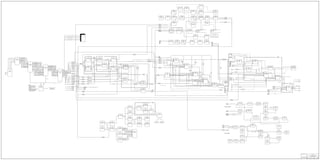
ERP System Process and Data Flow in Gane & Sarson Notation
- 1. Combined diagrams from Team Interviews 11 March 1998 Manufacturing Level 1 Gane & Sarson Models Current System State SIZ FSCM NO DWG NO REV E+ 2.1 SCALE 1 : 1 SHEET 1 OF 2 Idea Generation P1-01 Concept Development P1-02 Resource Plan P1-03 Prepare to Sell P1-04 Component Availability Master Product Plan Sales History Product Ideas Competitive Analysis Physical Mockups Project Cost Sales Volumes Mfg Techniques Target Pricing Test Results Prod Specs 3D Models 2D Drawings Tooling Project Schedule Introduction Dates Key Items 3D Models Spec / Design Freeze Produce Key Items Costing Testing Packaging Prelim BOM Model Numbers NC programs 2D Shop Dwgs Potential Vendors Part # Assigned Prelim Routings Sales Budget Customer Service Plans Training Plans Order Processing Plan Pilot Run Plan Vendor Determination Mstr Prod Schedule Mfg Material Plan QA Plan Shipping Plan Lead Time Plan Cmplt Cust Srv Plan Cmplt Purch Plan Cmplt Mstr Prod Plan Cmplt QA Plan Cmplt Lead Time Plan Cmplt Logistics Plan Finalize Wghts / Cubes Finalize BOM's Finalize Dwgs Finalize NC Pgms Finalize Inst Shts Production Training Finalize Wrk Inst 6 P0 6 P0 Routings Planning BOM's 6 P0 Planning Information 1 3 2 1 Product Planning P1-00 Market Research Product Changes P1-06 ECR Form Necessary Changes ECR Form ECR Form Notification of Change to Effected Areas: (P-01,02,03,04,05,07) NOTE: ECR's can come from any process after product introduction, including the following: Develop Products, Take Orders, Plan Production, Producer Product, Deliver Products, & Service the Customer Design/Proto Review Pilot Run Findings System verification Production Design Validation BIFMA Certification Final test Results Receive Order from SAP P2-04 Receive Outside Order (Hard Copy) P2-01 Enter Order Into EN44 P2-03 Archive Fulfilled Order P2-06 Credit Check P2-07 Logia Updates Copics (Order Dependent) P2-10 Allocate Logia ATP Date in EN44 P2-09 Send Acknowledgement to Customer P2-11 Copics Confirms Receipt to Logia P2-12 Logia Send Demand to Copics P2-13 To Master Schedule Deliver the Product Run Logia BOM Purge Process P2-15 Update Activity Status in Logia P2-16 Audit Promise Date File P2-17 Send File Back To SAP P2-18 Generate Price and Cost File P2-19 Send File Back to SAP P2-20 To Master Schedule Audit Order P2-02 Deliver the Product D1 Product Definition Data Base End Items Bill of Materials Routings P2-14 Warehouse Removes Demand from Copics Produt_ID D1 Master Schedule Database Quantity Demand Data 4 P4 4 P4 5 P3 5 P3 Product Information 2 1 3 2 Enter Order Into Logia (Automated) P2-04 Generate ATP Update (Automated) P2-08 Enter Order Into Logia (Manual) P2-04 Generate ATP Update (Automated) P2-08 Ship Information 13 P5 6 9 P5 12 P5 ATP Information Master Schedule Information KOG Sales Outside Sales Harpers Review Ordered Enter Order into MacPac P2-03 Adjust Shipment Date P2-09 Audit Order Generate Manual ATP Create Manufacturing Orders To Master Schedule 5 P3 3 Order Information is sent to Product_ID P2-21 Resource Planning P3-01 Time Phased Requirement (MRP) Records P3-07 Detailed Capacity Planning (Machine Center Constraints) P3-08 Production Planning (Capacity Lead Planning) P3-03 Detailed Material Planning P3-05 Vendor / Supplier Systems P3-10 Shop Floor Scheduling (Shop Order Release - SOR) P3-09 Demand Management P3-02 Bookings Inventory Lvl Shipments Production Sums or $ Master Production Scheduling P3-04 Customer Orders < Lead Times Configured Model Confirmed Orders Net of Forecast Forecast Input for Shop Floor Planning Information Key Constraint Wrk Ctr Shop Floor Reqmt's Material Requirements Inventory Information D2 Bills of Material D3 Routing Information