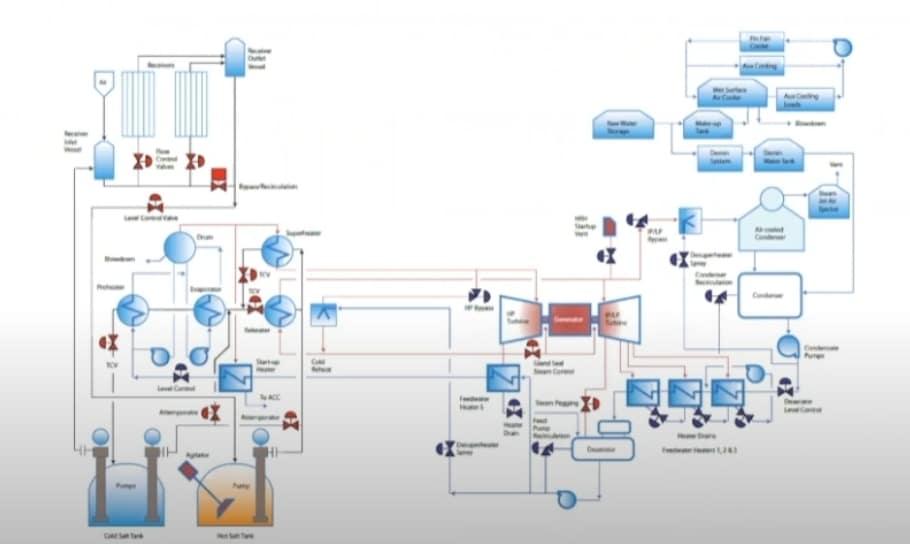
What is Saturated Water?
We called the water that has reached saturation temperature saturated water. When continuing to heat the water but the temperature remains the same, it produces vapor with water called wet saturated steam, until all the water becomes steam, it is called dry saturated steam or called saturated steam.
The saturated state of steam is called saturated steam, and liquid water is called saturated water. At this moment, the temperature of steam and liquid is the same, known as the saturation temperature which is expressed in Ts, the pressure of steam is called saturation pressure which is expressed in Ps.
Saturated aqueous solution refers to certain conditions when the water can no longer dissolve a substance and reach the saturated state of this substance, but this saturated aqueous solution can also dissolve other substances, and the solubility of the substances inside and not affect each other.
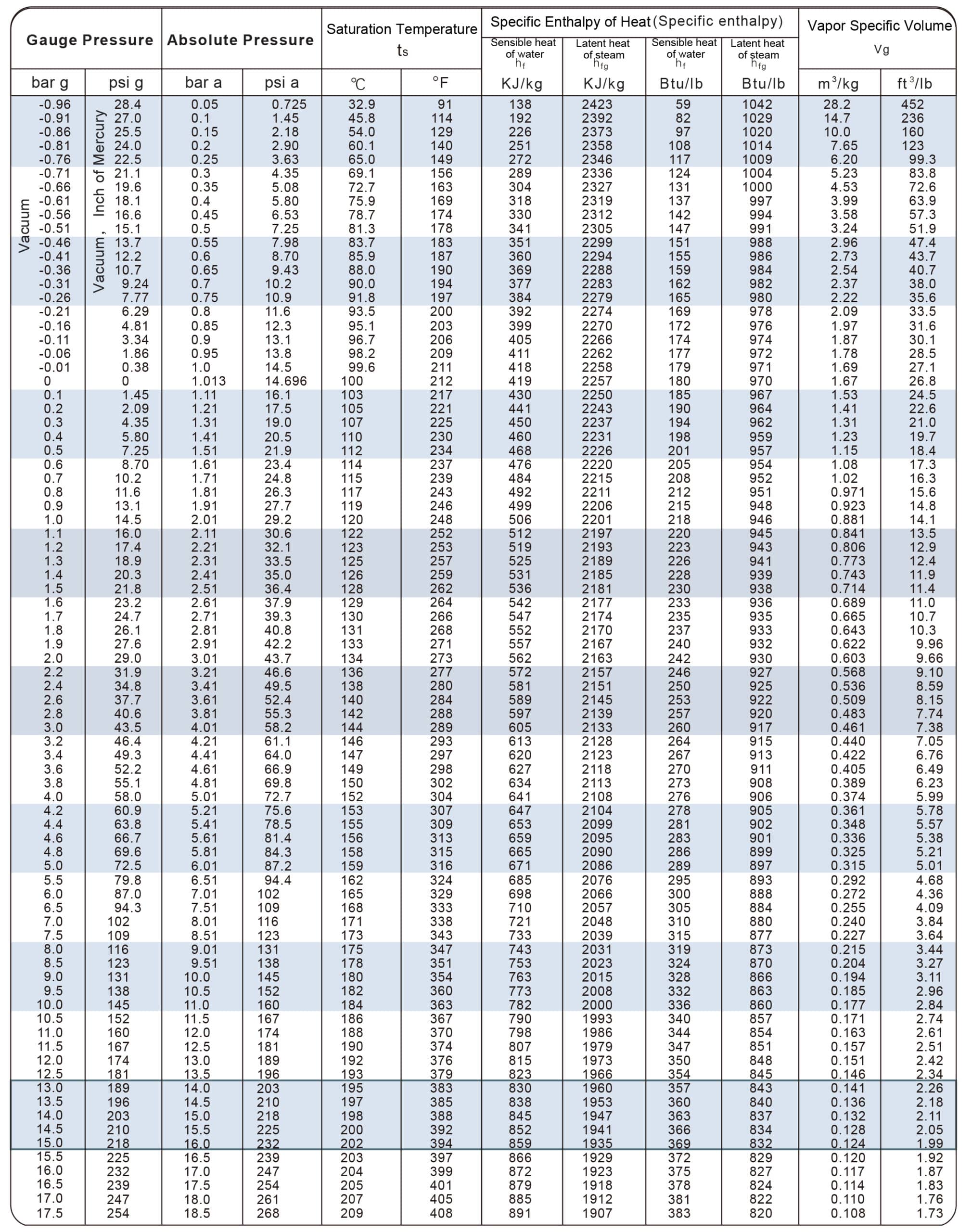
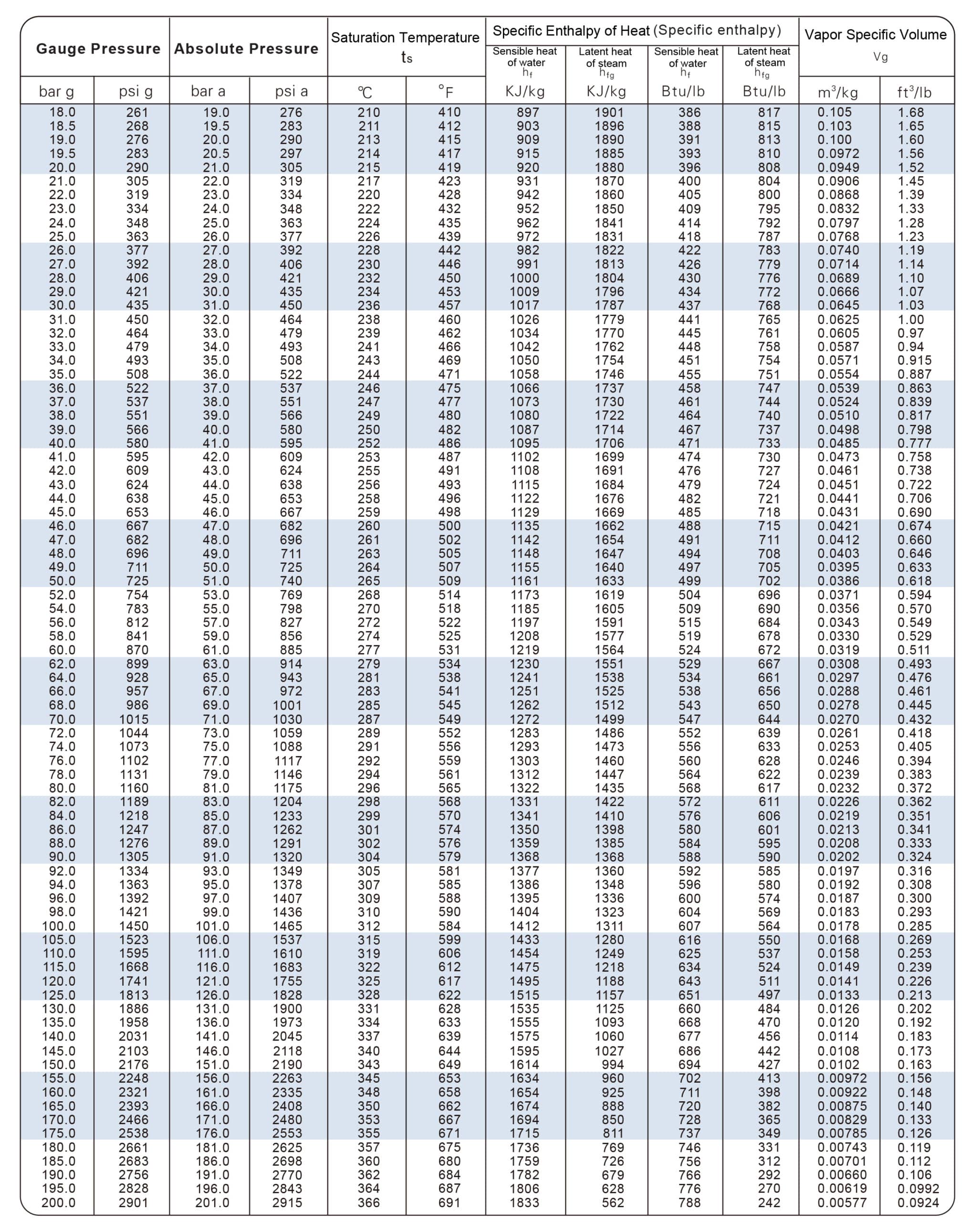
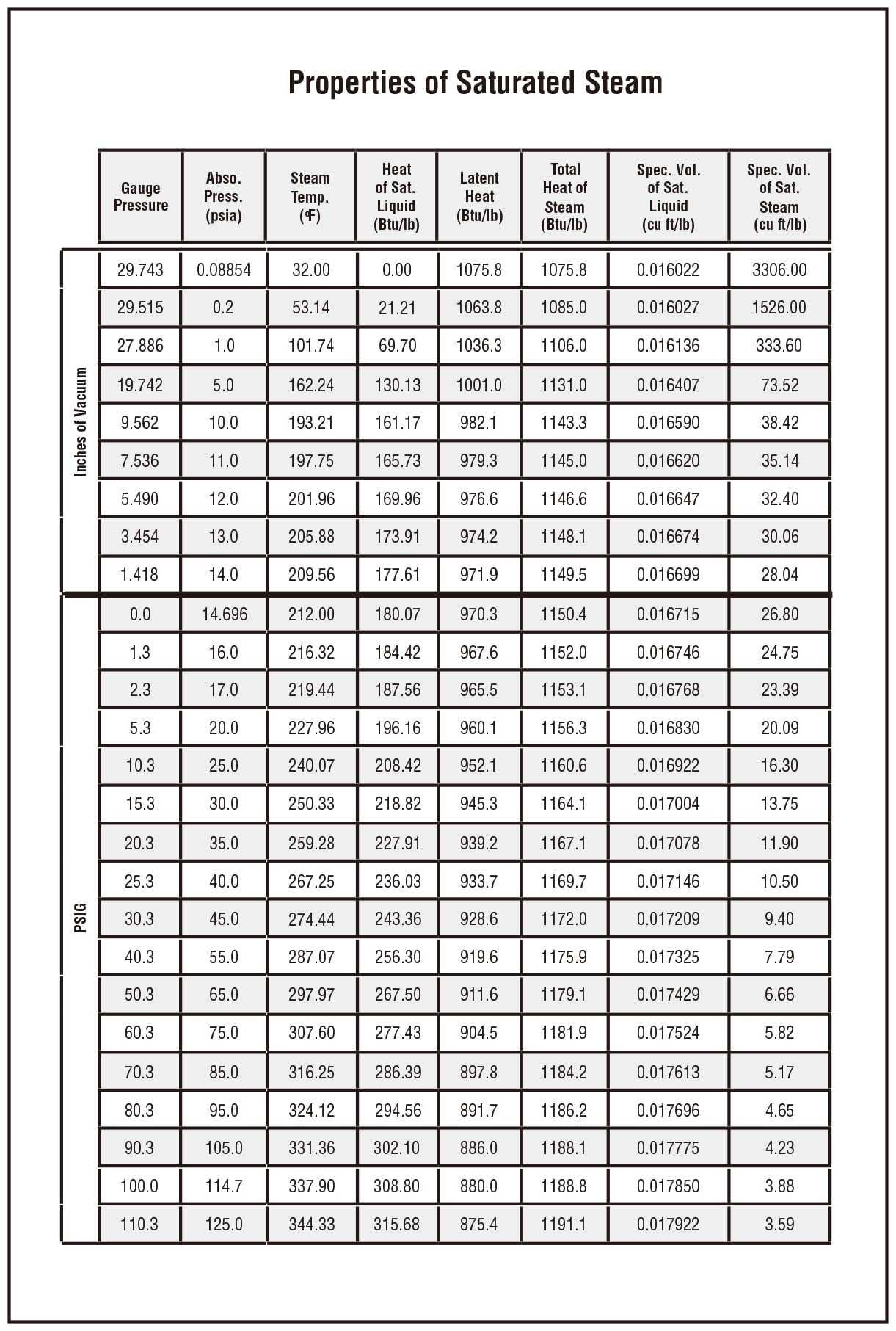
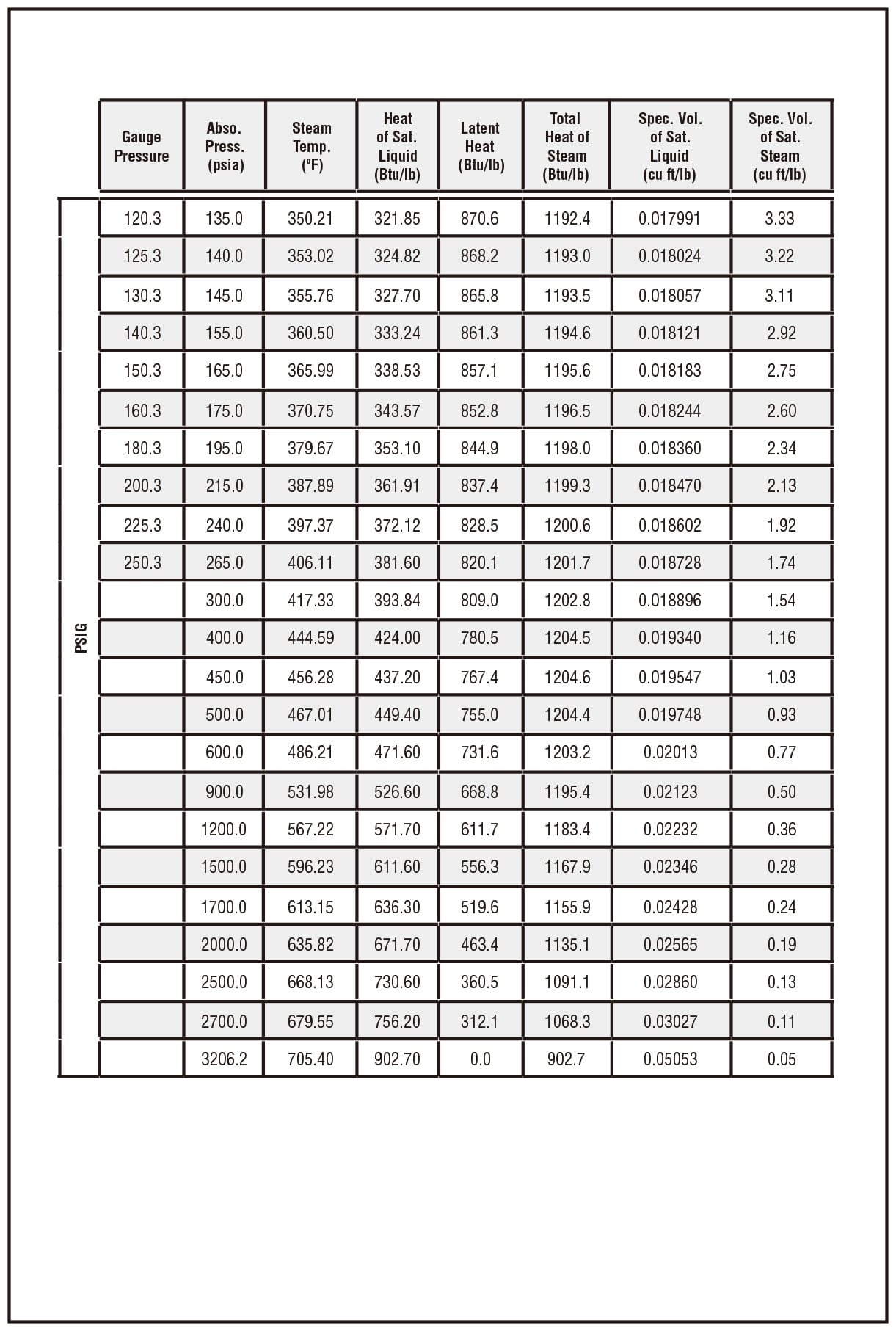
| Temperatur e t/℃ | Absolute Pressure p/kPa | Density of Water Vapor ρ/kg·m-3 | Enthalpy H/kJ·kg-1 | Enthalpy H/kJ·kg-1 | Heat of Vaporization r/kJ·kg-1 |
