BANKING
THE ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY IN TRANSFORMING THE BANKING INDUSTRY
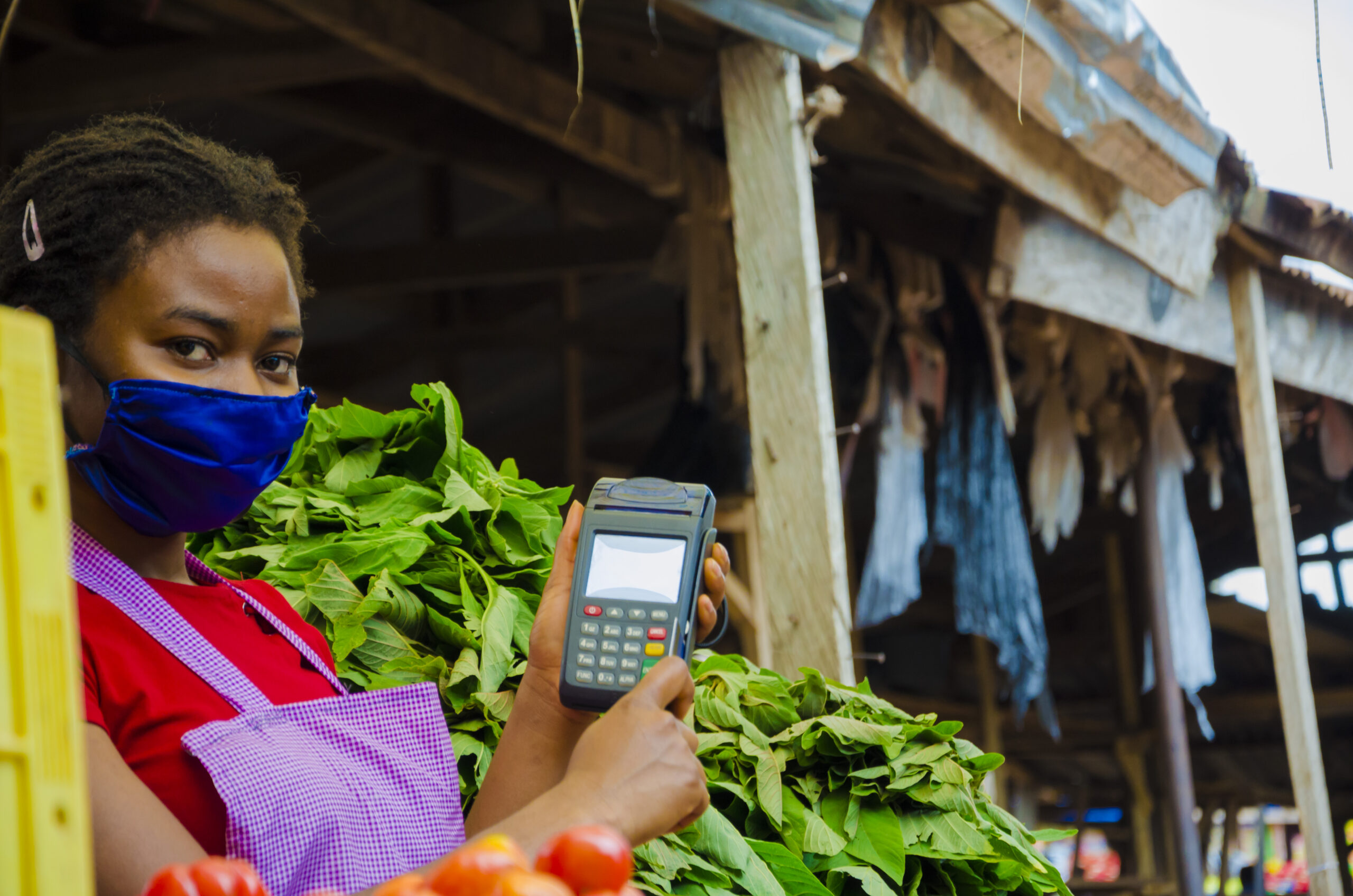

THE ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY IN TRANSFORMING THE BANKING INDUSTRY
INTRODUCTION
Without a doubt, it is trite and common knowledge that a plethora of sectors, systems, and industries have been transformed by technology, and the banking industry is no exception. Over time, the banking business has seen major changes as a result of advances in digital innovation. This article investigates how technology has shaped the modern banking sector, highlighting crucial elements including customer experience, operational effectiveness, security, and the rise of fintech businesses.
