Loading AI tools
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
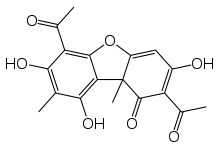
Usnic acid is a naturally occurring dibenzofuran derivative found in several lichen species with the formula C18H16O7. It was first isolated by German scientist W. Knop in 1844[2] and first synthesized between 1933 and 1937 by Curd and Robertson.[3] Usnic acid was identified in many genera of lichens including Usnea, Cladonia, Hypotrachyna, Lecanora, Ramalina, Evernia, Parmelia and Alectoria. Although it is generally believed that usnic acid is exclusively restricted to lichens, in a few unconfirmed isolated cases the compound was found in kombucha tea and non-lichenized ascomycetes.[4][5]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,6-Diacetyl-7,9-dihydroxy-8,9b-dimethyldibenzo[b,d]furan-1,3(2H,9bH)-dione | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.310 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H16O7 | |
| Molar mass | 344.319 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 204 °C (399 °F; 477 K) |
| <0.001 g/L (25°C)[1] | |
| Solubility in acetone | 0.077 g/L[1] |
| Solubility in ethyl acetate | 0.088 g/L[1] |
| Solubility in furfural | 0.732 g/L[1] |
| Solubility in furfuryl alcohol | 0.121 g/L[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
At normal conditions, usnic acid is a bitter, yellow, solid substance.[6] It is known to occur in nature in both the d- and l-forms as well as a racemic mixture. Salts of usnic acid are called usnates (e.g. copper usnate).
Usnic acid is a secondary metabolite in lichens whose role has not been completely elucidated. It is believed that usnic acid protects the lichen from adverse effects of sunlight exposure and deters grazing animals with its bitter taste.
Usnic acid is a polyketide biosynthesized via methylphloroacetophenone as an intermediate.[7]

Usnic acid and its salts are idiosyncratically associated with severe hepatotoxicity and liver failure.[8][9] Daily oral intake of 300–1350 mg over a period of weeks has led to severe hepatotoxicity in a number of persons.[10][11]
Sodium usnate was one ingredient in a product called "Lipokinetix" that was claimed to induce weight loss via an increase in metabolic rate. Lipokinetix has been the topic of an FDA warning in the USA[12] due to potential hepatotoxicity, although it is unclear yet if any toxicity would be attributable to the aforementioned salt. Lipokinetix also contained norephedrine (PPA), caffeine, yohimbine and 3,5-diiodothyronine.
Usnic acid has been found to have adrenergic activity in both frog and earthworm nerve junction models in preliminary research.[13]
It is possible to determine the content of usnic acid in lichen extract using reversed-polarity capillary zone electrophoresis or high performance liquid chromatography analysis.[14] A spot test using anisaldehyde reagent was developed to detect usnic acid in lichens, producing a distinctive magenta color reaction that works reliably in the presence of most other lichen substances and can aid in identification, particularly in species where visual detection of usnic acid's natural pale yellow color is difficult.[15]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.