Biology 102 Lab 12 Digestive System Enzymes Activity

Biology 102 Lab 12 Digestive System Enzymes: Activity, Purpose, and Optimal Conditions 1

Objectives for Today • Become more familiar with some of the enzymes used for chemical digestion • For each enzyme used in today’s experiment, you should know: – Their major action, i. e. , the type(s) of substrates on which they act – Their primary site of action in the body – The optimal p. H at which they work – Additional factors, if any, they need to work efficiently 2
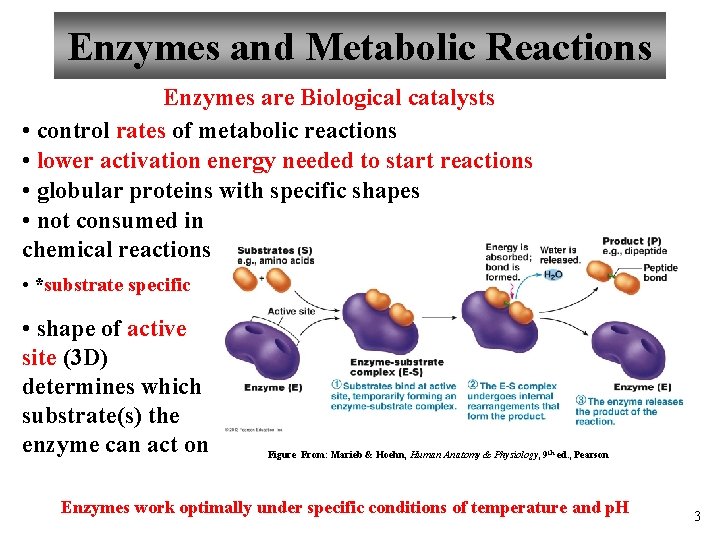
Enzymes and Metabolic Reactions Enzymes are Biological catalysts • control rates of metabolic reactions • lower activation energy needed to start reactions • globular proteins with specific shapes • not consumed in chemical reactions • *substrate specific • shape of active site (3 D) determines which substrate(s) the enzyme can act on Figure From: Marieb & Hoehn, Human Anatomy & Physiology, 9 th ed. , Pearson Enzymes work optimally under specific conditions of temperature and p. H 3
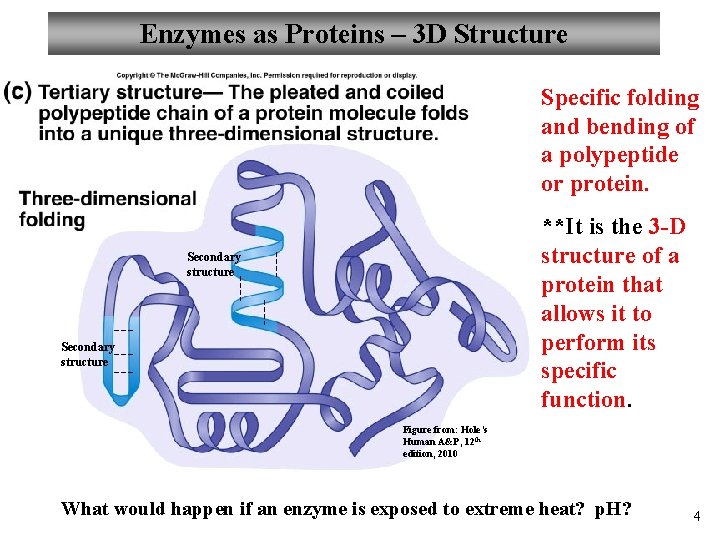
