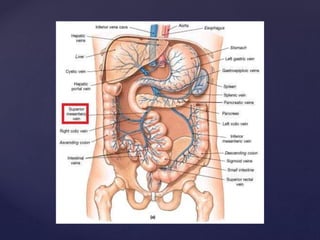
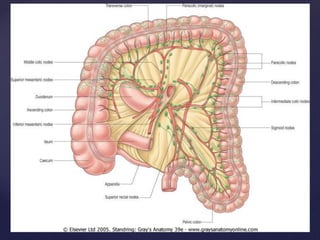
Gross anatomy of the jejunum , including blood and nerve supply, venous and lymphatic drainage.
- 1. { Gross Anatomy of the Jejunum including blood and nerve supply, venous and lymphatic drainage.
- 2. 1 شديد رفيق بن مصطفى بن عاصم 435032467 2 الدايل عبدالرحمن بن يوسف بن عبدالرحمن 435031641 3 الغامدي لوفه آل عبدهللا بن سعود بن عبدهللا 435031674 4 العتيبي الغبيوي تركي بن بندر بن فراس 435031634 5 الشريف الحامد عبدهللا بن غالب بن فهد 435032389 6 المطيري الصيعري عائض بن عيد بن فيصل 435031637 7 الحربي أحمد بن موسى بن متعب 435032375 8 الحارثي الهميلي عبدهللا بن عيضه بن محمد 435032399 9 الحربي مشعل عبدالرحمن 435031643 Teamwork :
- 3. Overview of Jejunum Gross Anatomy of the Jejunum . Blood Supply . Venous Drainage . Nerve Supply . lymphatic drainage . Relations of Jejunum . Location of Jejunum . MCQ In Summary . Topic objectives:
- 4. • The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine . • It is connecting the duodenum to the ileum , it is about 8 ft (2.4 m). • The jejunum begins at the duodenojejunal flexure. Overview of Jejunum
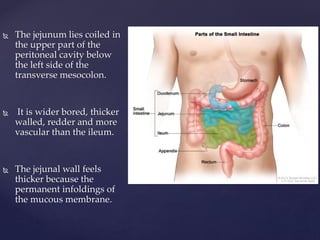
- 5. The jejunum lies coiled in the upper part of the peritoneal cavity below the left side of the transverse mesocolon. It is wider bored, thicker walled, redder and more vascular than the ileum. The jejunal wall feels thicker because the permanent infoldings of the mucous membrane.
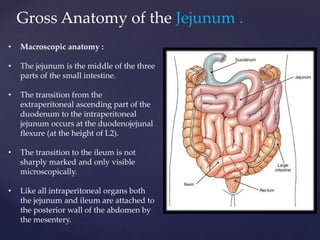
- 6. Gross Anatomy of the Jejunum . • Macroscopic anatomy : • The jejunum is the middle of the three parts of the small intestine. • The transition from the extraperitoneal ascending part of the duodenum to the intraperitoneal jejunum occurs at the duodenojejunal flexure (at the height of L2). • The transition to the ileum is not sharply marked and only visible microscopically. • Like all intraperitoneal organs both the jejunum and ileum are attached to the posterior wall of the abdomen by the mesentery.
- 7. Jejunum ▪ Most absorption of nutrients occurs here ▪ Chemical digestion occurs here ▪ Long finger shaped villi ▪ Thick walled and wide lumen
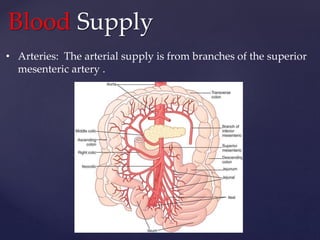
- 8. Blood Supply • Arteries: The arterial supply is from branches of the superior mesenteric artery .
- 9. Venous Drainage of Jejunum • Venous drainage of jejunum is by superior mesenteric vein. • The superior mesenteric vein reach to the point it unites with the splenic vein and form the Portal vein(hepatic portal vein). • The superior mesenteric vein go with (accompanies) the superior mesenteric artery to it’s right and anterior of the superior mesenteric vein.
- 11. Nerve Supply of jejunum • Nerve Supply of jejunum derived from : • sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves . • The sympathetic innervation is carried by the nerves of superior mesenteric plexus, the parasympathetic innervation by the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X).
- 13. lymphatic drainage • Lymphatic vessels of the jejunum pass into mesenteric nodes via the lacteals of the villi. • They do not reach the superior mesenteric nodes, which the blood vessels follow. • All the efferents pass into the intestinal lymph trunks, which then enter the cisterna chyli or the abdominal confluence of lymph trunks. • The cisterna chyli drains into the thoracic duct.
- 14. mesenteric nodes
- 16. Relations of jejunum The jejunum begins at the duodenojejunal flexure at the level of second lumbar vertebra. the duodenojejunal flexure is located on left of the aorta.
- 17. Location of Jejunum Most of the jejunum Lies in the upper part of the abdominal cavity and to the left of the midline. The coils of jejunum is attached to the posterior abdominal wall by a fan-shaped fold of peritoneum known as the mesentery of the small intestine.
- 19. MCQs 1- Venous drainage of jejunum is drawn by : a- superior mesenteric artery b- inferior mesenteric artery c- superior mesenteric vein d- inferior mesenteric vein 2- At what level does the jejunum begin : a .Thoracic XII. b .Lumber III. . c .Lumber II. d .Sacrum. 3- Lymphatic vessels within the bowel villi, which carry the lipids to the circulatory system, are known as: a. vessels. b. ductules. c. canaliculi. d. lacteals.
- 20. The jejunum makes up about it is 8 ft ((2.4 m)). The arterial supply is from branches of the superior mesenteric artery . Veins drain into superior mesenteric vein The sympathetic innervation is carried by the nerves of superior mesenteric plexus, the parasympathetic innervation by the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X). Lymph vessels pass through many intermediate mesenteric nodes & finally reach superior mesenteric nodes (situated around origin of mesenteric artery) In Summary
- 21. THANK YOU