Roof Framing
- 1. Wood Frame Construction ROOF FRAMING Terms Shapes/Styles Framing Conditions Roof Pitch/Slope Professor Richard luxenburg AIA Department of Architecture and Interior Design Anne Arundel Community College Buckwalter Hoouse, PA Hugh Newell Jacobsen, Architect
- 3. GABLE Triangular part of the wall under each end of a roof gable rake board
- 5. VALLEY Low points formed by the intersection of two roof slopes (forming a trough to direct water). Formed by valley rafters Diagonal rafter that supports the valley intersection DORMER Structure protruding through the plane of a sloping roof Has its own roof structure A small secondary roof structure RIDGE Top part of gable or hip roofs Area where rafters meet ridge board Where the roof “folds” over the top
- 6. Framing a Roof Opening for a Dormer DOUBLE HEADER RAFTERS DOUBLE TRIMMER RAFTER
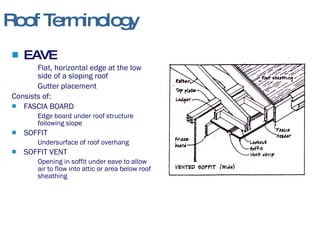
- 7. Roof Terminology EAVE Flat, horizontal edge at the low side of a sloping roof Gutter placement Consists of: FASCIA BOARD Edge board under roof structure following slope SOFFIT Undersurface of roof overhang SOFFIT VENT Opening in soffit under eave to allow air to flow into attic or area below roof sheathing
- 8. Eave - Horizontal roof edge Rake - Sloping roof edge Terminology
- 9. Eave Detail Metal Drip Edge Soffit Wood Metal Plastic Gutter Fascia
- 10. Rake and Eave Connections
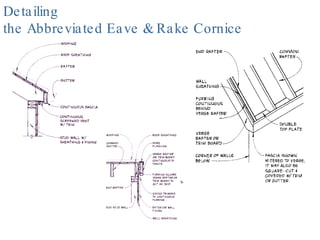
- 11. Detailing the Abbreviated Eave & Rake Cornice
- 12. A ladder of lookouts supports and provides a nailing surface for a boxed-in rake. SMALL OVERHANG LARGE OVERHANG Soffit Details
- 14. ROOF SHAPES & STYLES FLAT minimal slope ¼” per foot SHED ( or mono-pitch) slopes in one direction slope can vary
- 15. ROOF SHAPES & STYLES GABLE Slopes in two directions Rafters (or truss) meet at top peak to a ridge board HIP slopes in four directions slope is constant on all sides
- 16. RIDGE CONNECTIONS Gable Roof
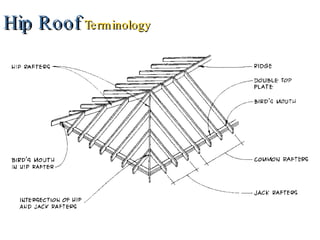
- 17. Hip Roof Terminology
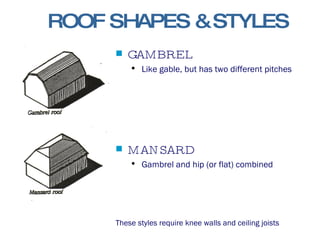
- 18. GAMBREL Like gable, but has two different pitches MANSARD Gambrel and hip (or flat) combined These styles require knee walls and ceiling joists ROOF SHAPES & STYLES
- 19. LEAN-TO ROOF SHED MEETING A WALL
- 20. FLAT ROOF OVERHANG CONDITIONS
- 21. Roof Trusses
- 23. Valleys in Trussed Roofs
- 25. ABBREVIATED EAVE FRAMED WITH TRUSSES BOXED-IN TOP CORD OF TRUSS EXTENDED TOP CORD WITH SOFFITED EAVE Cornice Details using Roof Trusses
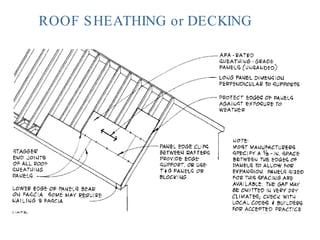
- 26. ROOF SHEATHING or DECKING
- 27. No SHEATHING with diagonal bracing for use with wood shingles and shakes
- 29. Plywood Clip: To prevent separation of roof sheathing at mid span between rafters or trusses Also allows moisture expansion of the sheathing; typically 1/8” spacing between panels
- 30. Roof Slope and Pitch Pitch as a: Ratio of vertical to horizontal. For example, a roof that rises 6 inches (or feet) for every 12 inches (of feet) of horizontal run has a 6/12 pitch.
Editor's Notes
- #10: Eaves Horizontal Roof Edges PROVIDE AN “OVERHANG” KEEP WATER OFF SIDING REALIZE THE VOLUME OF WATER ALSO CAN PROVIDE “SHADE” Rakes Sloping Roof Edges AUTHOR SHOWS FLUSH W/ SIDING OFTEN AN OVERHANG TO PREVENT STAINING OVERHANG SUPPORTED BY “LOOKOUTS” Edge Details INSTALLED PRIOR TO ROOFING Fascia & Rack Boards Fascia @ Eaves Rake Boards @ Rakes Metal Drip Edges TO KEEP WATER OFF TRIM & SIDING