AN OVERVIEW OF THE BANKING INDUSTRY
The banking sector witnessed a major change over several centuries before the impact of technology.
Banking has its origins in prehistoric societies like Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece. In those early days, the main functions of banking were moneylending, safeguarding valuables, and promoting trade credit management. The main storage locations for goods and riches were temples and royal treasury.
In some areas, banking started to take shape as specialized institutions during the Middle Ages. Early financial hubs were formed by the Italian city-states, especially Florence and Venice. These cities’ businesspeople organized into “partnership banks,” which promoted commerce and capital investment. Cross-border transactions were made possible by the letters of credit that these banks also issued and honored.

THE ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY IN TRANSFORMING THE BANKING INDUSTRY
Modern financial techniques were more prevalent during the Renaissance. The first contemporary banks started to appear in the 17th century, including the Bank of Stockholm in Sweden (1656) and Banca Monte dei Paschi di Siena in Italy (1472). These banks provided a range of services, including as loans, exchange of currencies, and deposit accounts.
The eighteenth and nineteenth centuries saw the the creation of central banks. One of the first central banks, the Bank of England was established in 1694 and was essential in maintaining the English economy. The monetary system was governed by central banks, who were also in charge of preserving reserves and producing currency.
The banking sector was significantly impacted by the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th and early 19th century. Commercial banks started to appear as industrialization increased in order to help businesses and offer financial services. These banks concentrated on facilitating internal and international trade, lending money, and accepting deposits.
Branch banking increased in popularity in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Banks started growing their networks by setting up numerous branches across various areas. However, the majority of banking activity, this growth allowed banks to serve a bigger consumer base geographically. still took place in person.
In the 20th century, technology started to have an impact on the banking sector. Telegraphs were used for bank-to-bank communication, which improved coordination and allowed for quicker financial data delivery. Banks began utilizing computerized accounting systems for bookkeeping and transactions in the 1950s and 1960s.
Automated teller machines (ATMs), which provided self-service access to cash withdrawals and account enquiries outside of regular banking hours, transformed banking in the 1960s. Credit cards and debit cards also became more widely used, streamlining payment methods and lowering the need for cash.
Banking underwent a big change with the introduction of personal computers and the internet in the late 20th century. Customers can now access accounts, conduct transactions, and get financial information through online banking tools. through way of websites. Banking services are now more convenient and accessible because to this digital shift.
Mobile technology and smartphones developed quickly in the twenty-first century, which fueled the growth of mobile banking applications. Customers can use these apps on their mobile devices to access their accounts, make payments, transfer money, and carry out other financial transactions. Additionally, the integration of cutting-edge technology like biometrics, blockchain, and artificial intelligence into financial systems is currently reshaping the landscape of the sector.
The banking sector has developed since the days of early moneylending and the introduction of technologically advanced financial services. By enhancing client accessibility, convenience, and efficiency, technology has completely transformed banking. The sector keeps evolving and embracing new technology developments, influencing the direction of banking.
IMPACT OF TECHNOLOGY ON BANKING INDUSTRY
A.POSITIVE
Innovation has transformed the banking sector by raising accessibility, effectiveness, security, and consumer satisfaction. It has made it possible for banks to adjust to changing consumer demands and market trends, spurring industry innovation and transformation. The banking business has seen tremendous change as a result of technology in a number of ways.
- Improved Customer Experience: The banking sector has seen a significant improvement in customer experience because to technology. Banking services are now easier for customers to access, more convenient to use, and more tailored thanks to digital tools and platforms. Customers can make transactions, manage accounts, and get access to financial data with the use of mobile banking applications. 24/7 customer assistance is provided by virtual assistants and chatbots, who rapidly respond to questions and address problems. Furthermore, the authentication process has been made simpler by technology like fingerprints and facial recognition, ensuring quick and secure access to accounts.
- Operational Efficiency: Technology has streamlined banking processes, leading to considerable increases in productivity and efficiency. The reduction of human errors and processing time has been achieved by automation and digitization of a variety of processes, including account opening, loan processing, and payment services. To find trends and successfully manage risk, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms examine enormous volumes of data. Informed judgments, tailored recommendations, and improved overall operational performance are all made possible by banks thanks to this.
