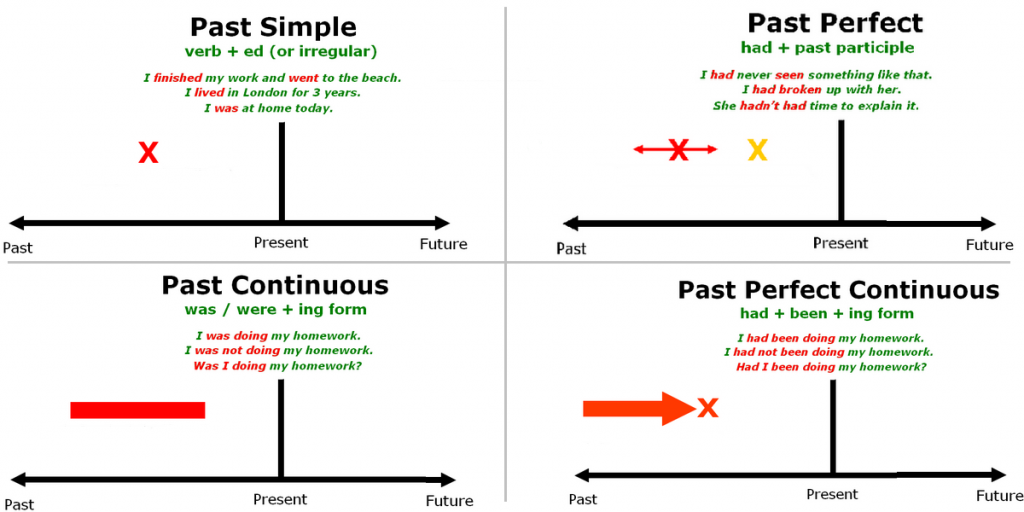
The past tense is one of three general English grammatical tenses whose function is to place an action or event in the past. All of the past tenses are really important to know. Without knowing them, you will not be fully prepared to understand sentences and you might misuse words. We begin this section with the four main tenses. These are:
Some of these tenses use auxiliary verbs and some of them use past tense verb forms. Fortunately, one past tense is used more than others – it is the most important one: the past simple. Without knowing the past simple, you will not be able to understand most sentences.
We use past tenses to talk about:
Anything in the past
We use past tenses generally to talk about some events in the past.
- He had worked there for 4 months.
- He moved to Oklahoma.
Referring to hypothetical present or future situations
Past tenses are very commonly used to talk about present or future situations.
- They are outside for 6 hours. I think they got hungry.
Wishes
These tenses are also used to wish for something. In these situations, we also refer to the future.
- I wish it was raining today.
- I wish we hadn’t spent so much time together.
Conditions
These tenses can also describe some kind of conditions.
- If you were playing, we would probably win.
- If he asked, I would help him.
Polite expressions in the present
Past tenses are also very often used to speak politely to someone.
- I just thought you wanted to be here.
- Excuse me, I was wondering if I could get a higher salary.
 1. Past simple tense
1. Past simple tense
This tense is used to describe completed actions or situations which started and finished in the past. This means these actions or situations don’t interfere with present or future events. You can use this tense every time you want to briefly describe what happened in the past.
The structure of a sentence in the past simple tense is:
Subject + past simple (verb + ed or irregular verb) + object.
Example:
- I saw you with him.
- He watered the garden.
In this tense we always use the verb in its irregular form (2nd form/past tense form). If the verb is not in its irregular form, we simply add the suffix –ed to the base form of the verb (to the infinitive form).
Negative
To construct a negative sentence, we add the auxiliary verb „not“ right after the verb „did“. The verb „did“ is used before the main verb in its infinitive form and indicates that it is the past simple tense. „Did“ is the irregular past tense form of the verb „do“.
When we use the auxiliary verb „did“, we do not add any suffixes to the main verb, nor do we use irregular verbs. When constructing negative sentences and questions in the past simple, we always use the main verb in its base form (infinitive form).
The structure of the sentence is:
Subject + did not + base form of verb (infinitive) + object.
Example:
- You didn’t do that even though I have told you to!
Questions
Questions are pretty similar to affirmative sentences, however we do not use irregular forms of the main verbs. As in negative sentences, we use only the infinitive form of the verb.
The structure of questions in the past simple is:
Did + subject + base form of the verb (infinitive) + object?
Example
- Did you water the garden?
