Crude oil
- 1. Crude Oil BTEOTSSSBAT: know the origin of crude oil understand the components and properties of hydrocarbons,
- 2. Key words Crude oil Compound Mixture Distillation Hydrocarbons Saturated Alkanes Covalent bond Evaporating Condense Fractional distillation Fractionating column Particulates Combustion Soot Biofuels
- 3. How crude oil was formed • Microscopic plants and animals die and fall to the sea bed • Layers of sand and mud form on top • Pressure and high temperature cause oil to form • Oil obtained by drilling
- 4. Oil is a fossil fuel Other fossils fuels are: Coal and Gas
- 5. Non-renewable Renewable Biofuels – ethanol and biodiesel made from plants
- 6. Crude oil is a mixture of a very large number of compounds. These compounds can be separated by distillation.
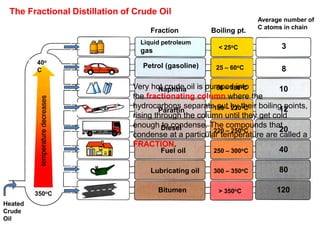
- 7. Heated Crude Oil 40o C 350oC Fraction Boiling pt. Liquid petroleum gas Petrol (gasoline) Naphtha Paraffin Diesel Fuel oil Lubricating oil Bitumen < 25oC 25 – 60oC 60 – 180oC 180 – 220oC 220 – 250oC 250 – 300oC 300 – 350oC > 350oC Average number of C atoms in chain 3 8 10 12 20 40 80 120 The Fractional Distillation of Crude Oil Very hot crude oil is pumped into the fractionating column where the hydrocarbons separate out by their boiling points, rising through the column until they get cold enough to condense. The compounds that condense at a particular temperature are called a FRACTION.
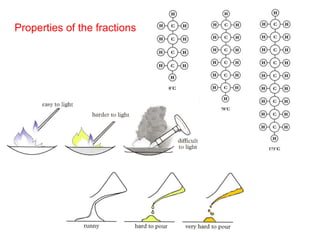
- 8. Properties of the fractions
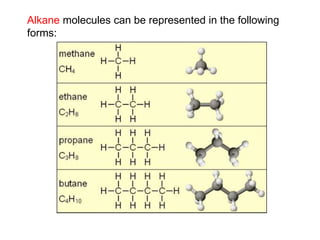
- 9. Most of the compounds in crude oil consist of molecules made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms only (hydrocarbons). Most of these are saturated hydrocarbons called alkanes. Write the chemical formula for these alkanes In general: CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 CnH2n+2
- 10. Alkane molecules can be represented in the following forms:
- 11. Fuels Most alkanes are used as fuels to produce useful forms of energy. When completely burned alkanes form carbon dioxide and water.
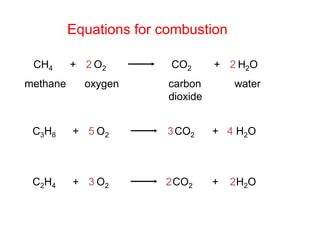
- 12. Equations for combustion CH4 methane + O2 2 2 oxygen CO2 carbon dioxide + H2O water CH+ 5 O3 CO+ 4 HO 38 2 2 2CH+ 3 O2CO+ 2 HO 24 2 2 2
- 13. Most fuels, including coal, contain carbon and/or hydrogen and may also contain some sulfur. The gases released into the atmosphere when a fuel burns may include: •carbon dioxide GLOBAL WARMING •water (vapour) •carbon monoxide •sulfur dioxide and ACID RAIN •oxides of nitrogen. Solid particles (particulates - sometimes called soot) may also be released. GLOBAL DIMMING