Fmla ada overlap
- 1. FMLA and ADA Overlap
- 2. Why Do We Care About FMLA and ADA Overlap Employers have responsibility to make sure employees receive the benefits and protections required by the laws Violations of these laws or error in application can result in massive lawsuits, huge settlements, back pay, reinstatement, retroactive pay, retroactive benefits, punitive damages Majority of unscheduled and scheduled absences are related to illnesses of employees and their family members, which may involve one or both laws
- 3. Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) Overview Became effective August 5, 1993 Entitles eligible employees to take up to 12 weeks unpaid leave Allows employees to balance work and family life Minimizes employee discrimination while promoting equal employment opportunities for men and women Administered and enforced by U.S. Dept. of Labor’s Employment Standards Administration, Wage and Hour Division
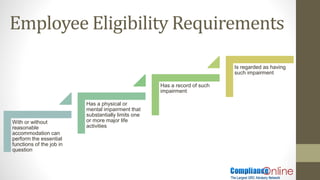
- 4. Employee Eligibility Requirements Work for a covered employer Have worked for the employer for a total of 12 months (doesn’t have to be consecutive) Have worked at least 1,250 hours over the previous 12 months Work at a location in the US where at least 50 employees are employed by the employer within 75 miles.
- 5. Eligible Reasons for FMLA Leave The birth and care of a newborn child of the employee The placement with the employee of a son or daughter for adoption or foster care Caring for a spouse, son, daughter, or parent with a serious health condition Taking medical leave when the employee is unable to work because of a serious health condition For qualifying exigencies arising regarding employee’s son, daughter, or parent while on active duty status
- 6. ADA Overview ADA prohibits employers from discriminating against qualified individuals with disabilities in job application procedures, hiring, firing, advancement, job assignments, pay, benefits, job training, and other employment practices. ADA covers employers with 15 or more employees. ADA also requires that employers provide reasonable accommodation for a known disability of a qualified applicant or employee if it would not impose an "undue hardship" on the operations of the employer's business. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) has primary responsibility for enforcing the employment- related portions of the ADA. The ADA Amendments Act of 2008 (ADAAA) was signed into law in 2008, effective January 1, 2009. ADAAA made changes to definition of disability. Made it easier for individuals to claim he or she has a disability within the meaning of the statute. ADAAA states that definition of disability should be interpreted in favor of broad coverage of individuals.
- 7. Employee Eligibility Requirements With or without reasonable accommodation can perform the essential functions of the job in question Has a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities Has a record of such impairment Is regarded as having such impairment
- 8. Reasonable accommodation may include Making existing facilities used by employees readily accessible to and usable by persons with disabilities Job restructuring, modifying work schedules, reassignment to a vacant position Acquiring or modifying equipment or devices; adjusting or modifying examinations, training materials or policies; and providing qualified readers or interpreters
- 9. FMLA ADA
- 10. Covered Employers Private employers with 50 or more employees State and local government employees and most federal government employers FMLA Private employers and employment agencies with 15 or more employees State and local governments, but not the federal government ADA
- 11. Qualifying Events FMLA Employee’s own serious medical condition; Serious medical condition of the employee’s spouse, child, or parent Birth, adoption, or foster care placement of a minor child Qualifying exigency arising from a family member’s call to active duty Family member’s injury or illness incurred or aggravated while on active duty military service ADA Qualified individual must have a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits a major life activity “Record of” such an impairment “Regarded” by others as having an impairment
- 12. Employee Eligibility Worked for 12 months and a total of 1,250 hours Individual with a disability who is qualified for the job in question Can perform the job with or without reasonable accommodation FMLA ADA
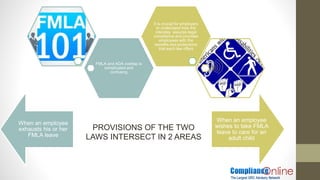
- 13. FMLA and ADA overlap is complicated and confusing It is crucial for employers to understand how the interplay assures legal compliance and provides employees with the benefits and protections that each law offers When an employee exhausts his or her FMLA leave When an employee wishes to take FMLA leave to care for an adult child PROVISIONS OF THE TWO LAWS INTERSECT IN 2 AREAS
- 14. Thank You To knowmoreonFMLAorADA visit www.complianceonline.com