Relational Model Concepts Relational Model Concepts The relational






















- Slides: 27

Relational Model Concepts

Relational Model Concepts • • • The relational model represents the database as a collection of relations. Each relation resembles a table of values. A table is called a relation. A row is called a tuple. A column header is called an attribute. The data type describing the type that can appear in each column is called a domain. A domain (D) is a set of atomic values.

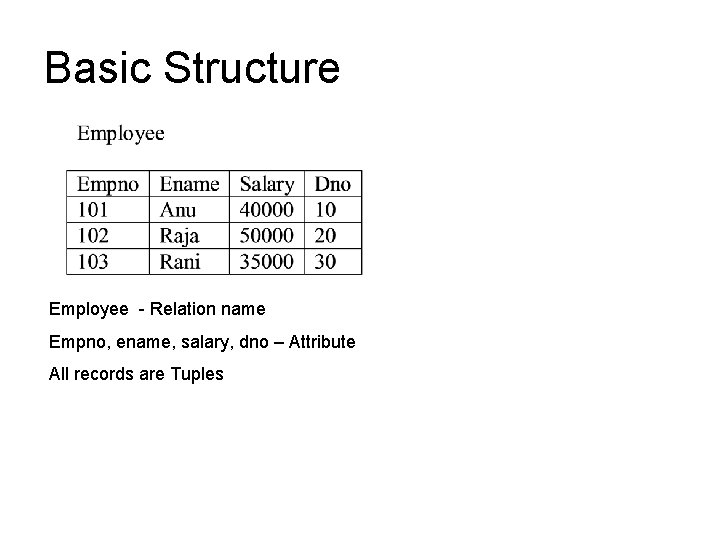
Basic Structure Employee - Relation name Empno, ename, salary, dno – Attribute All records are Tuples

Query Language • Categories – Procedural • Example Relational Algebra – Non Procedural • Example Relational Calculus

Relation Algebra • It is procedural language • It consists of set of operations that take one or more relations as input and produces new relation as output. The operation can be divided into three parts Basic operations Additional operations Extended operations

Basic operations • • • Select ( ) Project ( ) Union (U) Rename ( ) Set difference (-) Cartesian product (x)

Additional operations • • Set intersection ( ) Natural join Division ( ) Assignment ( )

Extended operations • Aggregate operations • Outer join

Basic operations The Select operation ( ) – It is used to select a subset of the tuples (records) from a relation that satisfy a selection condition. Syntax <select condition> (R) Note : R is table name Example 1) dno=10 (emp) 2) ename=‘raja’(emp) Note : Display eno, ename, salar dno (all heading)

Project operation The required attributes alone can be listed from a relation (selects certain columns from the table) Syntax <select condition> (R) Note : R is table name Example 1) eno, salary (emp) display eno, salary (two column) 2) ename dno=10 (emp) Note : Display ename column only

The union operation (U) • RUS is all tuples that are either in R or in S. Duplicate tuples are eliminated. Syntax RUS Example ename (emp 1) U ename (emp 2)

The Set difference operation ( - ) • It is used to find tuples that are in one relation but are not in another. • Syntax R-S • Example ename (emp) U ename (empit)

Cartesian Product operation (X) • It allows us to combine information from any 2 relations. Syntax R X S = { tq/t R and q s} • Example dno=10 (emp X dept)

Rename operation ( ) • Allow us to name the relational algebra expressions • Allow us to refer to a relation by more than one name. Example temp ( eno, salary (emp))

