The Plot
- 1. KEYWORDS AND CONCEPTS: PLOT BY: STEFANI NICOLE D. ALCANTAR KARLO EDESSON P. ABRIL
- 2. WHAT IS A PLOT? In literature, a plot is all the events in a story particularly rendered towards the achievement of some particular artistic or emotional effect.
- 3. TYPES OF PLOTS: PYRAMIDAL EPISODIC EPIPHANIC
- 4. Pyramidal Plot The most basic and traditional form of plot Mostly, are plot structures of short stories Can be analyzed using Gustav Freytag’s Triangle that was originally based on Aristotle’s Plot with Unity of Action
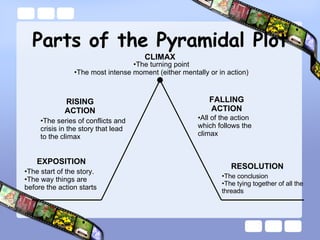
- 5. Parts of the Pyramidal Plot EXPOSITION RISING ACTION CLIMAX FALLING ACTION RESOLUTION The start of the story. The way things are before the action starts The series of conflicts and crisis in the story that lead to the climax The turning point The most intense moment (either mentally or in action) All of the action which follows the climax The conclusion The tying together of all the threads
- 6. Some Prose with Pyramidal Plots A Rose for Emily by William Faulkner The Piece of String by Guy de Maupassant The Flood in Tarlac by Gregorio Brilliantes
- 7. Episodic Plot Features distinct episodes that are related to one another but that can also be read individually, almost as stories by themselves Mostly, are plot structures of novels
- 8. Some Prose with Episodic Plots Don Quixote by Miguel de Cervantes Huckleberry Finn by Mark Twain Harry Potter Series
- 9. Epiphanic Plot Where the protagonist gains a sudden insight into his condition or circumstances, caused by his struggle with antagonistic forces, that leads him/her to take action that brings on the climax or reversal
- 10. Plots can be told… in chronological order using flashbacks “ in medias res ”
- 11. In Medias Res: What is it? Latin for " into the middle of things “ a literary and artistic technique where the narrative starts in the middle of the story instead of from its beginning
- 12. “ In Medias Res” Examples John Milton’s Paradise Lost and Inferno Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey The East Indian Mahabharata Edgar Allan Poe’s The Tell-Tale Heart
- 13. Sources http://www.wikipedia.org http://encarta.msn.com/ http://www.cnr.edu/home/bmcmanus/freytag.html http://www.natf.org/wad/lexicon.htm