Skin
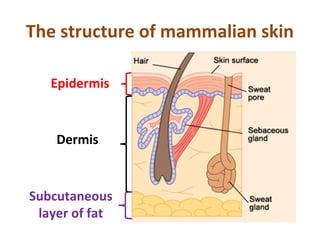
- 2. The structure of mammalian skin Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer of fat
- 3. Function of the adipose/fat layer: 1. provides a store of energy 2. forms an insulating layer: prevents heat loss Subcutaneous layer of fat
- 4. Question: Sep, 2011 Give a biological explanation for each of the following: Aquatic mammals such as whales have a thick layer of blubber. (3)
- 6. 3 layers in epidermis: cornified granular malpighian
- 7. New skin cells are made all the time at the : cornified granular malpighian
- 8. Growth of the epidermis: cornified 4 The dead cells become hard and flat and flake off. The cells are cut 3 off from the blood granular supply and so die. 2 This cell enters the granular layer. Cells in this layer malpighian 1 divide to produce two cells.
- 9. Functions of the cornified layer: i) reduces water loss ii) keeps out microbes Cornified layer dead cells
- 10. Function of the malpighian layer: cells divide by mitosis to form the granular layer Granular layer Malpighian layer: produces melanin
- 11. Functions of melanin: 1. absorbs ultraviolet rays 2. gives colour to the skin
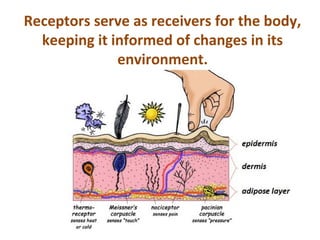
- 14. What is present in the dermis? sensory nerve endings sweat glands hair follicles capillaries Let’s f ind out the f unction of each.
- 15. Where are the sensory nerve endings located?
- 16. Receptors serve as receivers for the body, keeping it informed of changes in its environment.
- 17. What is present in the dermis? sensory nerve endings sweat glands hair follicles capillaries
- 18. sweat pore evaporation Section through skin epidermis The sweat gland dermis extracts sweat from the blood and passes it up sweat duct the duct to the skin surface where it evaporates sweat gland blood vessel 0.25 mm
- 19. Question: SEP, 2010 What is sweat made up of? (3) Water Salts Urea A little lactic acid
- 20. Sweat cools the body as it evaporates The skin
- 21. Evaporative cooling Hippos bathing
- 22. Explain why a person is advised to take a salt tablet after staying in the sun for a long time. To replace salts lost in sweat.
- 23. Question: SEP, 2010 On hot days the volume of urine lost is less than on cold days. Explain why. (4) Cold days: Hot days: No/less sweat Water lost in sweat
- 24. Urine changes colour The more dilute the urine is, the lighter is its colour.
- 25. What is present in the dermis? sensory nerve endings sweat glands hair follicles capillaries
- 26. A hair follicle is a deep pit lined with granular and malpighian cells Hair Hair follicle Blood vessels
- 27. It is not painful to cut your hair. Why? Hair is made of dead cells. Human hair: made of the protein keratin
- 28. Hair erector muscle Erector Thicker layer of muscle Thinner layer of air is trapped. contracted air is trapped. Hot day Cold day
- 30. Head louse clings to hair
- 31. Thickness of fur varies according to season
- 32. Sebaceous / Oil gland produce sebum - waterproof
- 33. What is present in the dermis? sensory nerve endings sweat glands hair follicles capillaries
- 34. Capillaries: bring food and oxygen to the skin and remove wastes capillary loops near the skin surface are important in controlling temperature
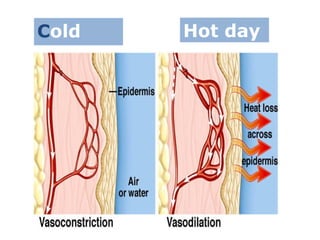
- 35. Cold Hot day day
- 36. Vasodilation If the temperature rises, the blood vessel dilates (gets bigger). This means more heat is lost from the surface of the skin
- 37. Vasoconstriction If the temperature falls, the blood vessel constricts (gets shut off). This means less heat is lost from the surface of the skin
- 38. Give a reason for this observation. A child looks pale in the face on a cold day but red after running a race. Vasoconstriction to Vasodilation to reduce heat loss. increase heat loss.
