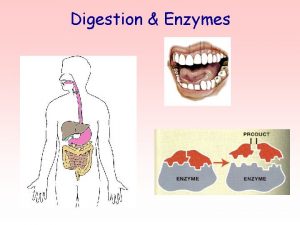
Human Digestion and Enzyme Hendra wijaya DIGESTIVE SYSTEM











































- Slides: 43

Human Digestion and Enzyme Hendra wijaya

DIGESTIVE SYSTEM

What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules which can pass through the wall of the gut into the blood.

Enzymes help in the breakdown of food, in a process called chemical digestion. Food contains carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, so a wide range of enzymes is needed. • Carbohydrases break down carbohydrates • Proteases break down protein • Lipases break down lipids


Carbohydrate digestion involves two stages: • First the breakdown of starch to maltose is catalysed by the enzyme amylase in the mouth and the lumen of the small intestine. • Secondly the breakdown of maltose to glucose is catalysed by the enzyme maltase inside the mucosa cells of the small intestine.


• Protein digestion in the lumen of the gut starts with an enzyme called endopeptidase that catalyses the breakdown of proteins to form polypeptides. • An enzyme called an exopeptidase catalyses the breakdown of polypeptides to produce dipeptides. • Inside the cells of the mucosa dipeptidase enzymes catalyse the breakdown of dipeptides into amino acids.


Lipid digestion only occurs in the lumen of the small intestine. • Lipid digestion cannot start in the stomach because conditions are too acidic for the lipase enzymes. • Bile salts found in bile produced by the liver break down the fat droplets into smaller droplets. • This process is called emulsification. It increases the surface area for the lipase enzymes to work on. • Lipase from the pancreas catalyses the breakdown of lipids into fatty acids and glycerol.

CLASSIFICATION OF ENZYME International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB)

CLASSIFICATION OF ENZYME

CLASSIFICATION OF ENZYME

REACTION OF ENZYME

REACTION OF ENZYME



Human digestive system

Mouth • Functions – mechanical digestion • teeth – break up food – chemical digestion (saliva) • amylase enzyme – digests starch • mucus – protects soft lining of digestive system – lubricates food for easier swallowing • buffers – neutralizes acid to prevent tooth decay • anti-bacterial chemicals – kill bacteria that enter mouth with food

Swallowing (& not choking) • Epiglottis – flap of cartilage – closes trachea (windpipe) when swallowing – food travels down esophagus • Peristalsis – involuntary muscle contractions to move food along


mouth break up food digest starch kill germs moisten food

Stomach • Functions – disinfect food • hydrochloric acid = p. H 2 – kills bacteria – food storage • can stretch to fit ~2 L food – digests protein • pepsin enzyme But the stomach is made out of protein! What stops the stomach from digesting itself? mucus secreted by stomach cells protects stomach lining

mouth break up food digest starch kill germs moisten food stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food sphincter

Ulcers • Used to think ulcers were caused by stress – tried to control with antacids • Now know ulcers caused by bacterial infection of stomach – H. pylori bacteria – now cure with antibiotics Colonized by H. pylori inflammation of stomach Free of H. pylori inflammation of esophagus H. pylori inflammatory proteins (Cag. A) cytokines cell damaging proteins (Vac. A) helper T cells neutrophil cells white blood cells

Small intestine • Functions – digestion • digest carbohydrates – amylase from pancreas • digest proteins – trypsin & chymotrypsin from pancreas • digest lipids (fats) – bile from liver & lipase from pancreas – absorption • nutrients move into body cells by: – diffusion – active transport This is where all the work is done!

Absorption in Small Intestines • Absorption through villi & microvilli – finger-like projections – increases surface area for absorption SMALL INTESTINES 6 meters long, but can stretch to cover a tennis court

mouth break up food digest starch kill germs moisten food liver produces bile - stored in gall bladder break up fats pancreas produces enzymes to digest proteins & starch stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food small intestines breakdown food - proteins - starch - fats absorb nutrients

Pancreas • Produces digestive enzymes – digest proteins • trypsin, chymotrypsin – digest starch • amylase – digest lipids • lipase • Buffers – neutralizes acid from stomach small intestine pancreas

mouth break up food digest starch kill germs moisten food pancreas produces enzymes to digest all foods stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food

Liver & Gall Bladder • Produces bile – breaks up fats – gallbladder only stores bile • that’s why you can have your gall bladder removed bile contains colors from old red blood cells collected in liver = iron in RBC rusts & makes feces brown

mouth break up food digest starch kill germs moisten food liver produces bile - stored in gall bladder break up fats pancreas produces enzymes to digest proteins & starch stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food

Large intestines (colon) • Function – re-absorbs water • use ~9 liters of water every day in digestive juices – if don’t reabsorb water would die of dehydration • > 90% of water re-absorbed – not enough water re-absorbed » diarrhea » can be fatal! – too much water re-absorbed » constipation • reabsorb by diffusion