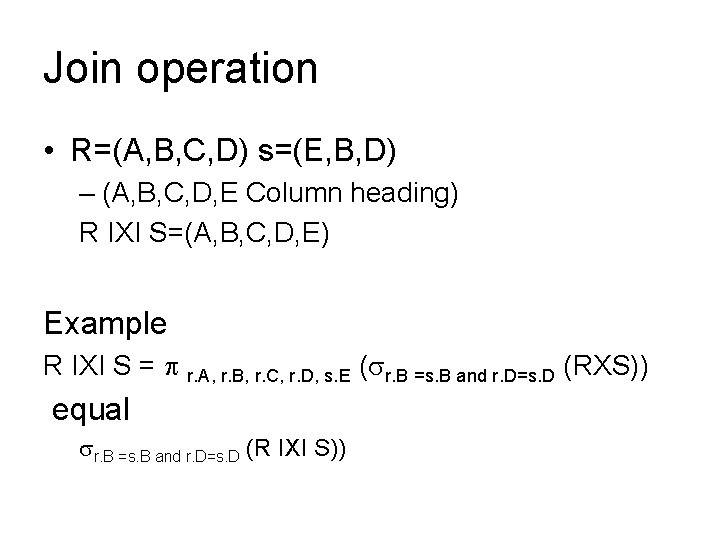
Join operation • R=(A, B, C, D) s=(E, B, D) – (A, B, C, D, E Column heading) R IXI S=(A, B, C, D, E) Example R IXI S = r. A, r. B, r. C, r. D, s. E ( r. B =s. B and r. D=s. D (RXS)) equal r. B =s. B and r. D=s. D (R IXI S))

• Division operation ( r s) R=(A 1, A 2, A 3, …… Am, B 1, B 2, B 3, ……. Bn) S=(B 1, B 2, …. . Bn) The result of r s is r s =(A 1, A 2, A 3, …… Am)

Assignment Operation ( ) • It can be assigned to a temporary relation variable (S). Example Temp ( ) eno, salary (emp) Temp 1 ( ) eno, salary>10000 (emp)

Aggregate functions • Aggregate function takes a collection of values and returns a single values as a result. AVG – average value MIN – minimum value MAX – Maximum value SUM – Sum of values COUNT – number of record

Syntax G Aggregate_function (attribute_name) (relation name) Example G Sum(salary)(emp) dno G Sum(salary)(emp) Find sum of salary for employees to each department.

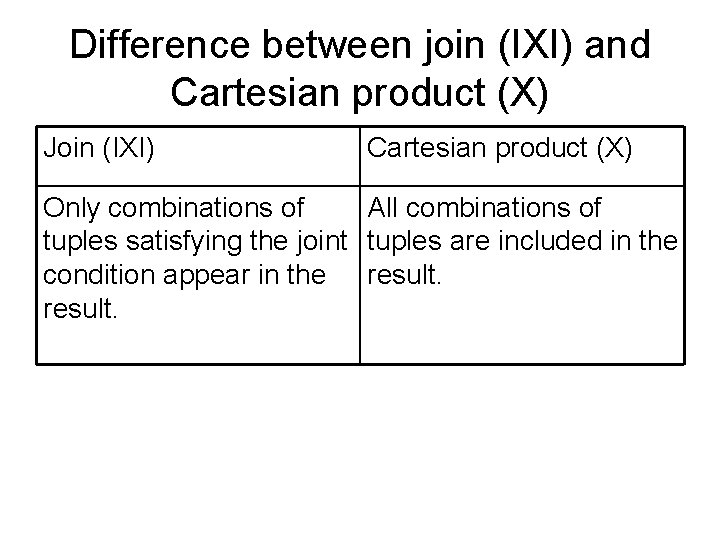
Difference between join (IXI) and Cartesian product (X) Join (IXI) Cartesian product (X) Only combinations of All combinations of tuples satisfying the joint tuples are included in the condition appear in the result.

employee (person_name, street, city) works (person_name, company_name, salary) Company (company_name, city) manages (person_name, manager_name) Consider the relation database, where the primary keys are underlined. Give an expression in relational algebra, SQL query of the following a) Find the names of all employees who work for First Bank Corporation b) Find the names and cities of residence of all employees who work for First Bank Corporation c) Find the names, street address, cities of residence of all employees who work for bank and earn more than Rs. 10, 000 per annum. d) Find the names of all employees in this database who live in the same city as the company for which they work. e) Find the names of all employees who live in the same city and on the same street as do their managers. f) Find the names of all employees in this database who do not work for First Bank Corporation

employee (person_name, street, city) works (person_name, company_name, salary) Company (company_name, city) manages (person_name, manager_name) a) Find the names of all employees who work for First Bank Corporation Relation Algebra person_name ( company_name="First Bank Corporation” (works)) SQL Query SQL> Select person_name from works where company_name=“First Bank Corporation”;