- Security and Fraud Prevention: The banking sector has long placed a high priority on security, and technology has been instrumental in further bolstering it. The risk of data breaches and unauthorized access has considerably decreased since modern security methods like two-factor authentication, encryption, and firewall systems have been implemented. Furthermore, AI-driven fraud detection systems are constantly being tracked and they help to examine client transactions to spot suspicious activity instantly. These technologies help banks comply with strict regulatory standards while also safeguarding client information.
- Fintech Disruption: Technological developments have sparked a growth in fintech firms. These adaptable and creative businesses make use of technology to offer cutting-edge financial solutions outside the conventional banking structure. Fintech platforms provide specialized financial services like cryptocurrency exchanges, robo-advisory, digital wallets, and peer-to-peer lending. Fintech firms upend conventional banking models with their user-friendly user interfaces and customized services, boosting competition and promoting industry-wide innovation.
- Data-driven Decision Making: Banks can collect and analyze enormous amounts of data on consumer behavior, market trends, and risk indicators with the aid of technology. This data-driven strategy enables banks to help improve overall operational efficiency, uncover new company prospects, handle risks effectively, and make educated decisions.
- Adopting Digital Transformation: Traditional banks have adopted digital transformation by integrating technology into all facets of their business operations in order to remain competitive. The infrastructure of legacy institutions has been improved, along with the online and mobile banking platforms, and powerful analytics tools have been put in place. Additionally, cooperation between established banks and fintech startups has increased as banks look to capitalize on the flexibility and creativity that these businesses offer. Through such agreements, established banks’ stability and brand awareness and fintech businesses’ technological skill are combined to create relationships that are advantageous to both parties.
B.NEGATIVE
While technology has obviously greatly improved the banking sector, there are some unfavorable effects as well. consider. The following are a few possible drawbacks of technology in banking:
- Employment Displacement: The growth of digital banking and automation have caused employment losses in some industries. Manual processes that were formerly completed by staff are being automated as banks adopt more technologically oriented solutions, potentially eliminating the need for human support.
- Digital Divide: Technology has improved banking convenience for many, but it has also widened the gap between the rich and the poor. Digital banking services may not be available to those without steady internet connectivity, access to technology, or digital literacy. Access to financial services may differ as a result.
- Security Risks: The risk of cyber threats rises as banking services become increasingly computerized and networked. Criminals and hackers might try to to take advantage of banking system flaws that could result in data breaches, identity theft, and financial losses.
- Customer Privacy Concerns: Concerns about client privacy have arisen as a result of banks’ extensive collection and storage of customer data. This presents issues with privacy and the potential for identity theft. client trust can be damaged through unauthorized access, data breaches, or releases of client information.
- Excessive Reliance On Technology: While automation and digital tools have simplified banking procedures, this can also have consequences. Customers may experience annoyance and inconvenience if they can’t quickly access their funds or complete transactions due to technical issues, system failures, or service interruptions.
It’s crucial to remember that these detrimental effects don’t just affect the banking industry, as They can be observed in a number of industries where technology is changing conventional methods of doing things. In order to reduce the negative effects of technology on the sector, banks need to be aware of these challenges and adopt plans to appropriately address them. These strategies should promote inclusivity, security, and customer-centric methods.
CONCLUSION:
Technology has revolutionized every facet of banking operations, proving to be a game-changer for the sector. It has transformed the client experience by making it possible to obtain financial services more quickly and conveniently while increasing security safeguards. Additionally, the emergence of fintech firms has upended conventional banking models, posing a threat to the status quo and encouraging innovation. With continuous breakthroughs in AI, blockchain technology, and data analytics paving the way, technology will continue to play a crucial part in determining the future of banking going ahead for additional transformational adjustments.
More from my site
BANKING
Afreximbank Acts as Joint Lead Manager on Ecobank Transnational Incorporated’s USD 400mn Senior Unsecured Note Issuance
The proceeds of the note will fund general corporate purposes of the issuer, including refinancing of a USD350 million senior bridge-to-bond loan facility that was jointly coordinated by Afreximbank in March 2024.
African Export-Import Bank (“Afreximbank”) (www.Afreximbank.com) is pleased to announce that it has successfully acted as Joint Lead Manager and Bookrunner on a USD 400 million 10.125% Rule 144a/RegS senior unsecured note issuance by Ecobank Transnational Incorporated (“ETI”) due in October 2029.
