are a complex mixture of several hundred materials. A mobile phone, for example, contains 500 to 1,000 components. Many of these contain toxic heavy metals such as lead, mercury, cadmium and beryllium, as well as hazardous chemicals, such as brominated flame retardants. Polluting PVC plastic is also frequently used.
- 76. Health Hazards 76 • Some brominated flame retardants, used in circuit boards and plastic casings, do not break down easily. Long-term exposure can lead to impaired learning and memory functions. They can also interfere with thyroid and estrogen hormone systems. • The cathode ray tubes (CRT) in monitors contain lead. Exposure to lead can cause intellectual impairment and damage the nervous, blood and reproductive systems. • Cadmium, used in rechargeable computer batteries, contacts and switches and in older CRTs, is highly toxic, primarily affecting the kidneys and bones. • Mercury, used in lighting devices for flat-screen displays, can damage the brain and central nervous system, particularly during early development. • Compounds of hexavalent chromium, used in the production of metal housings, are highly toxic and carcinogenic to people. • Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a chlorinated plastic used in some electronics products and for insulation on wires and cables. Chlorinated dioxins and furans are released when PVC is burned. These chemicals are highly persistent in the environment and many are toxic even in very low concentrations.
- 77. Recyclers 77 Two Recognized by EPA •Responsible Recycling Practices (R2) sustainableelectronics.org •e-Stewards® e-stewards.org
- 78. Recyclers 78 Computer Ministry compministry.org Monday - Friday: 9:00am - 4:00pm Saturday: 9:00am - 1:30pm 5 Pleasant View Drive Mechanicsburg, PA 17050
- 79. Battery Recyclers 79 Staples Lowes Home Depot Radio Shack AutoZone Best Buy Batteries +
- 80. Eagle Project 80
- 81. Digital TechnologyDigital Technology 9. Do ONE of the following: a. Investigate three career opportunities that involve digital technology. Pick one and find out the education, training, and experience required for this profession. Discuss this with your counselor, and explain why this profession might interest you. b. Visit a business or an industrial facility that uses digital technology. Describe four ways digital technology is being used there. Share what you learned with your counselor. 81
- 82. Digital TechnologyDigital Technology For February: 1. Finish reading the merit badge pamphlet 2. Complete the worksheet 3. Bring your completed Blue Card 4. Do the 3 Projects (Requirement 6) 5. Requirement 8 (Recycling) 6. Requirement 9 (Careers) 82
Editor's Notes
- #2: Introduction Replaces Computer MB You probably know more than me about the latest technology, Old Fart! Simple Rules: Scout Oath & Scout Law.
- #3: Blue Card should be filled out, legible and signed by your scoutmaster. Blue Card is your admission ticket…should be filled out, including my information. You should have a workbook printed out and filled out to the best of your ability.
- #4: Who read the pamphlet? The Workbook is NOT required, but highly recommended. When I checkoff requirements, I will need to look at what you have written. Cyber Chip – Requirement #1 Should already be done! If it has not, make sure it is before February.
- #5: Our troop has used a Tech Chip for years. We don’t clip corners…like cub scouts might for their Widdlin’ Chip…we take it. Must be re-learned by teaching it to other scouts using the EDGE method. Every year.
- #6: Different Level depending on your grade. Must be recharged every year. BSA is embracing technology. Teaches internet safety. We won’t be covering it…you should have already earned it.
- #7: Emphasis is on Brief. Requirement says “Discuss” not “listen” so you need to engage. If you do not participate, you will not complete this requirement, or others that require similar actions. Much more fun to look to future advances….
