1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
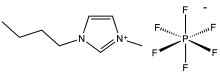
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, also known as BMIM-PF6, is a viscous, colourless, hydrophobic and non-water-soluble ionic liquid with a melting point[1] of -8 °C. Together with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, BMIM-BF4, it is one of the most widely studied ionic liquids. It is known to very slowly decompose in the presence of water.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-butyl-3-methylimidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate | |
| Other names
BMIM-PF6 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.203.179 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15F6N2P | |
| Molar mass | 284.186 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Light yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.38 g/mL (20 °C) |
| Melting point | −8 °C (18 °F; 265 K) |
| insoluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Preparation and uses
BMIM-PF6 is commercially available. It may be obtained in two steps: BMIM-Cl is synthesized by alkylating 1-methylimidazole with 1-chlorobutane. A metathesis reaction with potassium hexafluorophosphate gives the desired compound; the tetrafluoroborate may be prepared by analogously using potassium tetrafluoroborate.[3]
BMIM-PF6 has been investigated in electrochemistry where it serves both as solvent and electrolyte.[4] and electrochemical CO2 reduction.[5]
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.