The proceeds of the note will fund general corporate purposes of the issuer, including refinancing of a USD350 million senior bridge-to-bond loan facility that was jointly coordinated by Afreximbank in March 2024.
The note issuance achieved peak orderbook oversubscription of 2.1x, backed by more than 70 high-quality and diverse investors comprising development finance institutions, asset managers, commercial banks and insurance companies from Africa, the UK, USA, Europe and the Middle East.
Professor Benedict Oramah, President and Chairman of the Board of Directors of Afreximbank, commenting on the transaction, said: “We are pleased to have supported Ecobank Transnational Incorporated (“ETI”) in placing the first public Eurobond issuance by any Sub-Saharan African financial institution since 2021, following our bridge financing support earlier in the year. This transaction underscores Afreximbank’s capacity and readiness to structure innovative market access solutions for our pan-African banking partners.”
Afreximbank’s Advisory and Capital Markets (ACMA) department acted as Joint Lead Manager and Bookrunner on the issuance, working alongside international and African partners.
Distributed by APO Group on behalf of Afreximbank.
More from my site
BANKING
International Islamic Trade Finance Corporation (ITFC) and the Central Bank of Nigeria Successfully

These workshops form part of ITFC’s Integrated Trade Solutions (ITS) framework, aligning with the organization’s goal of providing holistic trade financing interventions in OIC member countries.
The International Islamic Trade Finance Corporation (ITFC) (www.ITFC-idb.org), a member of the Islamic Development Bank (IsDB) Group, in partnership with the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), successfully concluded a workshop on Non-Interest Banking and Trade Finance in Nigeria. Held from 17th to 19th September 2024 in Abuja, the sessions aimed to enhance capacity and knowledge in Islamic banking principles, trade finance products and services, and how different financial toolkits are applied in Islamic finance from operational and business perspectives.

Nigeria’s Islamic finance industry, valued at US$3.8 billion, is one of the major Shariah compliant industries in Africa. Despite some challenges such as low public awareness and a smaller capital base compared to conventional banks, Islamic finance has been substantially contributing to reduce financial exclusion and improve access to affordable finance in the country. The three-day workshop was designed to bridge prevailing knowledge gaps focusing on key areas such as Sukuk issuance and main non-interest banking products basics.
Delivered under ITFC’s Integrated Trade Solutions framework, the workshop equipped professionals with the skills to promote Islamic finance in Nigeria while also highlighting ITFC’s wide range of trade financing services.
Participants reported a significant boost in understanding Islamic banking and trade finance, and the workshop showcased ITFC’s contributions to economic development through sustainable financial solutions.
Eng. Nasser Al Thakair, ITFC, remarked: “ITFC is committed to supporting Nigeria’s efforts in Islamic finance, tailoring this workshop to address the unique challenges faced. We will continue to provide the expertise and financial backing needed to grow Islamic finance in Nigeria and beyond.”
Over 30 professionals from the Central Bank of Nigeria, non-interest banks, and other financial institutions attended, further advancing Islamic finance in the country.
As Nigeria positions itself as a leading market for Islamic finance in Africa, ITFC remains dedicated to advancing trade finance and supporting the growth of the sector for long-term economic impact.
Distributed by APO Group on behalf of International Islamic Trade Finance Corporation (ITFC).
About the International Islamic Trade and Finance Corporation (ITFC):
The International Islamic Trade Finance Corporation (ITFC) is a member of the Islamic Development Bank (IsDB) Group. It was established with the primary objective of advancing trade among OIC member countries, which would ultimately contribute to the overarching goal of improving the socioeconomic conditions of the people across the world. Commencing operations in January 2008, ITFC has provided over US$75 billion of financing to OIC member countries, making it the leading provider of trade solutions for these member countries’ needs. With a mission to become a catalyst for trade development for OIC member countries and beyond, the Corporation helps entities in member countries gain better access to trade finance and provides them with the necessary trade-related capacity-building tools, which would enable them to successfully compete in the global market.
