Unit 26 Agriscience Animal anatomy physiology and Nutrition













- Slides: 25

Unit 26 Agriscience Animal anatomy, physiology, and Nutrition.

Feed costs are the highest costs incurred when feeding animals Nutrition is the science of supplying the correct amount of feed material so the Animal can grow, reproduce, work, or supply us with food. Poor nutrition in humans can lead to diseases or poor health. Poor nutrition in animals can lead to disease and poor health. These Conditions will cause the animal perform poorly making them more Costly to raise.

Ration: Is a specific amount and type of food fed to an animal to achieve A desired outcome. Many things influence the type of ration an animal needs. Age, production, gain desired, size, type of digestive system, and sex can affect the Animals needs. Balanced ration: Makes sure all of the animals needs are taken care of. Protein, Vitamins, Minerals, energy

Animal anatomy and physiology Physiology: Internal functions and vital processes of animal organs Body Systems Skeletal, muscular, circulatory, respiratory, nervous, Urinary, endocrine, digestive, and reproductive. Anatomy: The study of these systems and their components.

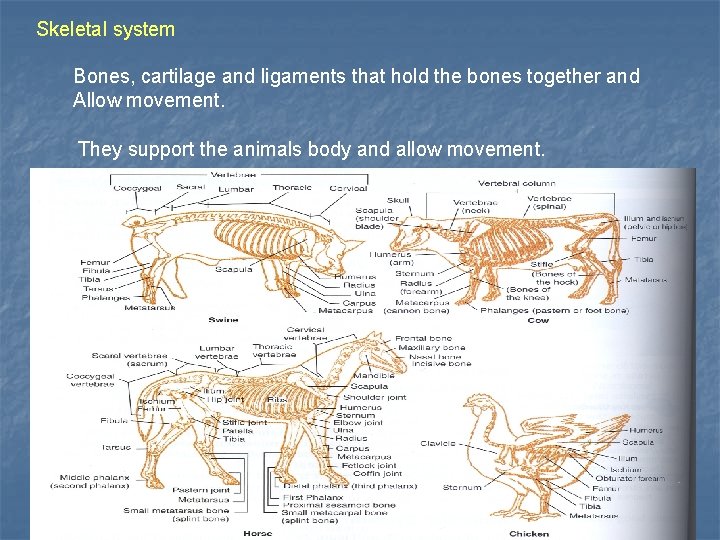
Skeletal system Bones, cartilage and ligaments that hold the bones together and Allow movement. They support the animals body and allow movement.

Many systems Work together Look at all the Parts that you Could memorize.

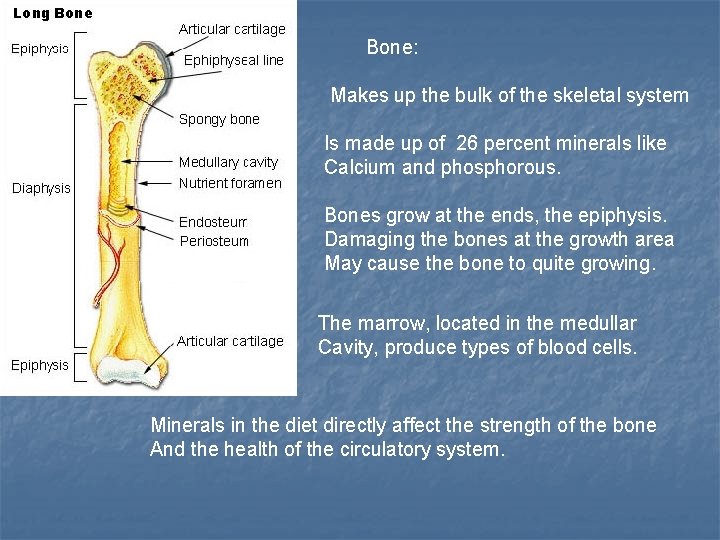
Bone: Makes up the bulk of the skeletal system Is made up of 26 percent minerals like Calcium and phosphorous. Bones grow at the ends, the epiphysis. Damaging the bones at the growth area May cause the bone to quite growing. The marrow, located in the medullar Cavity, produce types of blood cells. Minerals in the diet directly affect the strength of the bone And the health of the circulatory system.