Enzymes as Proteins – 3 D Structure Specific folding and bending of a polypeptide or protein. **It is the 3 -D structure of a protein that allows it to perform its specific function. Secondary structure Figure from: Hole’s Human A&P, 12 th edition, 2010 What would happen if an enzyme is exposed to extreme heat? p. H? 4

Enzymes used in today’s experiment 1. Salivary amylase – – Starch (polysaccharide) → Maltose (disaccharide) Salivary glands What do you predict is its optimum temp/p. H? How would we know if this reaction has occurred? IKI – Potassium Iodide Benedict’s Reagent What is an experimental control? What kinds of controls are there? 5
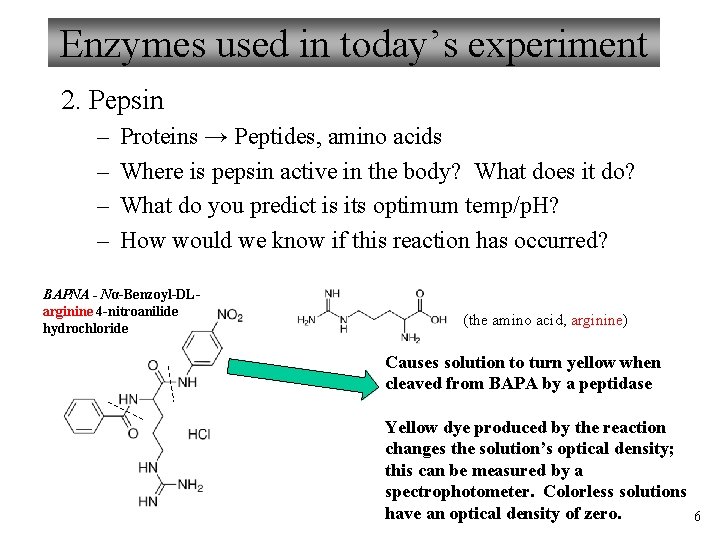
Enzymes used in today’s experiment 2. Pepsin – – Proteins → Peptides, amino acids Where is pepsin active in the body? What does it do? What do you predict is its optimum temp/p. H? How would we know if this reaction has occurred? BAPNA - Nα-Benzoyl-DLarginine 4 -nitroanilide hydrochloride (the amino acid, arginine) Causes solution to turn yellow when cleaved from BAPA by a peptidase Yellow dye produced by the reaction changes the solution’s optical density; this can be measured by a spectrophotometer. Colorless solutions have an optical density of zero. 6