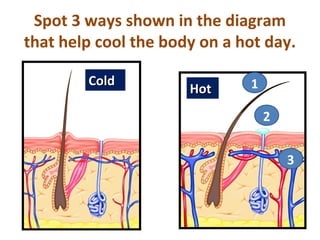
- 39. Spot 3 ways shown in the diagram that help cool the body on a hot day. Cold 1 Hot 2 3
- 41. 5 functions of the skin: 1. Protection – barrier to microbes reduces water loss absorbs UV rays
- 42. 5 functions of the skin: 2. Sensation sensory cells make the body aware of the changes around it through pain, touch, heat cold and pressure
- 43. 5 functions of the skin: 3. Formation of vitamin D by the action of sunlight on the skin
- 44. 5 functions of the skin: 4. Temperature regulation helps to keep a constant body temperature 5. Excretion removes urea in sweat
- 45. Question: Sep, 2011 Give a biological explanation for each of the following: African elephants flap their large ears frequently in hot weather. (4)
- 47. Balance in heat gain and heat loss HEAT GAIN HEAT LOSS
- 48. Ways to GAIN heat 1) INTERNAL CHANGES 2) EXTERNAL CHANGES
- 49. Ways to GAIN heat 1) INTERNAL CHANGES i) reactions release heat ii) muscular contractions release heat IRATION RESP
- 50. Ways to GAIN heat 2) EXTERNAL CHANGES i)body absorbs heat if temperature is more than 37°C ii) hot foods and drinks add heat
- 51. Ways to LOSE heat a)conduction, convection, radiation b) evaporation of sweat c) cold air inhaled d) cold drinks and food
- 53. Find the SA:Vol of the cube Area of 1 side = length x width = 1 x 1 = 1 cm2 Area of 6 sides = 1 x 6 = 6 cm2 Volume = length x width x height = 1 x 1 x 1 = 1 cm3 Surface area to volume ratio = 6:1
- 54. Find the SA:Vol of the cube Area of 1 side = 2 x 2 = 4 cm2 Area of 6 sides = 4 x 6 = 24 cm2 Volume = 2 x 2 x 2 = 8 cm3 Surface area to volume ratio = 3:1
- 55. What happens to the SA:Vol ratio as the cube increases?
- 56. 2 cubes were immersed in a dye for the same amount of time. They were removed and cut in half. Explain the result.
- 57. Rate of diffusion is the same in all cubes BUT distance to centre is different
- 58. A LARGE organism has a small surface area to volume ratio which means: 1. little heat is lost 2. cannot take in oxygen from the body surface by diffusion
- 59. Curling up when cold reduces surface area for heat loss
- 60. A large organism needs a: Circulatory system Breathing system Why does an amoeba lack a circulatory system? Being small, it has a large surface area to volume ratio. Materials reach all parts of the cell quickly.
- 61. A SMALL organism has a large surface area to volume ratio which means: 1. a lot of heat is lost 2. can take in oxygen from the body surface by diffusion
- 62. Which animal has the higher metabolic rate?
- 63. Arctic animals Are large Have small ears Thick fur
- 64. Two species of Lepus adapted to live at different temperatures. Explain how.
- 65. A baby and an adult, both naked, are placed in a room at a low temperature. Which one loses heat faster and dies first? Why? Small body- Large body- large SA: Vol ratio small SA: Vol ratio
- 66. Rule is: LARGE animals in cold climates SMALL animals in hot climates Large body- Small body- little heat loss large heat losses
- 68. fish, reptiles, amphibians and invertebrates absorb heat from their surroundings - this is called basking are poikilotherms Marine iguana basking
- 69. birds and mammals produce heat inside their bodies are homeotherms
- 70. Endotherms insulate their body by: Feathers Fur Blubber
- 71. Question: MAY, 2011 Give a biological explanation for each of the following situations: a)A volunteer student sat in a sauna (a chamber with a temperature reaching 80°C for an hour. Sweat production increased rapidly. (3)
- 72. Increase in external environmental temperature will result in an increase in the internal body temperature. Body produces sweat to regulate the internal temperature. Evaporation of sweat cools down the body temperature.
- 73. Question: MAY, 2011 Give a biological explanation for each of the following situations: b) A young child falls in a frozen lake in winter. The child starts shivering vigorously after being pulled out of the lake. (4)
- 74. Muscles contract and relax quickly – this produces heat. The heat generated in the muscles warms the blood as it flows through them. The blood distributes this heat all over the body.
- 75. Question: MAY, 2011 List THREE ways by which the parents of a child who fell in a frozen lake in winter can prevent further heat loss. (3)
- 76. Provision of dry clothes/moving child next to a warm environment such as a heater/removing cold clothes and covering child with a blanket/ Help child to take a warm bath Provide a warm drink or fluid such as soup.
- 77. Question: SEP, 2010 Give a biological explanation for each of the following statements: In cold weather we tend to shiver and eat more. (3) Shiver: to produce heat Eat more: higher rate of respiration = more heat
- 78. So cool!! THE END