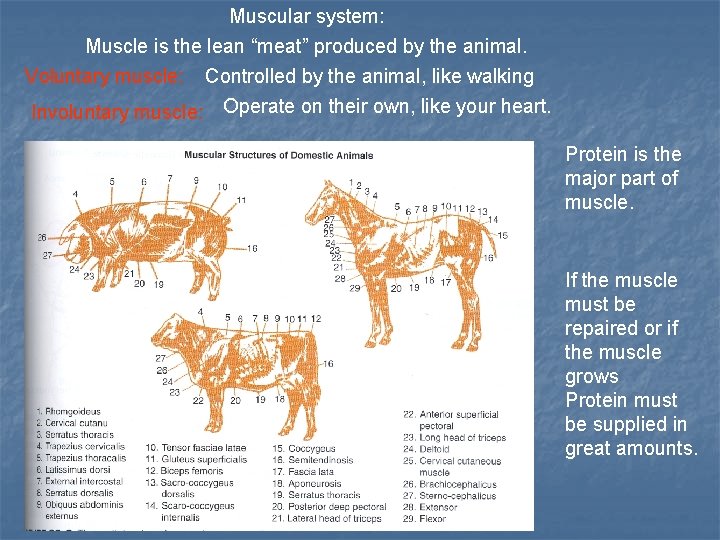
Muscular system: Muscle is the lean “meat” produced by the animal. Voluntary muscle: Controlled by the animal, like walking Involuntary muscle: Operate on their own, like your heart. Protein is the major part of muscle. If the muscle must be repaired or if the muscle grows Protein must be supplied in great amounts.

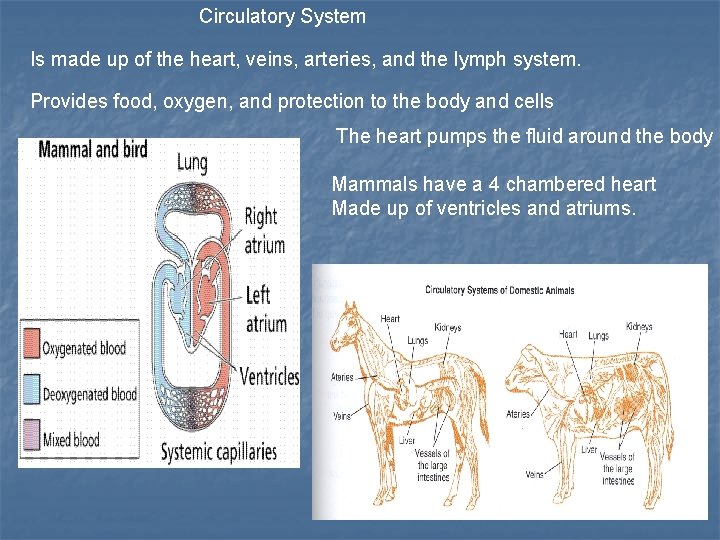
Circulatory System Is made up of the heart, veins, arteries, and the lymph system. Provides food, oxygen, and protection to the body and cells The heart pumps the fluid around the body Mammals have a 4 chambered heart Made up of ventricles and atriums.

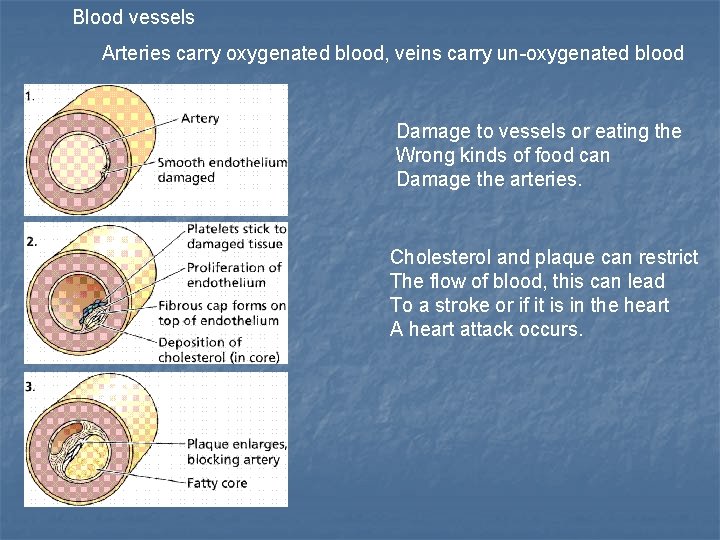
Blood vessels Arteries carry oxygenated blood, veins carry un-oxygenated blood Damage to vessels or eating the Wrong kinds of food can Damage the arteries. Cholesterol and plaque can restrict The flow of blood, this can lead To a stroke or if it is in the heart A heart attack occurs.

