Hip Dysplasia in Babies – Signs, Diagnosis and Treatment

- What Is Developmental Dysplasia of Hips (DDH) in Infant?
- What Causes Hip Dysplasia in Babies?
- Who Are at Higher Risk of Getting DDH?
- What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Hip Dysplasia in a Young Child?
- Diagnosis of DDH
- Treatment of Baby Hip Dysplasia
- Can You Prevent Hip Dysplasia in Infants?
- When to Consult a Doctor
- Long-Term Outlook for Baby With Congenital Hip Dysplasia
As a baby starts growing up, there are a lot of development milestones he will begin to hit at various stages of his life. One of the primary ones on these lines is the ability to pull himself up and attempt to walk. This usually takes place as the baby starts getting a year old, but could happen earlier or later too. Many attempts continue during this period, leading up to the final success. But, newborn hip dysplasia might be present if your child fails to show such signs. Walking tendencies could be absent, or the legs might not be straight, or could be a little bent. Such signs, including walking on tiptoed feet could all indicate a similar problem.
What Is Developmental Dysplasia of Hips (DDH) in Infant?
Congenital hip dysplasia in newborns or even ones that form later in life is all related to the hip joint. The joint in the hip is of the ball and socket type, which is kept in place by utilizing a variety of ligaments. However, in some children, these ligaments are not as firm and tight as they ought to be, causing them to loosen up and cause hip dysplasia to set in. 1 in 1,000 newborns tends to suffer from this problem right from birth, but only a few of them require treatment for its correction.
What Causes Hip Dysplasia in Babies?
The reasons behind hip dysplasia manifesting in some babies are multi-faceted. These tend to be dependent on a number of factors, some of which are a result of genetic traits, while others could be entirely environmental or even circumstantial. Gender plays an important role in this as well, since the documented cases of hip dysplasia have shown that female babies tend to be at a higher risk of developing this condition as compared to male babies.
Apart from various hereditary conditions that could affect the presence of hip dysplasia in a child, the circumstantial or environmental conditions that cause this depend quite a lot on the internal constitution of the mother’s body. Secretion of certain hormones could result in the baby responding ineffectively to them, and resulting in the hip development to be impacted due to it. The orientation of the baby in the breech position in the womb has also been concluded to result in this condition. If the uterus of the mother is excessively constricted that restricts free movement for the child, hip dysplasia could manifest in the baby as a result of it.
Who Are at Higher Risk of Getting DDH?
Since the environmental conditions are dependent on the intrauterine position of the child, first-time babies are comparatively at a higher risk, since the uterus is not as elastic as it needs to be on the first go. A few other factors contribute to an increased risk of hip dysplasia as well, namely:
- Any aspects that lead to a link with various orthopaedic problems, which could either be a result of a congenital issue, or any other deformities as well as syndromes
- The orientation of the baby where the feet are pointing towards the birth canal called breech position, or any other position that isn’t ideal for delivery
- A presence of hip dysplasia history within the family, or a certain propensity for ligament related problems, especially loose ligaments.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Hip Dysplasia in a Young Child?
In most of the cases, babies that have had hip dysplasia have either a partial or a complete dislocation of the hip, where the ball within the joint doesn’t stay at the ideal position within the socket. As a result, this is usually observed externally as some problems related to the hip itself.

- The legs of the child generally seemed to be spaced much wider than they ought to be.
- The skin that is present between the thighs and the buttocks seems to be folded unevenly.
- In certain cases, the leg that is situated on the side of the dislocated turns slightly outward or seems to be so.
- One leg might appear to be shorter in length than the other, due to the dislocation.