- #8: Abacus, or counting frame, is a calculating tool that was in use centuries before the adoption of the written modern numeral system and is still widely used by merchants, traders and clerks in Asia and Africa. Logarithms were introduced by John Napier in the early 17th century as a means to simplify calculations. They were rapidly adopted by navigators, scientists, engineers, and others to perform computations more easily, using slide rules and logarithm tables. Tedious multi-digit multiplication steps can be replaced by table look-ups and simpler addition because of the fact—important in its own right—that the logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors: log_b(xy) = log_b (x) + log_b (y), provided that b, x and y are all positive and b ≠ 1. Slide Rule: a mechanical analog computer. The slide rule is used primarily for multiplication and division, and also for functions such as roots, logarithms and trigonometry, but is not normally used for addition or subtraction. Pascaline, invented by Pascal, was primarily intended as an adding machine (The First Calculator) which could add and subtract two numbers directly, but its description could, with a bit of a stretch, be extended to a "mechanical calculator, in that at least in principle it was possible, admittedly rather laboriously, to multiply and divide by repetition.
- #9: The Jacquard loom is a mechanical loom, invented by Joseph Jacquard, that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with complex patterns. The loom was controlled by a "chain of cards", a number of punched cards, laced together into a continuous sequence. Charles Babbage designed the first automatic computing engines. He invented computers but failed to build them. The first complete Babbage Engine was completed in London in 2002, 153 years after it was designed. Difference Engine No. 2, built faithfully to the original drawings, consists of 8,000 parts, weighs five tons, and measures 11 feet long. George Boole developed logic that allows thoughts to be expressed in mathlike terms. AND, OR, NOT. Still used today in code.
- #11: Census every 10 years…by 1880 over 49 million people…took 7 years to complete. Herman Hollerith developed a punch card machine; every person had a card with various data on it.
- #12: general purpose electro-mechanical computer that was used in the war effort during the last part of World War II to break the German Enigma Code Machine.
- #13: first electronic general-purpose computer. It was digital and capable of being reprogrammed to solve "a large class of numerical problems“ Rumors/ legend is that the Philly lights would dim when it was powered on. 5 million hand soldered joints. Used for hydrogen bomb research.
- #14: Transistors, much smaller than vacuum tubes and 1,000 times faster.
- #15: Next breakthrough…Integrated Circuits! AKA microchip. Which led to CPUs, all the integrated circuits onto one chip…made the personal computer possible.
- #16: This computer was one of the first "home" computers ever made, it was sold as a kit, but for additional money, you could buy one fully assembled. It had no keyboard, the "program" had to be entered with the switches located on the front panel of the "computer", and as it didn't have video output (yet), the result was displayed via LEDs. Bill Gates, Paul Allen, and Monte Davidoff created BASIC for the Altair, and formed…Microsoft Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak formed Apple, and in 1977 released the Apple II, the first color computer.
- #17: Bill Gates, Paul Allen, and Monte Davidoff created BASIC for the Altair, and formed…Microsoft. Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak formed Apple, and in 1977 released the Apple II, the first color computer. Original IBM Microsoft computer was $3,000, over $7,500 in today’s dollars. First Apple II was around $1,300. In 1980 you have the IBM Personal Computer being released which combined with their licensing model that allows "clones" kick starts computers on user desks "decentralizing" IT outside of the datacenter. It also leads to computers at home. Grandparents: Mechanical cash registers / mechanical adding machines. Then digital calculators limited functions (+/-*%). Data delivered to them via "greenbar reports" printed on impact or maybe dot matrix printers. Later some interaction with dumb terminals. IT was centralized in the computer room, only used at work. Parents: Personal computers on desks at work. Personal computers at home were mostly used stand-alone. You carried data to-from work via 1.44MB floppy diskettes. If you wanted to go "on-line" you used dial-up modems to services like AOL or CompuServe. Later we get connected to the internet...
- #18: "Moore's law" is the observation that, over the history of computing hardware, the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years.
- #19: "Moore's law" is the observation that, over the history of computing hardware, the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years.
- #20: Zeros and Ones
- #21: Memory - sometimes confused between RAM vs Storage SSD have replaced HDD
- #22: Numbers you can’t even comprehend.
- #23: 35 years…64x more data, almost weightless, relatively cheap.
- #24: The original design would have been cool…only those who had earned the merit badge would be “in the know”…too bad it couldn’t be produced. Wonder why another symbol wasn’t selected when the original wouldn’t work? What might have been a good symbol to represent this merit badge?