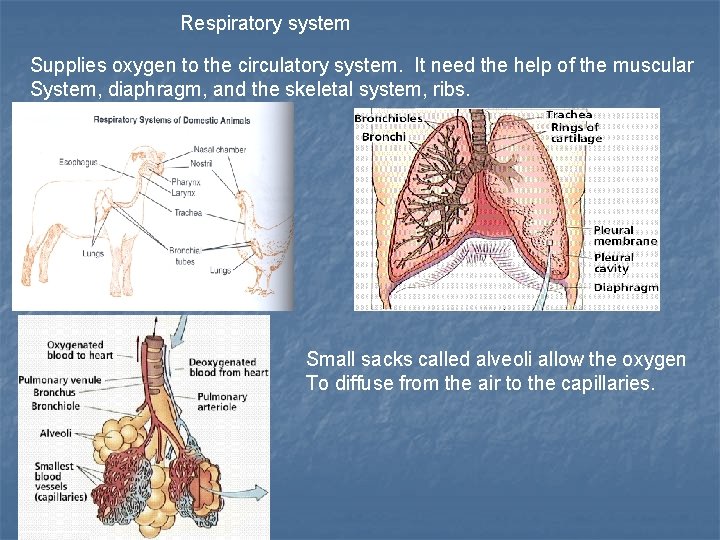
Respiratory system Supplies oxygen to the circulatory system. It need the help of the muscular System, diaphragm, and the skeletal system, ribs. Small sacks called alveoli allow the oxygen To diffuse from the air to the capillaries.

Respiratory system This shows all of the small passages In the human lung. This system must also Clean and warm the air. Most animals have a common Opening for the digestive and Respiratory systems. It divides At the Larynx.

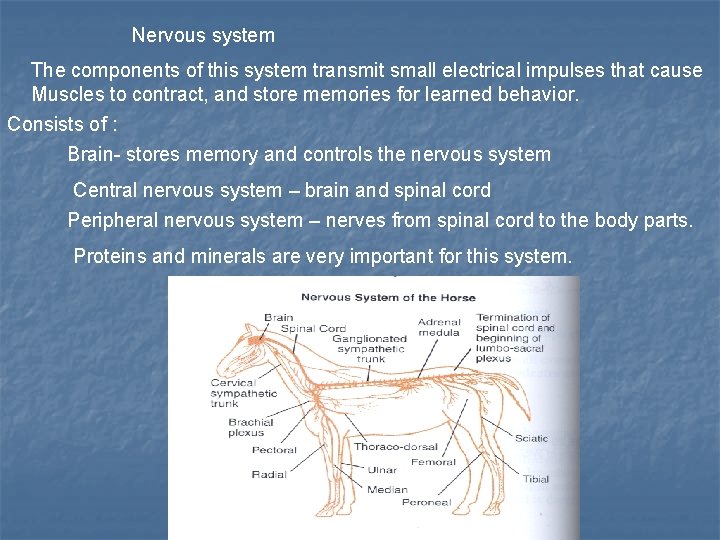
Nervous system The components of this system transmit small electrical impulses that cause Muscles to contract, and store memories for learned behavior. Consists of : Brain- stores memory and controls the nervous system Central nervous system – brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system – nerves from spinal cord to the body parts. Proteins and minerals are very important for this system.

