Bohemond I of Antioch, also known as Bohemond of Taranto, was a prominent medieval noble and military leader who played a significant role in the First Crusade and the establishment of the Crusader state of Antioch. Here’s an overview of Bohemond I:
The First Crusade
Early Life and Background:
Bohemond was born around 1054 to Robert Guiscard, a Norman nobleman and Alberada of Buonalbergo, making him a member of the powerful Hauteville family.
His father, Robert Guiscard, was a renowned military leader who played a pivotal role in the Norman conquest of southern Italy.
Participation in the First Crusade:
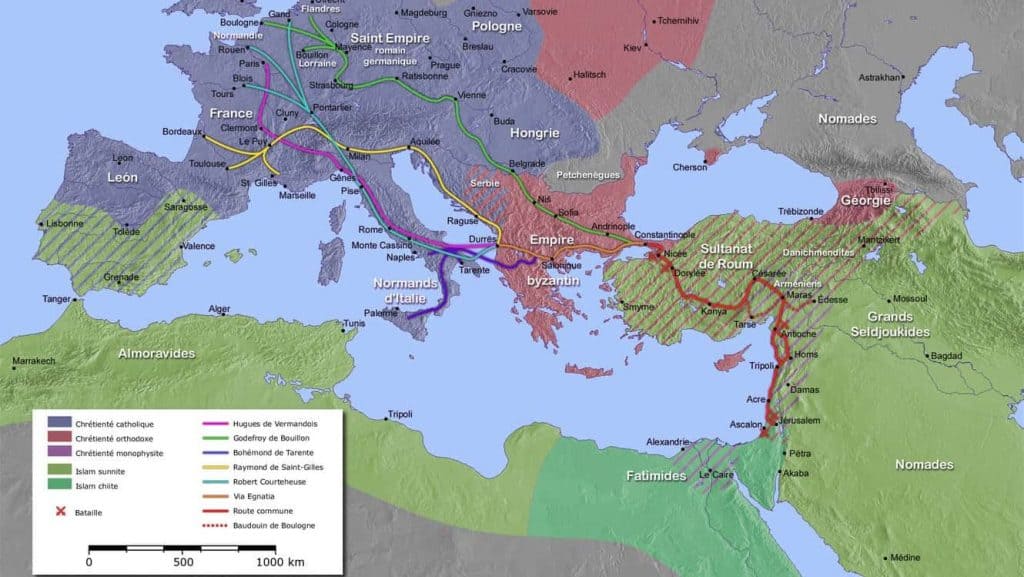
So Bohemond joined the First Crusade in 1096, where he assumed a prominent role as one of the leaders of the Crusader army.
Furthermore, he was known for his martial prowess and tactical acumen, which contributed significantly to the successes of the Crusader forces during the campaign.
Bohemond I of Antioch – Siege of Antioch:
Bohemond’s most notable achievement during the First Crusade was capturing the city of Antioch in 1098 after a lengthy and grueling siege.
This conquest established the Principality of Antioch, one of the Crusader states in the Holy Land.
Conflict with Other Crusader Leaders:
Bohemond’s leadership and ambitions sometimes led to conflicts with other prominent Crusader leaders, including Raymond IV of Toulouse.
Disputes over control of territories and political power were common among the Crusader leaders.
Ruler of Antioch:
Bohemond became the first ruler of the Principality of Antioch and assumed the title of Prince of Antioch.
He ruled the principality from 1098 until he died in 1111 and played a vital role in consolidating and defending its territory.
Later Life and Death:
Bohemond continued to be involved in the Crusader states’ affairs and the region’s broader politics.
He died in 1111 and was succeeded by his son, Bohemond II.
Legacy:
Bohemond I is remembered as one of the first Crusade’s most charismatic and skilled leaders.
So, his capture of Antioch was a significant achievement, but his territorial ambitions and conflicts with fellow Crusader leaders are also part of his legacy.
Lastly, The Principality of Antioch, established under his rule, endured for nearly two centuries, and Bohemond’s role in its foundation is a central aspect of his historical legacy.
Ultimately, Bohemond I of Antioch remains a prominent figure in the history of the Crusades and the establishment of Crusader states in the Holy Land. His leadership and military exploits contributed to the Christian presence in the region during the medieval era. For more about him, go to Wikipedia!