- #25: Get up, and walk for 10 seconds…How many steps did you take? How many steps to walk around Earth? Well lets do math here. The circumference of earth is 24,901.55 miles. In feet that is 131,480,184'. If a regular person takes a step of approx 2 feet, then it would take a person 65,740,092 steps. That means you could walk around the Earth over 304 times in 10 seconds! How fast for could a computer hike the Appalachian Trail. It’s 2,168.1 miles long, which means 11,447,568 feet. 5,723,784 steps, means a computer could hike the AT 3,494 times in 10 seconds…still not really comprehendible…how about in one second. A computer could hike the AT about 350 times in one second. It takes us 5-7 months to do it once! We could do it 350 times in somewhere around 175 years! It takes about the same amount of computing to answer one Google Search query as all the computing done -- in flight and on the ground -- for the entire Apollo program, all 11 years, 17 mission program!
- #26: The amount of computing power in things like ENIAC compared with a new computer, even something like a super cheap calculator. You're talking about numbers that are millions and trillions of times different, which we can't comprehend. As an example, IPv4 vs IPv6, there aren't even enough IP4 addresses to give out one to each Chinese person, let alone the rest of the world. But there are enough IP6 addresses to give a few million to each grain of sand on the entire planet.
- #27: What will the future be like? Chromebooks, Cloud computing…already here.
- #28: Wearables to monitor your health, virtual reality projections, sensors everywhere to monitor things (temperature, weather, YOU), Internet of Things, IPv6, biological/digital hybrid systems, Quantum computing, non-binary logic, optical circuits, expansion of the surveillance state, drones, RFIDs or facial recognition to monitor your movements, data mining to "profile" you (by corporations and the gov.), general loss of anonymity, increased dependence on computers.
- #29: What will the future be like?
- #30: Can you imagine this?
- #31: You either need to participate or write down your answers. You must actively engage to complete this merit badge.
- #32: Text is entered by humans or could be scanned using Optical Character Recognition. doc, docx, and PDF are not really text files. They're in a binary format. Sound is sampled. A simple analog sine wave is sampled into digital form. Pictures are divided into cells and each one represents a lightness and color value. Videos are not necessarily a series of pictures; almost none are. They are a set of key frames (pictures) followed by a serious of change data to that picture. New pictures are provided when A) a significant change in the picture occurs (scene change) or B) periodically to ensure the change data hasn't drifted. You see this when a video is horribly out of sync in certain blocks of the data; the change data and the key frames have gotten out of sync.
- #33: The "restored" block for Lossy should be the same size as the original but speckled with 'holes'. A 3 minute song run through an MP3 encoder is still 3 minutes long but the fidelity of the sound is reduced to make it smaller. The higher the sampling rate the better the quality but the larger the file.
- #34: Left is the original; Right is a lossy compressed version of same sound file.
- #35: You might not be able to see the difference in the butterfly or the mountain, but the kid’s face is easy to see the loss in quality.
- #36: A digital scale, useful, accurate. Made better with a wireless connection to the internet, so you can track your weight without remembering to write it down.
- #37: Mr. Hand? The first cell phones were useful. We were no longer tied to the home or a cord. We could make calls from the car or anywhere close to a cell tower. How that first cell phone has changed…we carry around mini-computers now, capable of things not even imaginable when I was a kid (back when dirt was invented). Word you may not know, and your kids certainly won’t (Long Distance Bill)
- #38: other similarities? other differences?
- #39: Networking allows devices to communicate with each other or the outside network. Sharing data, sharing devices, monitoring (e.g. baby monitor), the router's NAT & firewall services protect the home devices from the outside net. Besides the ethernet, you can also have a bluetooth personal area network (PAN).
- #40: A possible diagram of a home network. What else could be there? Wireless printer? Security cameras? Bluetooth?
- #41: An office network could look like this. What else could be on an office network?