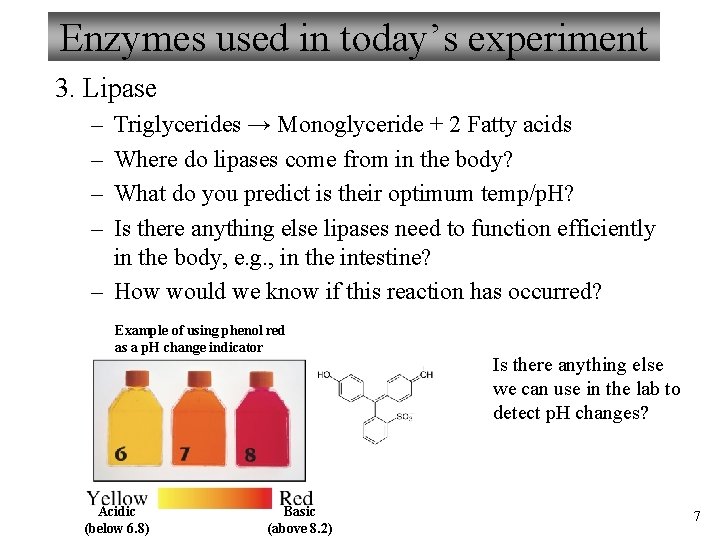
Enzymes used in today’s experiment 3. Lipase – – Triglycerides → Monoglyceride + 2 Fatty acids Where do lipases come from in the body? What do you predict is their optimum temp/p. H? Is there anything else lipases need to function efficiently in the body, e. g. , in the intestine? – How would we know if this reaction has occurred? Example of using phenol red as a p. H change indicator Acidic (below 6. 8) Basic (above 8. 2) Is there anything else we can use in the lab to detect p. H changes? 7
Using Physio. Ex 9. 1 Physio. EX 9. 1 is current 8
Using Physio. Ex 9. 1 Note: Physio. Ex 9. 1 is most current version 9
Using Physio. Ex 9. 1 10
Using Physio. Ex 9. 1 11
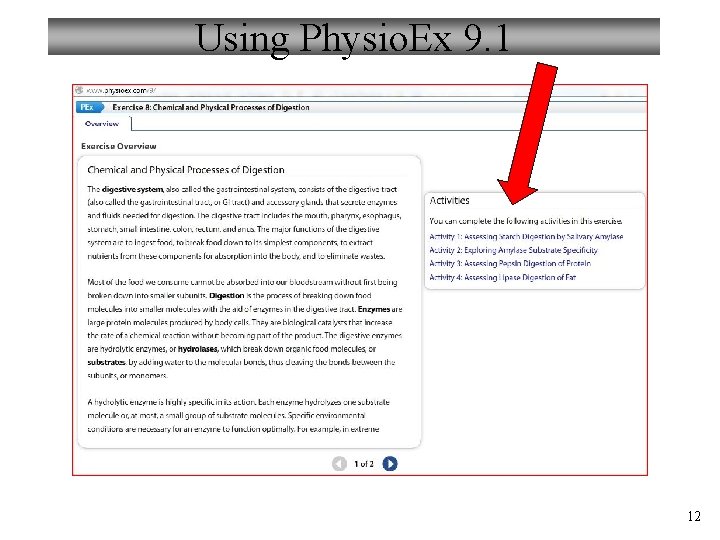
Using Physio. Ex 9. 1 12
Using Physio. Ex 9. 1 13
Using Physio. Ex 9. 1 14
Using Physio. Ex 9. 1 Note: Save this to the desktop and name the file: Lab 12_<Day>_Group<#>. pdf Email me the file (gerianne@ccm. edu), and be sure to email one to yourself and the other members of your group if you want a copy for studying. Put the names of your group members in the subject line of the email followed by ‘Lab 12’. 15