Machined Parts Unit Assemblies Cell Level Planning Provide ATP P3-06 D1 Planning BOM Allocation Schedule Resources Shop Floor Scheduling SOP Confirmed Ship date Sales Forecast Sales Forecast PO's SUM's SOR Docs Master Schedule Information Product ID Labels Material Plan Independent Reqmt's, Qty & Due Date Min/Max 5 P2 1 P2 Master Schedule Updates Current Production Schedule (Pre SOP) 5 2 BOM's Order Entry from SAP Purchasing Plan Routing Info 3 P2 2 P2 Inv Info Customer Order within Lead Times Machine Components P4-02 Storage P4-01 Build Products P4-03 Finish Products P4-04 Trim Subassemblies P4-05 Pack Product for Shipment or Warehouse P4-06 Receiving Raw Materials Purchased Parts Purchased Parts Assemblies and Units Metal Components Laminates Fabricated Metal Finished Units Machined Wood Parts SOR (M.O.) Work Instructions Drawings Inventory Information Inventory Information Inventory Information Inventory Information Work Instructions Product Cost Mstr Sched Update Shipping Info Invoice Info Finished Units BOM BOM BOM Finished BOM Drawings Assemblies and Units Work Instructions Laminates 4 P3 11 P1 10 P1 Drawings 1 P5 Work Instructions BOM Laminates Purchased Parts Dwgs SOR (JIT List) CNC Programs Fab Metal SOR (JIT) Fabricated Metal Finished Units BOM Drawings Work Instructions Finished Units SOR (M.O.) Purchased Parts Purchased Parts 1 3 5 5 12 P1 Q Parts Q Parts Q Parts xx P5 6 Harpers 3 P5 4 P5 Product ID Labels Ship Product P5-07 Prepare for Shipment P5-06 Crate Product for Overseas Shipments P5-05 Stage Products P5-01 Warehouse Products P5-04 Shuttle Products P5-03 Schedule Truck (Loading Plan) P5-02 Barcoded Information Shuttle Report (Max PayLoad) Delivery Date Barcode Scan Cube / Weight Ship To Information Inventory Location Shipping Labels Confirmation of Pick List (Final Scan) Pick List (Max Payload) Crate Report (Max Payload) Bingo List (Artec) Bill of Lading Packaging List Release Delivery Export Documents Ford, Sal, FL, KUP1 NOF, SC, Artec, KUP2, Bor Harpers NOF-SC, Artec, KUP2, Bor Product Shipment Ford, Sal, FL, KUP1&2 NOF, SC, Artec, KUP1&2, Bor NOF-SC, Artec, KUP2, Bor Harpers Ford, Sal, FL, KUP1 Consolidate Shipment 1 P4 1 A1 1 A1 1 A1 Harpers Release Finished Goods Inventory Owned by KOG Sales P5-08 Harpers 1 2 1 4 5 6 7 8 11 14 15 3 2 16 17 18 2 P4 4 P4 3 P4 Inventory Information Inc & Ready to Ship (Max Payload)16 Stop Number Product Reserve for SO17 Q parts 1 P4 18 Invoice Created On Time Calc 5 4 NOF-SC, Artec, KUP1&2, Bor HarpersShuttle Product Shuttle Accept Call from Dealer P7-01 Accept Call from Customer P7-02 Locate Product Information P7-03 Identify Quality Issues P7-04 Enter Issue Into QTS P7-05 Locate Technical Information P7-06 Locate General Information P7-07 Locate Installation Information P7-08 Respond to Customer P7-09 Call Plant Price List Other PDA KRL Magic Copics Price List PQA Member Call Plant Call Plant Magic / Copics Kimball Care Other PQA Generate Service Orders P7-10 Generate Replacement Orders P7-11 Approve Repair Changes P7-12 Additional Discount P7-13 Notify Service Via Resolution Form P7-14 Customer Service Issues Credit P7-15 Look Parts in Copics P7-16 Put Information in Description of Order P7-17 Send KForm to Data Mot Team P7-18 Process Order P7-19 Enter Orders P7-20 Setup Model D1 SAP D2 Legacy Notify Customer Via Resolution Form P7-16 PQA or Customer Service Issues Credit P7-18 5 P1 1 Credit Check P6-01 Take Order Ship Product Establish Credit For Customer P6-02 Enter Customer into EN01 P6-03 Invoice Customer P6-05 Receive Payment P6-08 Review A/R File P6-07 Collection of Undisputed Accts. P6-09 Post to A/R File P6-06 Credit Hold P6-10 Maintain Credit File P6-04 Purchase Request P6-11 Issue P.O. P6-12 Record in GL Account P6-13 Send to Customer P6-14 Petty Cash Request