QUALITY GRADES Grade A fluid milk Grade B


QUALITY GRADES • Grade A: fluid milk • Grade B: processing and manufacturing (cheese/butter)


MAJOR PRODUCTS • Fluid milk: –whole milk, – 2%, – 1%, –nonfat milk (less than. 5% fat), –chocolate milk


• Fermentation (grade A): • The addition of “good” bacteria to milk • cultured buttermilk • yogurt

• Cream (grade A): • half & half (11% fat); • light cream (18%fat); • sour cream (18%fat) • whipping cream (30%fat); • heavy cream (36%fat);

• Butter • Canned milk • evaporated milk (60%water removed); • sweetened condensed milk • Non-Fat Powdered milk


• Cheese • Fresh • Aged • Ice cream products • Ice cream • Ice milk • Frozen Yogurt

MILK BY-PRODUCTS • Buttermilk • from butter • dried for baking or fresh • Whey • from cheese • dried or concentrated

COMPONENTS OF MILK v Water v Fat v Protein v Lactose v Minerals 88. 0% 3. 5% 3. 2% 4. 6% 0. 7%
INFLUENCES ON COMPONENTS • Breed of cow • • Each individual animal Stage of lactation Feed - Age - Climate Frequency of milking
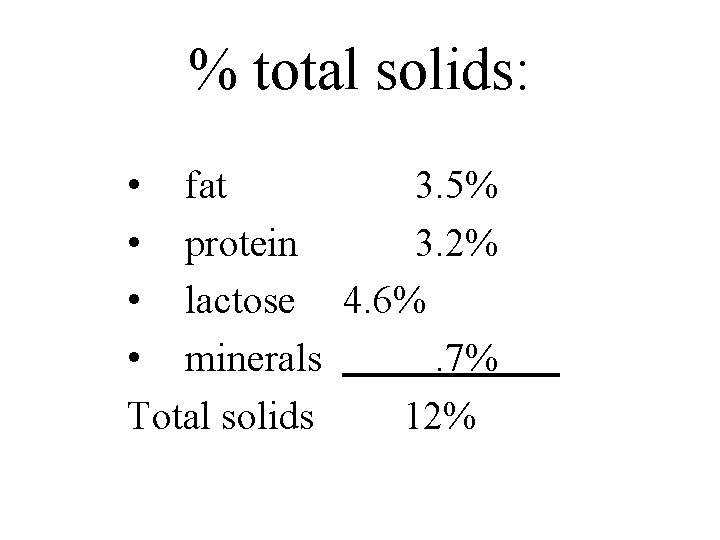
% total solids: • fat 3. 5% • protein 3. 2% • lactose 4. 6% • minerals. 7% Total solids 12%

• The minimum legal composition of whole milk: • not less than 3. 25% fat • not less than 8. 25% solids-not-fat

STEPS IN PROCESSING v Standardization v adjust fat v Clarification v remove foreign matter v Pasteurization v destroy bacteria with heat

v Homogenization vbreak-up fat globules so the cream doesn’t float to top v Packaging v Dating vguaranteed drinkable 7 days beyond date v Storage

TRENDS IN CONSUMPTION • Prior to 1945: – whole and condensed milk and butter most popular • After 1945 – – more ice cream and cheese

• Since 1975 – shift from whole to low fat “lite” cheese – and from regular ice cream to ice milk • Recently yogurt and frozen yogurt

The End
- Slides: 20