What You Should Do in Lab Today… • Using the DVD version or online version of the software, access Physio. Ex 9. 1 in Mastering A&P and do Exercise 8: – Salivary amylase (Activities 1 and 2) – Pepsin (Activity 3) – Lipase (Activity 4) • For each experiment, – Be sure to do the pretest – Answer the ‘Prediction’ questions as you go – Generate a PDF file to submit as your lab report (so, you will be submitting 4 PDF files) • Also submit a Summary Table Lab Report (hard copy) from your group. 16

For next lab… • Gross/microscopic anatomy of the urinary system – Human models – Cats • Gross anatomy of the reproductive system – Human models (no, not live ones!) – Cats 17
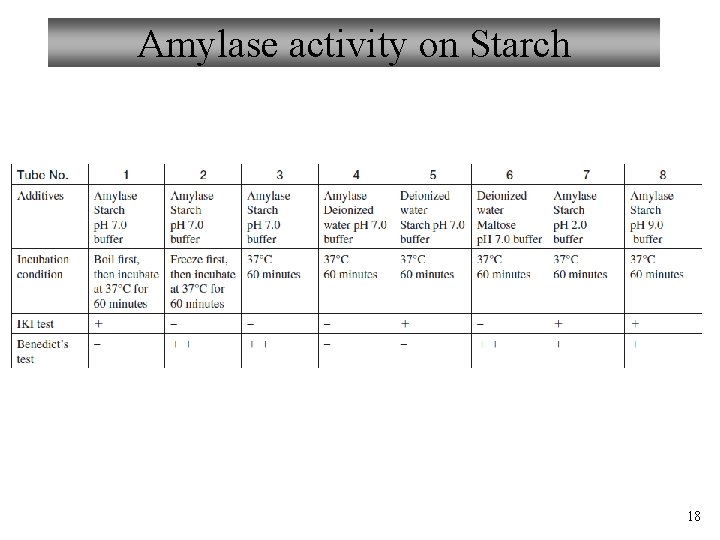
Amylase activity on Starch 18
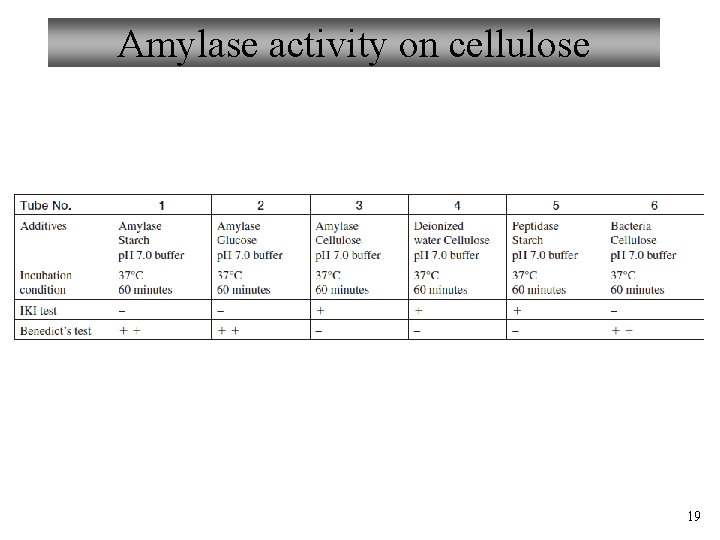
Amylase activity on cellulose 19
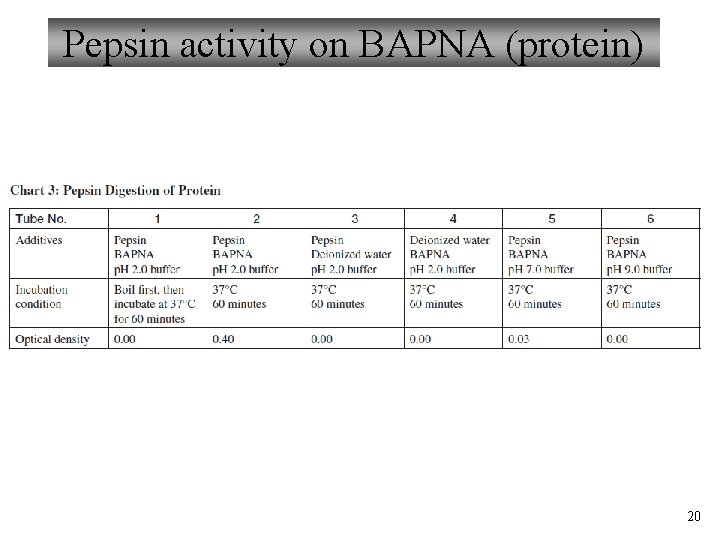
Pepsin activity on BAPNA (protein) 20
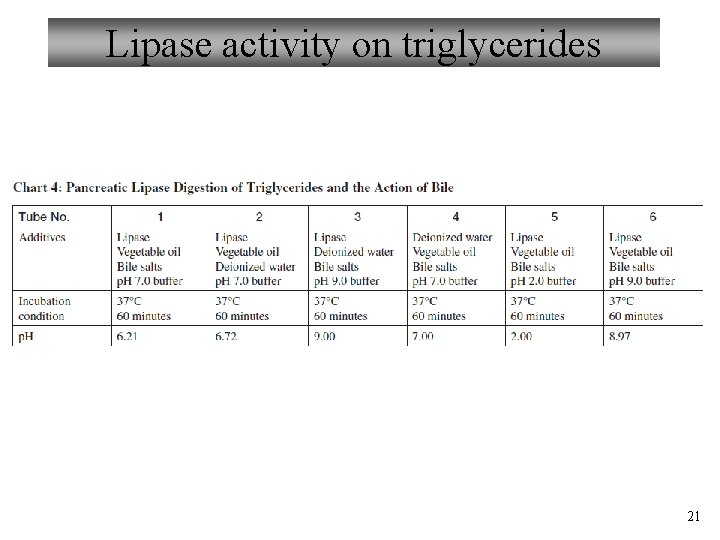
Lipase activity on triglycerides 21
- Slides: 21