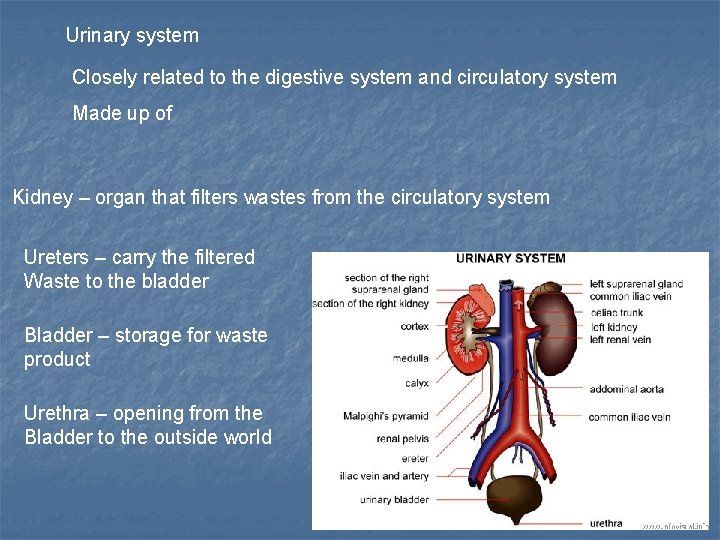
Urinary system Closely related to the digestive system and circulatory system Made up of Kidney – organ that filters wastes from the circulatory system Ureters – carry the filtered Waste to the bladder Bladder – storage for waste product Urethra – opening from the Bladder to the outside world

Endocrine system A group of ductless glands that release hormones into the blood stream. Hormones are chemicals that cause certain body parts to work Daylight, stimulation, and age can trigger the release of hormones. Oxytocin is a hormone that is released after giving birth in females. Sometimes not enough is release, the cow may not clean or let down Milk for the calf. Injecting the cow with oxytocin will make her clean out the afterbirth and She will be able to give the calf milk.

Digestive system Breaks down food into particles that the circulatory system can absorb And transport. The digestive system starts with the mouth and ends at the anus. There are three important digestive systems in farm animals Monogastric – one chambered system, like humans and pigs Require high quality feeds, few roughages. Animals are good at Converting food to muscle Polygastric – many chambered system, called ruminant digestive system Can use low quality feeds. A symbiotic relationship between bacteria And the cow. The bacteria also synthesizes some vitamins Avian – digestive system in birds Birds have no teeth so the digestive system must provide a means To break down the food.

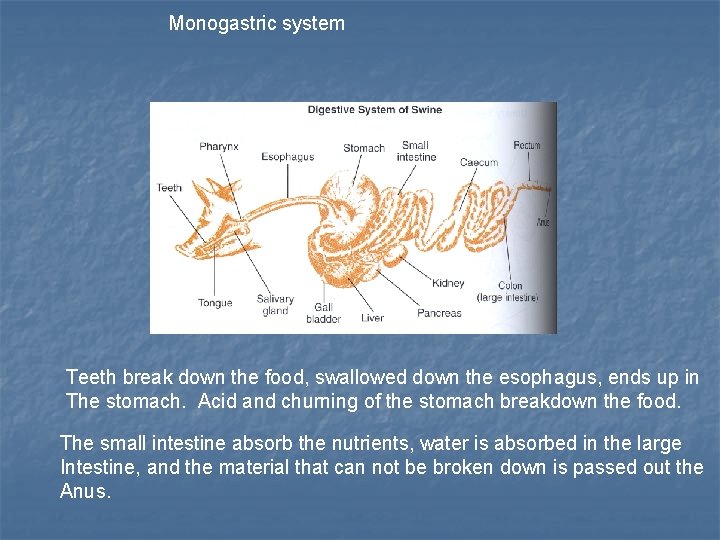
Monogastric system Teeth break down the food, swallowed down the esophagus, ends up in The stomach. Acid and churning of the stomach breakdown the food. The small intestine absorb the nutrients, water is absorbed in the large Intestine, and the material that can not be broken down is passed out the Anus.

Ruminant digestive system The mouth grinds, and the esophagus transports The food to the rumen. It passes by the reticulum Where heavy particles fall out. The rumen is a large Vat with bacteria in it. As they break down the material They create gas. The cow regurgitates some of the Material (chews her cud) and some gas escapes. After The material is done is passes to the omasum and Extra water is absorbed. It travels to the abomasum Where the bacteria is harvested by the acid in the stomach. Absorption is much like monogastrict animals