P6-18 Petty Cash Process P6-17 Check Request P6-16 Expense Report P6-15 A/P File Update P6-20 Receiving P6-24 Return Rejected Material P6-25 Match Invoice to P.O. & Receiving Documents P6-19 Issue Check P6-22 Update Check Register P6-23 Void Check P6-21 Material Input P6-26 AVendor Invoice Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable B.O.L. Packing List QA Report Capital Request MRP Request Purchase Request Form Customer Order Request For Credit D & B Report Credit References A Credit Check Prior to Shipping P6-01 4 P1 2 8 P1 1 4 P1 3 7 7 P1 1 P1 4 3 P3 2 2 P4 3 6 P4 2 P3 6 2 P3 5 7 P4 1 7 1 P3 1 P6 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 4 P3 7 6 P1 6 7 7 P3 8 1 P3 7 7 P3 6 6 P3 5 1 P7 8 1 P4 19 P5 1 8 P3 4 P5 5 P4 19 Master Scheduling 4 P4 3 4 P4 4 P5 3 1 P6 4 4 P5 2 5 P4 Invoice Information Invoice Information 2 P2 4 P2 5 5 P3 4 9 P5 4 12 P5 13 P5 4 P2 9 4 P2 13 4 P2 12 13 P1 10 13 10 P5 8 P1 4 7 P1 1 15 12 1 P4 11 1 P4 10 3 P4 9 4 P4 2 P3 4 14 1 P2 5 P4 id Project Folder 2 P3 Copy of PO Stop Number
- 2. 01 Master Product Plan 02 Competitive Analysis 03 Product IDEAS 04 Sales History 05 Tollgate Findings & Sign Off Doc. 06 Product Line Offering Conceptual Sketches MS Project MS Word IDEAS SDRC MS Excel 07 Estimated Project Costs (return map) IDEA Generation P1-01 08 Estimated Sales Volume 09 Target Pricing 10 Product Spec's (Prelim.) 11 3D Solid Models / 2D Drawings 12 Prelim. ProductTest Results 13 Product Line Offering Document 14 Updated Project Schedule 01 Product Line Offering Document 02 3D Solid Models 03 2D Drawings 04 Product Specifications 15 Preliminary Routings & NC Programs 16 Test Results of Key Items MS Project Copics IDEAS SDRC MS Excel Data IN Data OUT Data USERS 07 Finalized Product Line Package Concept Development P1-02 08 Finalized Project Objectives 09 Finalize Sales Projections 10 Collateral & Promotional Plan 11 Solid Models of Key Items 12 Drawings of Key Items 13 BOM's of Key Items 14 Preliminary costing 05 Target Pricing 06 Estimated Sales Volume 18 Tollgate Findings & Sign Off Doc. 19 Preliminary Packing Requirements 17 Updated Project Schedule OV Email Logia 01 Spec Freeze 02 Phase III Tollgate Findings/Approval 03 Project Plan (Targeted Intro. Date) 04 Sales Strategy Plan MS Project MS Word 07 Sales/Mfg. Training Plan Resource Planning P1-03 08 Mfg. Materials Plan 09 Production Plan 10 Quality Assurance Plan 11 Marketed Leadtime Plan 12 Logistics/Shipping Plan 13 Update Master Project Schedule 14 Tollgate Findings & Sign Off Doc. 05 Customer Service Plan 06 Order Process Plan OV Email 01 Completed Plans From Planning Phase 02 Outputs From Concept Development Phase 03 2D Drawings 04 NC Programs 15 Installation Instruction Sheets 16 Product Cubes & Weights MS Word Copics IDEAS SDRC MS Excel Data IN 07 Finalized Packaging Designs Prepare to Sell P1-04 08 Routings 09 Actual Product Cost 10 Collateral Materials 11 Planning Data 12 Planning BOM's 13 BOM's 14 Completed Plans From Planning Phase 05 Pilot Run Findings 06 3D Solid Models 18 Tollgate Findings & Sign Off Doc. 17 Final Test Results OV Email Logia 01 Sales & Operation Plan 02 Market Research 03 Product Spec's 04 Design Criteria 05 Sales Projection 06 Price Target MS Project MS Word/ Excel IDEASEmail 01 Product Spec's 02 Design Criteria 03 Sales Projection Seating Engineering P1-03 01 SEE OUTPUUT from CONCEPT 07 Budgeted Tooling Cost Seating Concept Phase P1-02 Seating Planning Phase P1-01 06 Product Spec's * Team Make-up * Model No. 07 Digital Models * Test Matrix * FTSG Testing Req. 08 Sketches 09 Scale Models 10 Product Spec's (Briefs) 04 Price Target 05 Budgeted Tooling MS Project MS Office IDEASEmail 11 Product Schedules * Concept Phase * Approval Form MS Project MS Office IDEASEmail 02 Product Spec's Patent