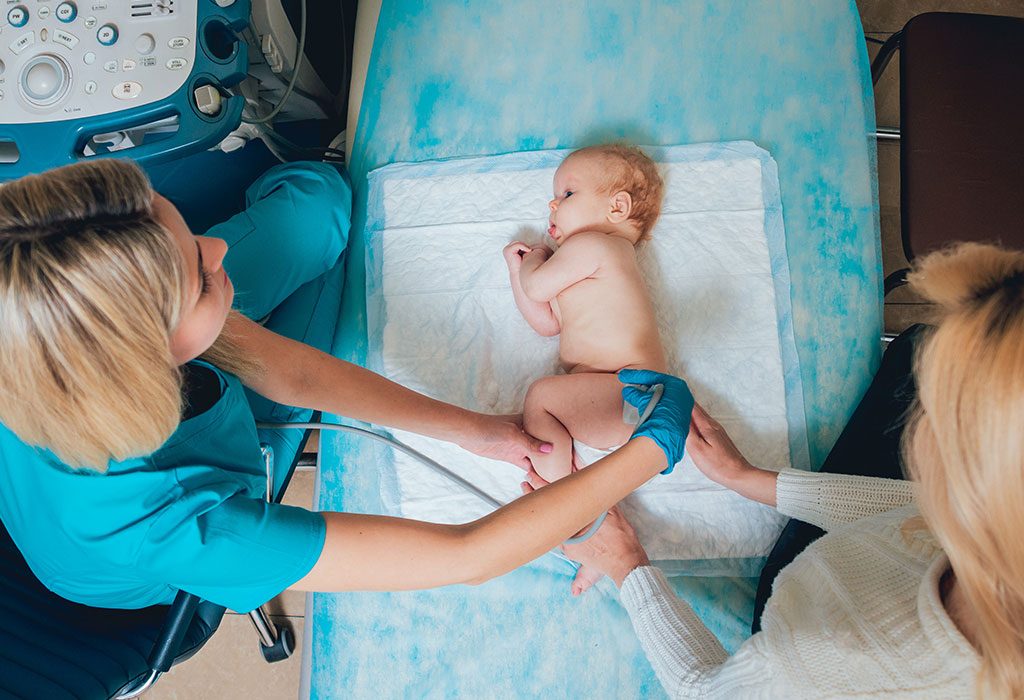
Diagnosis of DDH
Most doctors tend to observe signs and symptoms of hip dysplasia in the baby right when he is born. Certain hospitals do conduct special screenings, such as NIPE within 72 hours of birth, to rule out the condition. In rare cases, hip dysplasia might not be evident until the child grows up. If signs of the condition might be apparent, or the doctor tends to notice a pattern in the family’s history supporting the condition, additional procedures might be undertaken to confirm the diagnosis.
In such procedures, a preliminary x-ray test is undertaken to get a better picture regarding the development and pattern of bones. This can clearly indicate if the joint has any displacement or not. These results are further compounded by using an ultrasound of the hip, giving a better idea of the placement of internal organs, and helping rule out any further complications.
Treatment of Baby Hip Dysplasia
Conditions of hip dysplasia in babies can be corrected by making use of certain supportive procedures or even by undertaking hip dysplasia surgery. There are various methods to carry out each of them.
1. Non-Surgical Treatment Methods
- If the case of hip dysplasia is mild, then doctors might choose to go ahead with a traction that pulls the ligaments and tightens them to keep them firm.
- A few cases make use of firm braces called hip abduction braces, which work towards adjusting the position of the ball and socket joint.
- An evolved version of the hip abduction brace is termed as a Pavlik harness. This, too, helps maintain a proper position of the joint but is much flexible in its use.

2. Surgical Treatment Methods
- One of the first steps that can be taken to correct the dysplasia is to carry out a surgery to repair the femur’s position. This is termed femoral osteotomy.
- If the dysplasia is more apparent due to the position of the hip, then a pelvic osteotomy could be conducted that works to correct the pelvis’ position.
- At times, it is the ligament that is the problem and not the bone position. Resorting to an open reduction surgery is needed in such a case, which is a bit more complex since stitches are used to tighten the ligaments and hold them together.
