The world of root vegetables is vast and diverse, with different types of tubers and corms being staples in many cultures. Two such popular roots are sweet potatoes and yams. While these two terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to two distinct types of plants with unique characteristics.
Similarities
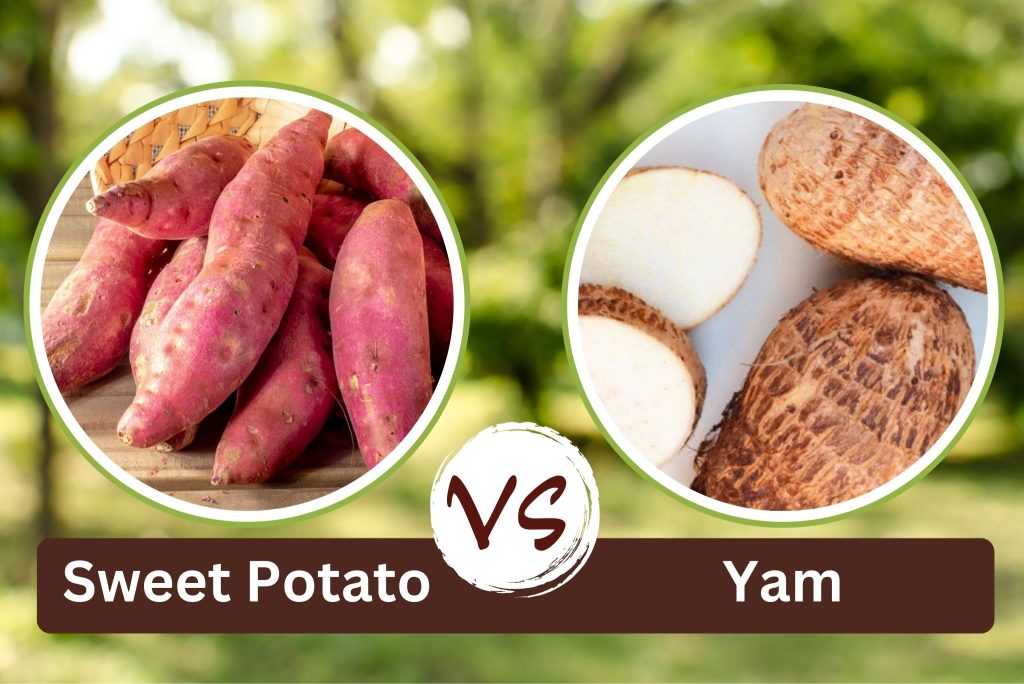
One of the main reasons for the confusion between sweet potatoes and yams is their physical appearance. Both have an oblong shape with a tapered end and a rough, dark exterior. They also both come in various colors such as orange, purple, and white.
Another similarity between sweet potatoes and yams is the fact that they are both root vegetables that are grown underground. They are also both considered to be starchy vegetables, meaning they contain a high amount of carbohydrates and are a good source of energy.
Differences
While sweet potatoes and yams may share some similarities, there are also significant differences between the two. The first major difference is their scientific classification. Sweet potatoes belong to the Convolvulaceae family, while yams belong to the Dioscoreaceae family. This means that they are not even related, despite their similar appearance.
Another notable difference between sweet potatoes and yams is their taste. Sweet potatoes have a sweet flavor, as the name suggests, while yams have a more starchy and earthy taste. This is due to the higher sugar content in sweet potatoes compared to yams.
I. Scientific Names and Family
Sweet potatoes belong to the Convolvulaceae family and have the scientific name Ipomoea batatas. Yams, on the other hand, belong to the Dioscoreaceae family and have various species within the genus Dioscorea.
II. Physical Characteristics
A. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are tuberous roots with an elongated shape and a smooth skin that can range from white to purple. The flesh can also vary in color, from white to orange or even purple. They have a sweet and starchy taste, making them a popular ingredient in both savory and sweet dishes.
B. Yams
Yams, on the other hand, are larger than sweet potatoes and have a rough, bark-like skin that is difficult to peel. They have a cylindrical shape and can grow up to 5 feet in length. Their flesh is usually white or yellow and has a drier texture compared to sweet potatoes. Yams have a milder flavor, making them more suitable for savory dishes.
III. Origin and Distribution
A. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are believed to have originated in Central or South America and were brought to Europe by Christopher Columbus. They are now cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions, including Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
B. Yams
Yams have a much longer history, with evidence of their cultivation dating back to 50,000 BC in Asia and Africa. They are still a major food source for many countries in these regions, and are also grown in other parts of the world such as the Caribbean and South America.
IV. Nutritional Value
Both sweet potatoes and yams are nutrient-dense foods with a variety of health benefits. They are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. However, there are some differences in their nutritional profiles:
A. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are particularly rich in beta-carotene, an antioxidant that is converted into vitamin A in the body. They also contain high levels of vitamin C, potassium, and manganese. Additionally, they have a lower glycemic index compared to yams, making them a better option for those with diabetes or insulin resistance.
B. Yams
Yams are a good source of fiber, potassium, and vitamin C. They also contain lower amounts of beta-carotene compared to sweet potatoes. However, they have a higher glycemic index and may cause a more rapid rise in blood sugar levels.
V. Culinary Uses
While both sweet potatoes and yams are starchy root vegetables, they have distinct differences in flavor and texture. This makes them suitable for different types of dishes.
A. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes have a sweeter, milder flavor compared to yams. They also have a softer, creamier texture when cooked, making them ideal for mashing or pureeing. They are commonly used in both sweet and savory dishes, such as casseroles, pies, and soups.
B. Yams
Yams have a more earthy and nutty flavor compared to sweet potatoes. They also have a firmer texture when cooked, making them suitable for roasting or grilling. In some cultures, yams are used in stews, salads, and even as a base for desserts.
VI. Conclusion
In conclusion, while sweet potatoes and yams are often used interchangeably, they have distinct differences in nutritional value and culinary uses. Both of these root vegetables offer unique health benefits and can be incorporated into a well-balanced diet. Whether you prefer the sweeter taste of sweet potatoes or the earthy flavor of yams, there are endless ways to enjoy these versatile and nutritious vegetables. So the next time you’re at the grocery store, don’t be afraid to try both and see which one you prefer.
- Cosmic Purple Carrot: Description, Origins, Uses & More… - December 24, 2024
- Black Sapote: Description, Origins, Uses & More… - December 24, 2024
- Amish Paste Tomato: Description, History, Benefits, & More… - December 19, 2024

1 thought on “Sweet Potato vs Yam: Explore the Differences”
Comments are closed.