Fundamental rights n duties
- 4. CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS 3. FUNDAMENTAL DUTIES 4. COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS of FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS and DUTIES 5. CONCLUSION
- 5. INTRODUCTION The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India. It lays down the framework defining principles powers, and duties of government institutions, and sets out fundamental rights, directive principles, and the duties of citizens. It is the longest written constitution of any sovereign country in the world, containing 448 articles in 25 parts, 12 schedules, 5 appendices and 98 amendments (out of 120 Constitution Amendment Bills).
- 6. Besides the English version, there is an official Hindi translation. Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar is widely regarded as The Father of the Indian Constitution.
- 7. FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS Fundamental Rights is a charter of rights in Constitution of India. Part - III of the Indian Constitution contains the list of Fundamental Rights. It guarantees civil liberties such that all Indians can lead their lives in peace and harmony .
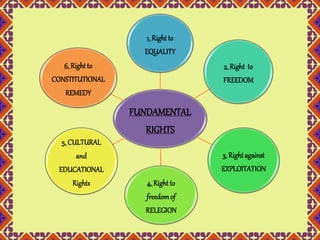
- 8. 1. Right to EQUALITY FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS 2. Right to FREEDOM 3. Right against EXPLOITATION 4. Right to freedom of RELEGION 6. Right to CONSTITUTIONAL REMEDY 5. CULTURAL and EDUCATIONAL Rights
- 9. 1.Right to Equality (under Article 14 – Article 18 ) It refers to the equality in the eyes of law, discarding any unfairness on grounds of caste, creed, race, religion, place of birth, sex. All human beings are born free and are equal in dignity and rights.
- 10. 2. Right to Freedom (under Article 19 – Article 22 ) This right provides various freedoms- Freedom of speech and expression, Freedom to form association or union, Freedom to move freely throughout the territory of India, Freedom to reside and settle in any territory of India, Freedom to practice any profession. Freedom
- 11. 3. Right against Exploitation ( under Article 23 – Article 24 ) These rights aim at protecting citizens from environmental, domestic and work hazards. It consist of 2 major provisions . First is the abolition of forced labor and second is the abolition of employing of the children under 14 years of age.
- 12. 4. Right to freedom of Religion (under Article 25 – Article 28 ) It supports the freedom of an individual or group that every citizen has the right to practice and promote their religion peacefully; the concept is generally recognized also to include the freedom to change religion or not to follow any religion.
- 13. 5. Cultural and Educational Right (under Article 29 – Article 30 ) This right allows every citizen of India to have a cultural and education up to where that person wants. No citizen shall be denied admission into any educational institution on basis of religion, race, caste, language or any of them.
- 14. 6. Right to Constitutional Remedies (under Article 32 ) It protect the rights of the citizens , they can stand up and fight for their fundamental rights. In case any of the rights denied to the resident of the country, the individual or the party has the right to present their case in a court.
- 15. FUNDAMENTAL DUTIES Fundamental Duties are the ones that are recognized as moral obligations the citizens are expected to perform. Article 51A under Part IV A of the Constitution of India speaks of the Fundamental duties. It was through the 42nd Amendment that these duties were introduced in the Constitution.
- 16. Fundamental Duties are :- 1. To respect the National Flag and the National Anthem. 2. To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom. 3. To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India . 4. Citizens should be ready to defend and render national service towards India.
- 17. 5. To promote harmony and the spirit of brotherhood among all people of India on religious or sectional diversities and to renounce practices derogatory to the dignity of women. 6. To value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture. 7. Natural environment including the forests, lakes, rivers and wildlife are expected to be preserved by the citizens.
- 18. 8. To develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform. 9. To safeguard public property and to avoid violence. 10. People are expected for the excellence of all the individuals and collective activities to help in the development of the country. 11. To provide opportunities for education to child between the age of 6-14 years.
- 19. Comparative Analysis of FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS and FUNDAMENTAL DUTIES
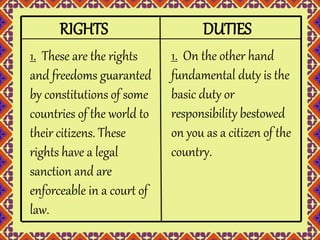
- 20. RIGHTS DUTIES 1. These are the rights and freedoms guaranted by constitutions of some countries of the world to their citizens. These rights have a legal sanction and are enforceable in a court of law. 1. On the other hand fundamental duty is the basic duty or responsibility bestowed on you as a citizen of the country.
- 21. 2. A fundamental right exists by virtue of the fact that you are a human being. 3. Fundamental right is based on privilege granted to you. 2. A fundamental duty exists as a responsibility on you as a human being. 3. Fundamental duty is based on accountability.
- 22. 4. There are 6 fundamental rights. 5. Any citizen for that matter can make full use of his fundamental rights pertaining to right to life, freedom of speech etc. 4. There are 11 fundamental duties. 5. Any citizen for that matter is expected to carry out fundamental duties fully well so that the society as a whole will be benefited.
- 23. CONCLUSION Fundamental Rights and Duties are of no use until we use our rights for the betterment of our society. Only written things are of no use until we make it in our practice. It’s time we live our differences behind, come together and fight for things that are fundamentally right. Lets show them our strengths in numbers and solidarity. THE REVOLUTION CAN HAPPEN
- 24. THANK YOU
- 25. Any Queries ?