| – | – | – | Liquid | Vapour/Steam | Vapour/Steam |
| 0 | 0.61 | 0 | 0 | 2491.1 | 2491.1 |
| 5 | 0.87 | 0.01 | 20.94 | 2500.8 | 2479.86 |
| 10 | 1.23 | 0.01 | 41.87 | 2510.4 | 2468.53 |
| 15 | 1.71 | 0.01 | 62.8 | 2520.5 | 2457.7 |
| 20 | 2.33 | 0.02 | 83.74 | 2530.1 | 2446.3 |
| 25 | 3.17 | 0.02 | 104.67 | 2539.7 | 2435 |
| 30 | 4.25 | 0.03 | 125.6 | 2549.3 | 2423.7 |
| 35 | 5.62 | 0.04 | 146.54 | 2559 | 2412.1 |
| 40 | 7.38 | 0.05 | 167.47 | 2568.6 | 2401.1 |
| 45 | 9.58 | 0.07 | 188.41 | 2577.8 | 2389.4 |
| 50 | 12.34 | 0.08 | 209.34 | 2587.4 | 2378.1 |
| 55 | 15.74 | 0.1 | 230.27 | 2596.7 | 2366.4 |
| 60 | 19.92 | 0.13 | 251.21 | 2606.3 | 2355.1 |
| 65 | 25.01 | 0.16 | 272.14 | 2615.5 | 2343.1 |
| 70 | 31.16 | 0.2 | 293.08 | 2624.3 | 2331.2 |
| 75 | 38.55 | 0.24 | 314.01 | 2633.5 | 2319.5 |
| 80 | 47.38 | 0.29 | 334.94 | 2642.3 | 2307.8 |
| 85 | 57.88 | 0.35 | 355.88 | 2651.1 | 2295.2 |
| 90 | 70.14 | 0.42 | 376.81 | 2659.9 | 2283.1 |
| 95 | 84.56 | 0.5 | 397.75 | 2668.7 | 2270.5 |
| 100 | 101.33 | 0.6 | 418.68 | 2677 | 2258.4 |
| 105 | 120.85 | 0.7 | 440.03 | 2685 | 2245.4 |
| 110 | 143.31 | 0.83 | 460.97 | 2693.4 | 2232 |
| 115 | 169.11 | 0.96 | 482.32 | 2701.3 | 2219 |
| 120 | 198.64 | 1.12 | 503.67 | 2708.9 | 2205.2 |