Search 03 Projected Income Product Name Mktng. Dvlp. Plan 04 Training Plan 05 Feasibility Verify Price To Sales Short List Mtrl 06 Prototypes QA Plan Dvlp. Test Criteria 07 Final Mtrl ?????? Quote Proc. Bid Tollgate Form 01 Requisition Tooling Tooled Part Verify Testing 02 List of Models for Pilot Run Model Spec's 03 Devel. Uphol. Spec Cover Patterns FAB Foam Pattern Glue Spec's Hand Cut Patterns 04 Potential Restrictions Sewing Spec's Model info Doc. IDEAS MS Office Projects PM & C SOR EN44 SAP Logia Copics 05 Model # Setup Pilot Run Walk list Prepare to Produce & Sell P1-04 EMAIL 06 Tollgate Signoff 01 Introduce Product to Market 02 ACK Orders MFG. PO's 03 Production Schedules Copics SOR PM & C SAPLogia Implement P1-05 MRP Leland 01 ECR Form Copics Logia Dem. Sol Share File Notelog EMAIL Seating Maintenance P1-06 Take Orders Specials For KOF Casegoods P - 02 01 TIF Report 02 Quote Request Form 03 Model Request Set-up 04 C & C (Change & Cancel) Dyna Plan Copics Data IN Data OUT Data USERS 05 Factory Order 06 Dyna Plan Spreadsheet EN44 O.V.TIF MRP Prod. ID IDEAS Master Production Scheduling P3-04 01 EN44 02 Wkly Release & SAP Demand Mgmt. 03 Capacity Report 04 Capacity Plan sums 05 Planning Data 06 Line Schedules 07 Product ID Labels 08 Manifests 09 Reports Dyna Plan O.V. Legacy (EN44) Mac Pac SAP Provide ATP P3-06 01 Capacity Report (SAP) 02 Sums Report 03 Scheduled Prod. Report 04 Confirmation Report (SAP) Dyna Plan SAP MRP P3-0701 Routings 02 BOM 03 Planning Data 05 Reports Dyna Plan Copics 04 Dyna Plan Schedule Shop Floor Scheduling P3-09 01 Parm Card Updates 07 SOR Documents / Shop Ticket Copics (SOR) 08 Shop Drawing 09 Product ID Labels 10 Reports Vendor Supplier System P3-10 01 Min/Max 04 PO #'s MRP 05 Inventory Info 02 Mat. Req. (MRP) 03 Supplier Info Leland Produce Product P-04 01 CNC Program 02 Drawings 03 SOR # 04 Shop Paper 05 NI's 07 Inventory Rec. 08 MS Updates 09 Cost 10 Shipping Info O.V. - shared MagicSOR Data IN Data OUT Data USERS 06 Shop Ticket Sum Report CopicsLogia MRP Prod. ID- Max payload Deliver the Product P5 - 00 01 Inventory Info (Order Level Detail) 02 Shipping Info 03 Product Cost 10 Bill of Lading Product ID Logistics & Maxpa- load 04 Shuttle Report 05 Shipping Label (Manifest) Product ID Label 06 Pick List 11 Packing List 12 Bingo Sheet 13 Export Documents (Furnished by Logistics) Finished Goods Ship System Manifest 07 Orders Ready For Shipment Report 08 Print Bill of Lading 09 Print Packing List (Bingo Sheet) Establish Credit For Customers (#2) P6-00 01 Customer Info 02 Dunn & Bradstreet Report 03 Service Order Parts Listing 04 Credit Limit 05 Enter Customer Info into System EN01 Mac Pac 06 Credit Info Maintain Credit Files (#4) P6-00 01 Financial Statement (Out of Date Report) 02 Credit Line (Out of Date Report) 03 Update Info in EN01 Review Aging Report File Weekly (#7) P6-00 01 Accts Received Aging Report 02 10 Day Letter 03 Turned Over to Collection Collection of Undisputed Accounts (#9) P6-00 04 Due & Payable Letter 01 Past Due Invoices 02 Order List 03 Customer Credit Line O.V. Purchase Request (#11) P6-00 01 Rec. Purchasing Info 02 Capital Request 03 Purchase Request Form 04 MRP Request 05 Issue PO Leland Vendor Remittances (#19) P6-00 01 Vendor Invoices 02 Rec. Records 03 Packing List 04 Invoice Approval 05 Buyer Exception Reports Leland Petty Cash (#18) P6-00 01 Petty Cash Receipts 02 Check Request Service the Customer P7-00 01 QTS Info 02 Kimball Care Tool (KCT) 03 Service Order Parts Listing 04 Order Info 05 KRL Info 07 QTS Report 08 Kimball Care Tool 09 Service Order ACK's 10 KRL Legacy (EN44) Mac Pac SAP 06 Copics Combined diagrams from Team Interviews 17 March 1998 Manufacturing Level 1 Gane & Sarson Data Model Relationships SIZ FSCM NO DWG NO REV E+ 2.1 SCALE 1 : 1 SHEET 2 OF 2