- #43: An application can start out with a white-board or story board set of ideas or sketches. Details are added to the design until the "story" of what the software should do is complete. Then the diagrams or sketches would go to a software developer who writes the instructions for the application using "source code". Source code are instructions for the computer that are in a human-readable format. The source code is sent through a "compiler" which verifies that the source code followed the correct syntax (coding rules) and translates the source code into "object code" which the computer can use to execute the instructions.
- #44: Word, part of the Microsoft Office suite, professional version $400! LibreOffice Writer, open source, FREE! Google Docs, also FREE, and cloud-based. You will use that for Requirement 6.
- #45: I grew up with Pong, Asteroids and Pac-Man. Today, the gaming industry is a multi-billion dollar industry. You certainly know much more about Games than I will ever know. What do you play? Why?
- #46: What utilities do you use?
- #47: Here’s one of my favorites…because of Photoshop and other photo editors, we can no longer trust any photograph! Ever. Unless you took it, you can’t trust it.
- #48: Google’s free Picasa.
- #49: iMovie for OSX
- #50: YouTube editor, Power Director, Final Cut.
- #51: Often included in “free” software.
- #52: First line of defense is using your own brain. Don't click on stuff. If you get a note from a friend, does it look like something he would send? Backup your data! Don't use IE. Use Firefox and turn off Java Script with "No Scripts" plug-in. Much more diligent in checking SSL certs than Chrome.
- #53: We’ll cover A. B & C need to be done at home.
- #54: Not sure how much detail they want here but you could include things like the router doing DHCP Client and Server functions, Network Address Transversal, and packet routing. Public vs. local IP addresses. WAN vs LAN. Another key concept is DNS name resolution.
- #58: Research and print out 3 examples of a campfire program or court of honor. If you are close to Eagle Scout, you might want to focus on an Eagle Court of Honor, as you should be planning this on your own!
- #59: https://dev.ssllabs.com/ssltest/ Great site for checking a security certificate. Run google.com through it and let me know what score Google gets? Think it is an A? Why not?
- #60: Hacker may have installed his certificate and is waiting for you to log in.
- #62: Two Factor Authentication or Multi Factor Authentication Good digital citizenship, taking care of your data, your security
- #63: Two Factor Authentication or Multi Factor Authentication Good digital citizenship, taking care of your data, your security
- #64: You must do THREE and you must share your work with me. Please use Google Docs. If you can’t for some reason, you can use a USB drive, but you might not get it back.
- #68: Would you want to include any of the parts from the anti-software patent movement? Touch on the topic of "patent trolls"? How about referencing a broken patent system that grants patents for obvious things like Amazon's one-click checkout or sliding screen contents using your finger?
- #70: fines and penalties Software theft is a serious matter. If you or your company get caught copying software, you may be held liable under both civil and criminal law. If the copyright owner brings a civil action against you, the owner can seek to stop you from using its software immediately and can also request monetary damages. The copyright owner may then choose between actual damages, which include the amount it has lost because of your infringement as well as any profits attributable to the infringement, or statutory damages, which can be as much as $150,000 for each program copied. In addition, the government can criminally prosecute you for copyright infringement. If convicted, you can be fined up to $250,000, sentenced to jail for up to five years, or both. Appeals court approves $675,000 fine for student who illegally downloaded 30 songsRead more: http://www.digitaltrends.com/music/appeals-court-denies-piracy-penalty-plea/#ixzz3O0L9KBV6 Follow us: @digitaltrends on Twitter | digitaltrendsftw on Facebook
- #71: Do you want to include anything on "copyleft", GPL, or Creative Commons? It's possible to get compensation for your "intellectual effort" without using copyright protection.
- #76: You might want to add something on cleansing the drives before disposing the computer equipment. Protect yourself by getting rid of your data with something like Darik's Boot and Nuke (DBAN) which wipes the entire drive.
- #78: Zero Export Recycler’s Mount Holly Springs The Computer Barn Carlisle e-Stewards – Every Staples
- #79: Zero Export Recycler’s Mount Holly Springs The Computer Barn Carlisle e-Stewards – Every Staples
- #80: Use rechargeable batteries