You’ve got company! • Living in the large intestine is a community of helpful bacteria – Escherichia coli: E. coli • digest cellulose – digests fruits & vegetables • produce vitamins – vitamin K & B vitamins • BUT generate gases – by-product of bacterial metabolism – methane, hydrogen sulfide – STINKY!

mouth break up food digest starch kill germs moisten food liver produces bile - stored in gall bladder break up fats pancreas produces enzymes to digest proteins & carbs stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food small intestines breakdown food - proteins - starch - fats absorb nutrients large intestines absorb water

Appendix Vestigial organ

mouth break up food digest starch kill germs moisten food liver produces bile - stored in gall bladder break up fats pancreas produces enzymes to digest proteins & carbs appendix stomach kills germs break up food digest proteins store food small intestines breakdown food - proteins - starch - fats absorb nutrients large intestines absorb water

Rectum • Last section of large intestines – eliminate feces – what’s left over? • undigested materials – mainly cellulose from plants – called roughage or fiber – keeps everything moving & cleans out intestines • masses of bacteria So don’t forget to wash your hands!

Eating a balanced diet • What happens if an animal’s diet is missing an essential nutrient? – deficiency diseases • • • scurvy — vitamin C (collagen production) rickets — vitamin D (calcium absorption) blindness — vitamin A (retinol production) anemia — vitamin B 12 (energy production) kwashiorkor — protein

Vegetarian diets • Need to make sure you get enough protein – 20 amino acids to make protein • 12 amino acids humans can produce • 8 we have to eat = “essential amino acids” – Grains (like corn) have 6 amino acids • missing 2 – Beans (like soybean & red beans) have 6 amino acids • missing different 2 • mix beans & grains for complete group of amino acids – – rice & beans taco/tortilla & beans tofu & rice peanut butter & bread

Balancing Blood Sugar levels Homeostasis insulin liver stores sugar body cells take up sugar from blood pancreas high reduces appetite liver blood sugar level low triggers hunger liver releases sugar liver pancreas glucagon Feedback

Feedback: Maintaining Homeostasis • Balancing glucose levels in blood depress appetite pancreas insulin cells take up glucose from blood liver takes up glucose for storage liver releases glucose to blood glucagon pancreas stimulate hunger

 Beta limit dextrin
Beta limit dextrin Mechanical digestion and chemical digestion venn diagram
Mechanical digestion and chemical digestion venn diagram Hendra simarmata
Hendra simarmata Arti nusyuz
Arti nusyuz Abdullah suriosubroto
Abdullah suriosubroto Definisi sdlc
Definisi sdlc Niko wijaya
Niko wijaya Buah polong di samping melakukan gerak
Buah polong di samping melakukan gerak Cakra wijaya kusuma
Cakra wijaya kusuma Vonny wijaya
Vonny wijaya Lily wijaya
Lily wijaya Yuliagnis transver wijaya
Yuliagnis transver wijaya Dr. juliana wijaya
Dr. juliana wijaya Respiratory system circulatory system digestive system
Respiratory system circulatory system digestive system Human digestive system facts
Human digestive system facts Human digestive system facts
Human digestive system facts Digestive system introduction
Digestive system introduction Introduction to digestive system
Introduction to digestive system Human digestive system in order
Human digestive system in order Write the correct sequence of human digestive system
Write the correct sequence of human digestive system Alimentary canal diagram
Alimentary canal diagram Digestive system diagram
Digestive system diagram Nervous system and digestive system
Nervous system and digestive system Figure 14-1 anatomy and physiology
Figure 14-1 anatomy and physiology Chapter 14 the digestive system and body metabolism
Chapter 14 the digestive system and body metabolism Digestive system vocabulary
Digestive system vocabulary Major and accessory organs of the digestive system
Major and accessory organs of the digestive system Chapter 14 the digestive system and body metabolism
Chapter 14 the digestive system and body metabolism Accessory organs
Accessory organs Digestive system and body metabolism
Digestive system and body metabolism Anatomy and physiology coloring workbook figure 14-1
Anatomy and physiology coloring workbook figure 14-1 Define todays
Define todays The digestive system and body metabolism
The digestive system and body metabolism Digestive and excretory system
Digestive and excretory system Questron technologies corp
Questron technologies corp Enzymes affect reactions in living cells by changing the
Enzymes affect reactions in living cells by changing the Define enzyme
Define enzyme Succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor malonate
Succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor malonate Sheep digestive system
Sheep digestive system Monogastric
Monogastric Food digestion energy transformation
Food digestion energy transformation Cecum ruminant
Cecum ruminant Ruminant stomach diagram
Ruminant stomach diagram øhuman digestive system
øhuman digestive system