employee (person_name, street, city) works (person_name, company_name, salary) Company (company_name, city) manages (person_name, manager_name) b) Find the names and cities of residence of all employees who work for First Bank Corporation Relation Algebra person_name, city ( company_name="First Bank Corporation” ^ employee. person_name=works. person_name (Employee X works)) SQL Query SQL> Select person_name, city from employee, works where company_name=“First Bank Corporation” and employee. person_name=works. person_name ;

employee (person_name, street, city) works (person_name, company_name, salary) Company (company_name, city) manages (person_name, manager_name) c) Find the names, street address, cities of residence of all employees who work for bank and earn more than Rs. 10, 000 per annum. Relation Algebra person_name, street, city ( company_name="First Bank Corporation” ^ Salary>10000 ^ employee. person_name=works. person_name (Employee X works)) SQL Query SQL> Select person_name, street, city from employee, works where company_name=“First Bank Corporation” and salary>10000 and employee. person_name=works. person_name ;

employee (person_name, street, city) works (person_name, company_name, salary) Company (company_name, city) manages (person_name, manager_name) d) Find the names of all employees in this database who live in the same city as the company for which they work. Relation Algebra person_name ( employee. city=company. city ^ employee. person_name =works. person_name^company_name=works. company_name (Employee X works X company)) SQL Query SQL> Select person_namefrom employee, works, company where employee. city=company. city and works. comapany_name = company_name;

employee (person_name, street, city) works (person_name, company_name, salary) Company (company_name, city) manages (person_name, manager_name) e) Find the names of all employees who live in the same city and on the same street as do their managers. Relation Algebra person_name ( employee. person_name=manges. person_name ^ company. city=employee. city (Employee X manages X company)) SQL Query SQL> Select person_name from employee , manages , company where employee. person_name=manages. person_name And company. city=employee. city;

employee (person_name, street, city) works (person_name, company_name, salary) Company (company_name, city) manages (person_name, manager_name) f) Find the names of all employees in this database who do not work for First Bank Corporation Relation Algebra person_name ( employee. person_name<> First Bank Corporation” (Works)) SQL Query SQL> Select person_name from works where company_name<> “First Bank Corporation”;
 Primary concepts of the relational database model
Primary concepts of the relational database model The limited tuple relational calculus equals:
The limited tuple relational calculus equals: Relational algebra and relational calculus
Relational algebra and relational calculus Relational algebra aggregate functions examples
Relational algebra aggregate functions examples Object relational and extended relational databases
Object relational and extended relational databases Relational algebra and relational calculus
Relational algebra and relational calculus Classification piaget
Classification piaget Database system concepts
Database system concepts Mapping of er model to relational model
Mapping of er model to relational model Hát kết hợp bộ gõ cơ thể
Hát kết hợp bộ gõ cơ thể Slidetodoc
Slidetodoc Bổ thể
Bổ thể Tỉ lệ cơ thể trẻ em
Tỉ lệ cơ thể trẻ em Chó sói
Chó sói Tư thế worm breton
Tư thế worm breton Chúa yêu trần thế
Chúa yêu trần thế Các môn thể thao bắt đầu bằng tiếng đua
Các môn thể thao bắt đầu bằng tiếng đua Thế nào là hệ số cao nhất
Thế nào là hệ số cao nhất Các châu lục và đại dương trên thế giới
Các châu lục và đại dương trên thế giới Cong thức tính động năng
Cong thức tính động năng Trời xanh đây là của chúng ta thể thơ
Trời xanh đây là của chúng ta thể thơ Mật thư anh em như thể tay chân
Mật thư anh em như thể tay chân 101012 bằng
101012 bằng Phản ứng thế ankan
Phản ứng thế ankan Các châu lục và đại dương trên thế giới
Các châu lục và đại dương trên thế giới Thơ thất ngôn tứ tuyệt đường luật
Thơ thất ngôn tứ tuyệt đường luật Quá trình desamine hóa có thể tạo ra
Quá trình desamine hóa có thể tạo ra Một số thể thơ truyền thống
Một số thể thơ truyền thống