| 125 | 232.19 | 1.3 | 525.02 | 2716.4 | 2191.8 |
| 130 | 270.25 | 1.49 | 546.38 | 2723.9 | 2177.6 |
| 135 | 313.11 | 1.72 | 567.73 | 2731 | 2163.3 |
| 140 | 361.47 | 1.96 | 589.08 | 2737.7 | 2148.7 |
| 145 | 415.72 | 2.24 | 610.85 | 2744.4 | 2134 |
| 150 | 476.24 | 2.54 | 632.21 | 2750.7 | 2118.5 |
| 160 | 618.28 | 3.25 | 675.75 | 2762.9 | 2037.1 |
| 170 | 792.59 | 4.11 | 719.29 | 2773.3 | 2054 |
| 180 | 1003.5 | 5.15 | 763.25 | 2782.5 | 2019.3 |
| 190 | 1255.6 | 6.38 | 807.64 | 2790.1 | 1982.4 |
| 200 | 1554.77 | 7.84 | 852.01 | 2795.5 | 1943.5 |
| 210 | 1917.72 | 9.57 | 897.23 | 2799.3 | 1902.5 |
| 220 | 2320.88 | 11.6 | 942.45 | 2801 | 1858.5 |
| 230 | 2798.59 | 13.98 | 988.5 | 2800.1 | 1811.6 |
| 240 | 3347.91 | 16.76 | 1034.56 | 2796.8 | 1761.8 |
| 250 | 3977.67 | 20.01 | 1081.45 | 2790.1 | 1708.6 |
| 260 | 4693.75 | 23.82 | 1128.76 | 2780.9 | 1651.7 |
| 270 | 5503.99 | 28.27 | 1176.91 | 2768.3 | 1591.4 |
| 280 | 6417.24 | 33.47 | 1225.48 | 2752 | 1526.5 |
| 290 | 7443.29 | 39.6 | 1274.46 | 2732.3 | 1457.4 |
| 300 | 8592.94 | 46.93 | 1325.54 | 2708 | 1382.5 |
| 310 | 9877.96 | 55.59 | 1378.71 | 2680 | 1301.3 |
| 320 | 11300.3 | 65.95 | 1436.07 | 2648.2 | 1212.1 |
| 330 | 12879.6 | 78.53 | 1446.78 | 2610.5 | 1116.2 |