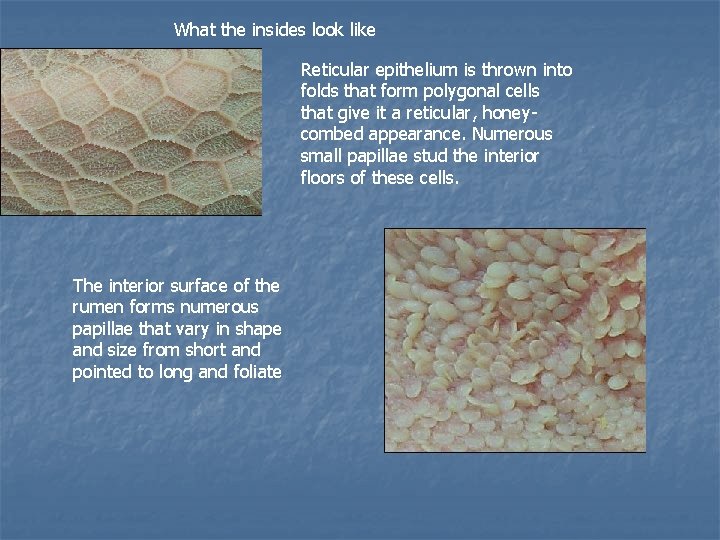
What the insides look like Reticular epithelium is thrown into folds that form polygonal cells that give it a reticular, honeycombed appearance. Numerous small papillae stud the interior floors of these cells. The interior surface of the rumen forms numerous papillae that vary in shape and size from short and pointed to long and foliate

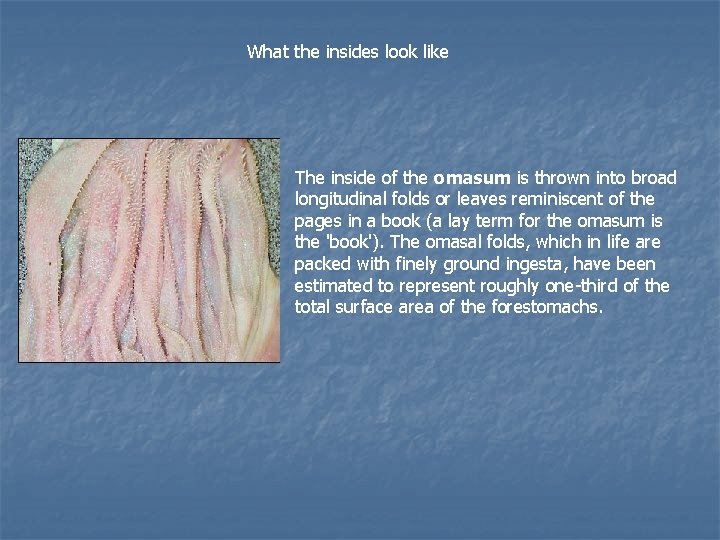
What the insides look like The inside of the omasum is thrown into broad longitudinal folds or leaves reminiscent of the pages in a book (a lay term for the omasum is the 'book'). The omasal folds, which in life are packed with finely ground ingesta, have been estimated to represent roughly one-third of the total surface area of the forestomachs.

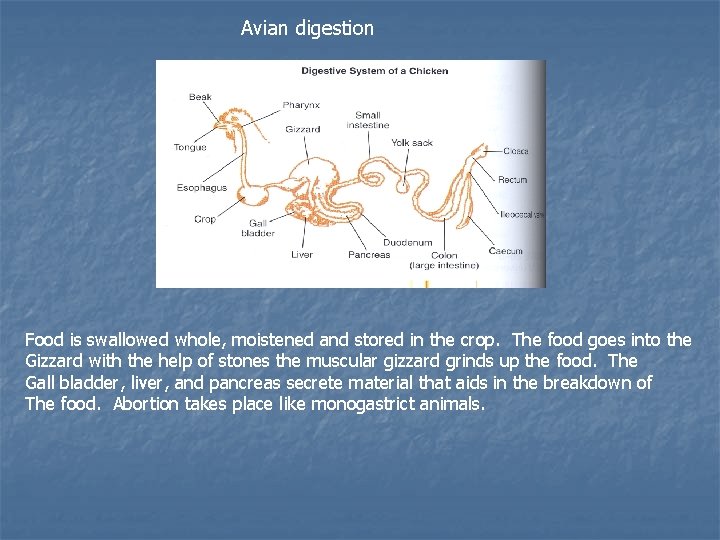
Avian digestion Food is swallowed whole, moistened and stored in the crop. The food goes into the Gizzard with the help of stones the muscular gizzard grinds up the food. The Gall bladder, liver, and pancreas secrete material that aids in the breakdown of The food. Abortion takes place like monogastrict animals.