More from my site
FINTECH
Kazang Pay launches card acquiring service in Zambia
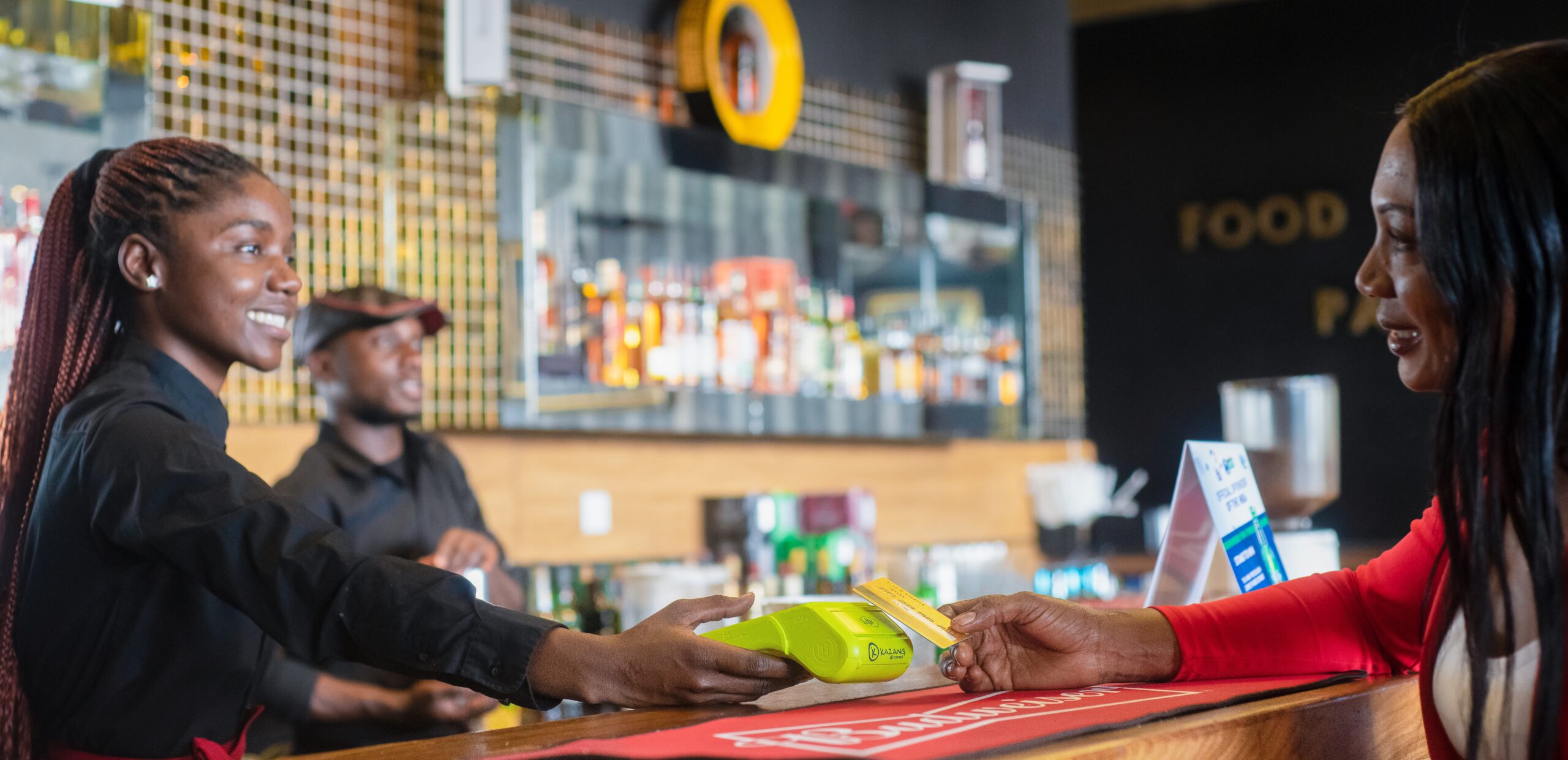

Kazang (www.Kazang.com), the prepaid value-added services (VAS) and card acquiring business within JSE-listed fintech Lesaka Technologies, has launched its Kazang Pay card acceptance solution for merchants in Zambia. Kazang Pay makes it affordable for merchants to accept card payments on the same Kazang terminal they use to sell prepaid products and services.

The Kazang Pay enabled terminal in Zambia accepts VISA debit and credit cards as well as mobile wallet payments. Payments are settled to the merchant’s Kazang wallet on the same day. It’s as easy as letting the customer tap or insert their bank card and enter their PIN on the secure scramble PIN pad.