| 340 | 14615.8 | 93.98 | 1562.93 | 2568.6 | 1005.7 |
| 350 | 16538.5 | 113.2 | 1636.2 | 2516.7 | 880.5 |
| 360 | 18667.1 | 139.6 | 1729.15 | 2442.6 | 713 |
| 370 | 21040.9 | 171 | 1888.25 | 2301.9 | 411.1 |
| 374 | 22070.9 | 322.6 | 2098 | 2098 | 0 |
What is a Saturated Liquid?
Saturated liquid refers to the saturated state of the liquid. At this time, the temperature of the gas and liquid phase is the same, which is called the saturation temperature t0, and vapor pressure is called saturation pressure P0. When the saturation temperature is certain, the saturation pressure is also certain. If the temperature increases, the speed of vaporization is accelerated, and the space vapor density will also increase. When increased to a certain determined value, the liquid and vapor will be re-established in dynamic equilibrium. At this time the liquid is called the new temperature of the saturated liquid.
What is a Compressed Liquid?
The conditions required to classify a solution as a compressed liquid are as follows.
- Its specific volume should be less than the specific volume of the liquid when it is saturated.
- The temperature should be lower than the saturation temperature.
- Its pressure should be greater than the saturation pressure.
- The enthalpy of the compressed liquid must be less than the enthalpy of the saturated liquid.
When we talk about compressed liquids, we imply that at any given temperature, their pressure is greater than their saturation pressure. In general, at a given temperature, compressed liquids can be considered saturated liquids.
What is the Difference Between a Saturated Liquid and a Compressed Liquid?
The key difference between saturated and compressed liquids is that we can generate a saturated liquid by adding solute to the solvent until we can not add more solute, while a compressed liquid is formed when we apply external pressure until the solution is compressed due to the reduction of the voids between the molecules.
Saturation and compression are important physical properties of any liquid. The large intermolecular spaces in liquids compared to solids means that they can be compressed by pressure. On the other hand, saturation is when we can no longer add solute to a liquid. When we put more pressure on a liquid outside of the atmosphere, the liquid tends to compress because there are spaces between the molecules. There is a difference between saturated and compressed liquids, which we will describe in short below.
Summary – Saturated Water Liquid VS. Compressed Liquid
| VS. Item | Saturated Liquid | Compressed Liquid |
| Definition | A liquid with a temperature and pressure is such that when trying to decrease the pressure without changing temperature, the liquid begins to boil. | A liquid under mechanical or thermodynamic conditions that force it to be a liquid. |
| Preparation | We can make a saturated liquid by adding solutes to a solvent until we cannot add any more solutes. | Forms when we apply an external pressure until the solution compresses due to the reduction of the empty spaces between the molecules. |
A liquid is a phase of matter that contains intermolecular spaces that are larger than those of a solid and smaller than those of a gas. This gives liquids the ability to flow. However, we can add solutes to a liquid (solution) to fill the spaces between molecules (intermolecular spaces). Or we can compress the liquid to reduce the voids. The difference between saturated liquids and compressed liquids is in the way they are prepared. We can also prepare a saturated liquid by adding solute to the solvent until we can add no more solute. Or when we apply external pressure until the solution is compressed due to reduction, thus creating voids between the molecules of the compressed liquid.