Feed stuffs, or food for animals Water: Is one of the most important feeds for animals. It helps regulate Body functions, transports food, regulates heat. Potable water means the water is fit for human consumption, Livestock water does not necessarily need to be potable. Protein: Used by the body to repair tissue, growth, and production. Higher quality protein is needed by monogastrict animals. Ruminant animals can use a lower quality protein. Protein is made up of nitrogen containing amino acids.

Carbohydrates: Primarily made up of Carbon Hydrogen and Oxygen. They supply quick Energy for the animal. Sugars supply the quickest energy. Simple Sugars include glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) and fructose. Lactose is found in milk. Starches are carbohydrates that last longer in the body. Potatoes, wheat, and cellulose. Excess carbohydrates are stored as body fat! Fat has 2. 25 time the Energy as carbohydrates do. Minerals: Used by the body to build bones and in other processes. Lack of essential Minerals will cause the animal to do poorly or even die. Vitamins: Used by the body to speed up or change body processes. Some like Vitamin D are made by the animals skin when exposed to sunlight.

Feed additives: These can be vitamins, minerals, growth promotants, and Antibiotics that will help meet the needs of the animal and increase Productivity. Over use of antibiotics have cause problems , what are they? Feed in general Range along with minerals and vitamins usually provide animals with Enough of the nutrients needed. Feeding animals to gain fast requires the use of other feed stuffs such as Grains and maybe even animal protein. Be careful of animal protein Because of diseases such as BSE

Composition and classification of feed Composition is usually based on dry matter basis. Water is removed and Then the feed is analyzed for protein, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals Books will have the “average” composition of different feeds as well as the Requirements of different animals. If you want to know what your feed Has you will have to send it off to be analyzed. Classification of feeds is usually based on the Total Digestible Nutrients (TDN) in the food. How much of the feed, after the water has Been taken out, is totally used with no waste products produced. Concentrates Feeds that are high in protein, low in fiber, and high in TDN. Grains, by products from the milling and brewing industry, oil seeds By products of the sugar industry, and animal by products. Roughages Feeds that are high in fiber, lower in protein, and lower in TDN. Plant material such as grass, hay, and silage.
 Agriscience unit 26 self evaluation answers
Agriscience unit 26 self evaluation answers Unit 26 animal anatomy physiology and nutrition
Unit 26 animal anatomy physiology and nutrition Anatomy and physiology unit 7 cardiovascular system
Anatomy and physiology unit 7 cardiovascular system Anatomical position
Anatomical position Stomach
Stomach Animal systems agriscience project ideas
Animal systems agriscience project ideas Livestock breed identification: swine - vocabulary
Livestock breed identification: swine - vocabulary Unit 13 biological cultural and chemical control of pests
Unit 13 biological cultural and chemical control of pests Melways legend
Melways legend Agriscience unit 14 completion answers
Agriscience unit 14 completion answers Unit 2 better living through agriscience
Unit 2 better living through agriscience Parts of the upper respiratory tract
Parts of the upper respiratory tract Tattoo anatomy and physiology
Tattoo anatomy and physiology International anatomy olympiad
International anatomy olympiad Woody stem parts
Woody stem parts Bone metabolism
Bone metabolism Stomach ulcer
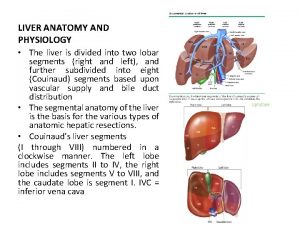
Stomach ulcer Liver anatomy and physiology
Liver anatomy and physiology Epigastric region
Epigastric region Hypogastric region
Hypogastric region Straw coloured fluid
Straw coloured fluid The central sulcus divides which two lobes? (figure 14-13)
The central sulcus divides which two lobes? (figure 14-13) Human anatomy and physiology seventh edition marieb
Human anatomy and physiology seventh edition marieb Http://anatomy and physiology
Http://anatomy and physiology Waistline
Waistline Appendicitis anatomy and physiology
Appendicitis anatomy and physiology