- If the child is more than 6 months old and less than 2 years of age, then your doctor might opt to go for closed reduction surgery. This involves minimal surgical incisions and using manual movements to guide the ball into the right position within the socket.
Can You Prevent Hip Dysplasia in Infants?
As mentioned earlier, the reasons for hip dysplasia are multi-faceted. So, a particular aspect cannot be focused on to reduce the chances, since it could even be caused due to hereditary reasons. Most babies keep their thighs closer to the stomach, resulting in flexed hips. However, as they start kicking around, they get back to an appropriate position rather soon.
In order to support this, it is necessary to allow free leg movement for your baby at all times. Do not wrap him up tightly in a cloth for long durations. Tight swaddling is largely avoided these days.
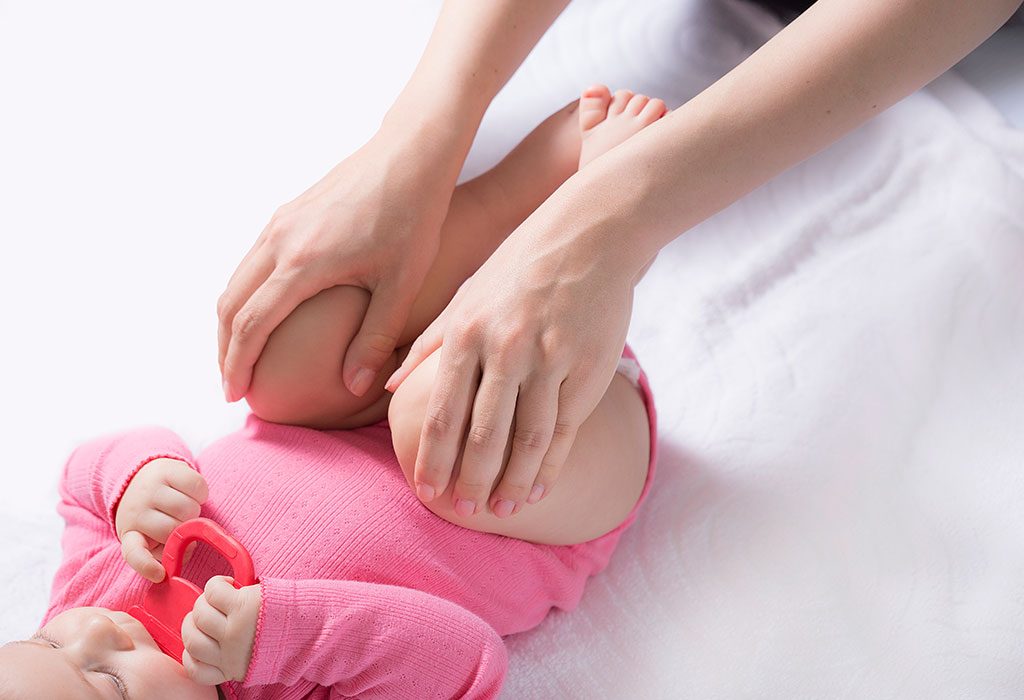

When to Consult a Doctor
It is necessary to call up your doctor and inform him of the baby’s condition following the surgery, if your child is suffering from excessively cold toes, a foul smell or any kind of swelling from the place of the cast or wound, or an onset of fever accompanied by pain in the body.
Long-Term Outlook for Baby With Congenital Hip Dysplasia
The earlier a corrective action is taken to treat the condition, the better the chances are for the baby to respond to the treatment. Non-surgical treatments also provide a good result. However, additional treatments might be required, as the body structure changes with the child’s age.
Development of hip dysplasia cannot be prevented directly, and it isn’t a condition that is developed due to carelessness on anyone’s part. Being vigilant about it is absolutely necessary, and nipping the problem in the bud can benefit your child to a large degree, allowing him to lead a normal life as easily as possible.
Also Read:
Clicky Hips In Infants
How to Swaddle a Baby?