Kazang operates around 12,000 VAS terminals in Zambia. The goal is to enable the majority to accept card payments over the next six months. Benefits to merchants include low transaction fees and no monthly terminal rental fee for those that meet a modest monthly transaction threshold as well as the opportunity to grow their business through card acceptance.
Kazang is Zambia’s largest VAS point-of-sale terminal provider, enabling mobile money payments, bank and mobile money cash in and out, bill payments, airtime, Zesco, and many other prepaid services on one platform. The addition of card acceptance makes the platform even more comprehensive for merchants and consumers alike.
The launch of Kazang Pay in Zambia follows the introduction of the solution in South Africa, where around 60,000 small and micro merchants use Kazang Pay to accept card payments. In Zambia, there are around 3.8 million debit, credit and ATM cards in issue and 41,000 point of sale (POS) terminals in place. The value of POS transactions has grown to K 111.4 billion by 2022 from less than K 20 billion in 2018, according to the Bank of Zambia.
Says Leon de Wit, managing director at Kazang Zambia: “Zambia has made enormous strides in terms of financial inclusion, with card usage and penetration growing at a rapid pace. With Kazang Pay, merchants can now easily accept card payments on the same all-in-one terminal they already use for vending of VAS products.
“Card transactions help merchants to grow basket sizes and potentially attract more customers, and at the same time, reduce the risks and costs of handling cash. Moving towards digitalised payments will also enable merchants to track sales, manage cash flow, and create a footprint that could make it easier for them to access loans.”
Ashley Naidoo, director of Kazang Pay in South Africa says: “Our Zambian merchants have eagerly embraced our card acquiring service as a valuable part of our one-stop solution. Following the launch of Kazang Pay in Zambia, we have seen higher VAS sales across our merchant base and much-improved merchant retention and with our card acquiring solution we now appeal to a broader merchant base.”
Distributed by APO Group on behalf of Kazang.
ABOUT KAZANG:
Kazang (www.Kazang.com) is a leading provider of cash and digital solutions to merchants in Southern Africa’s informal economies. Our fintech solutions include a diverse range of value-added services (VAS), card acquiring, secure cash vaults and supplier payments platforms. Operating with a network of approximately 90,000 active devices, we process approximately 2.2 million transactions daily in markets such as South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, and Zambia.
We are dedicated to helping small and medium merchants grow and succeed, through increasing their sales, making their businesses more efficient and reducing their risks with its holistic portfolio of products and services. Kazang is a member of Lesaka Technologies (https://LesakaTech.com).
ABOUT LESAKA TECHNOLOGIES, INC:
The Connect Group and Kazang was acquired by Lesaka Technologies, Inc. in April 2022. Lesaka Technologies, (Lesaka™) is a South African Fintech company that utilizes its proprietary banking and payment technologies to deliver superior financial services solutions to merchants (B2B) and consumers (B2C) in Southern Africa. Lesaka’s mission is to drive true financial inclusion for both merchant and consumer markets through offering affordable financial services to previously underserved sectors of the economy. Lesaka offers cash management solutions, growth capital, card acquiring, bill payment technologies and value-added services to retail merchants as well as banking, lending, and insurance solutions to consumers across Southern Africa.
Lesaka has a primary listing on NASDAQ (NasdaqGS: LSAK) and a secondary listing on the Johannesburg Stock Exchange (JSE: LSK). Visit www.LesakaTech.com for additional information about Lesaka Technologies (Lesaka ™). $LSK / $LSAK
More from my site
-
EDUCATION3 years ago
Jamb Cut-Off Mark for A Law Degree in Nigerian Universities
-
BANKING2 years ago
POLARIS Bank Transfer Code| How to Activate the USSD Banking Code
-
BANKING2 years ago
Union Bank Transfer Code| How to Activate the USSD Banking Code
-
BANKING2 years ago
FIRST Bank Transfer Code| How to Activate the USSD Banking Code
-
BANKING2 years ago
How to Check UBA Account Balance From Anywhere
-
BANKING2 years ago
GT Bank Transfer Code| How to Activate the USSD Banking Code
-
BANKING2 years ago
Check GTB Account Balance via Internet and USSD Code
-
BANKING2 years ago
ZENITH Bank Transfer Code| How to Activate the USSD Banking Code