Adverbs used with the past simple
In the past simple, we often use adverbs ending with the word „ago“: a week ago, three days ago, two years ago, etc., adverbs starting with the word „last“: last week, last year, last month, last three days, last Monday, or other basic adverbs like yesterday, a few days ago, and many others.
 2. Past continuous tense
2. Past continuous tense
This tense is commonly used to talk about longer actions in the past which are usually interrupted by some other event in the past (by a shorter action in the past simple). We can this tense when there are two actions happening at the same time, to talk about a situation at a specific point in time in the past, or to describe a story that occurred in the past.
The structure of a sentence in the past continuous tense is:
Subject + was/were + verb(-ing) + object.
In the past continuous, we use the progressive aspect (form –ing). By using the suffix –ing, we make it clear that the action was happening for a longer period of time. We also use the 2nd form (past tense form) of the verb „to be“ which is „was/were“. This auxiliary verb is used to describe that we are talking about a situation in the past instead of in the present.
Example:
- They were eating a pizza.
- She was feeling fine.
Negative sentences
Negative sentences are easy to construct. We just add the word „not“ right after the auxiliary verb „was/were“. The rest of the sentence is the same:
Subject + was/were + not + verb(-ing) + object.
Example:
- I was living in Ukraine for 3 years.
Questions
Questions in the past continuous are constructed the same way as affirmative sentences – we just switch the subject with an auxiliary verb. The structure of the question is:
Was/were + subject + verb(-ing) + object?
Example:
- Was she doing your homework?
Adverbs used with the past continuous
If we talk about a specific time, we use adverbs like: o’clock, yesterday morning, a week ago, last month, etc.
If we line up and limit the time period, we use: between, from-to, during, etc.
When we are talking about two or more actions happening at the same time, we use adverbs like: and, when, while, etc.
 3. Past perfect tense
3. Past perfect tense
This tense is slightly more difficult than the previous two tenses. We use the past perfect to talk about actions that happened before some other previous action in the past. Sometimes students overuse this tense by using it to describe almost any event that occurred in the past. Pay attention and make sure to use it only to describe events happening before a previous action in the past.
In this tense we use the auxiliary verb „have“ in its past participle form „had“. We use this verb in front of the main verb, which is also used in its past participle form.
The structure of the sentence is:
Subject + had + past participle + object.
Example:
- I had eaten a lot before I came in.
Negative
In negative sentences we simply add the negative „not“ right after the auxiliary verb „had“. The structure of negative sentences is:
Subject + had not/hadn’t + verb in past participle + object.
Example:
- I had not eaten anything before I came in.
Questions
Questions are also pretty easy to construct. We just place the verb „had“ at the beginning of the sentence then continue with using the same structure as we would for affirmative sentences. The structure of the sentence is:
Had + subject + verb in past participle + object?
Example:
- When had you eaten dinner?
 4. Past perfect continuous tense
4. Past perfect continuous tense
The past perfect tense is very similar to the past perfect continuous tense. We use it to talk about actions that started in the past, continued for a while and ended in the past because of some other event.
We can also use this tense if we do not know whether the event ended or not. The important thing to note is that the event is happening – we do not care to know whether it ended or not.
In this tense we generally use three verbs. The first one is the verb „had“ in its past participle form, the second one is the verb „been“ in its past participle form, and the third verb is the main verb in its base form with the suffix –ing, which describes a progressive aspect.
The structure of the sentence is:
Subject + had + been + verb (-ing) + object.
Example:
- I had been doing my homework when you came in.
Negative
Negative sentences are similar in construction to affirmative ones. The only thing we need to change is to add the auxiliary verb „not“ after the verb „had“. The rest of the sentence is the same. The structure of the sentence is:
Subject + had + not + been + verb (-ing) + object.
Example:
- I had not been watering our garden since Tuesday.
Questions
To construct a question in the past perfect continuous, we just need to change the order of the words. We put the verb „had“ in front of the whole sentence, leaving the rest of the sentence the same. The structure of the sentence is:
Had + subject + been + main verb (-ing) + object?
Example:
- Had you been playing football when it started to rain?
Past tenses are very important to know. We need to remember all the irregular verbs to be able to speak in English. If we do not know them, we won’t be able to construct sentences in any past or other tenses.
It is also important to note that we have to pay attention to the 1st, 2nd and 3rd person point of view and the number of subjects. Past tenses are a little bit harder than present tenses, but without them we would be unable to understand and talk about a lot of situations and events.