What is Solid State Physics Solid State Physics












- Slides: 14

What is Solid State Physics? ?

• Solid State Physics is about many different kinds of solids. • Semiconductors are a special category. • We'll discuss the microscopic physics of mostly, CRYSTALLINE solids, including metals, insulators, & semiconductors.

Decreasing Size The Structure of Physics Increasing Speed Large Size >> Atomic Size Small Size < ~ Atomic Size Low Speed High Speed v << c Classical Mechanics v<~c Special Relativity (Newton, Hamilton, Lagrange) (Einstein) Quantum Mechanics Relativistic Quantum (Schrodinger, Heisenberg) Mechanics (Dirac) Atomic Physics Quantum Field Quantum Theory Electrodynamics Molecular (Chemical) Physics Solid State Physics Nuclear & Particle Physics (Gluons, Quarks, Leptons, Strong Nuclear Force) Quantum Chromodynamics Feynman, Schwinger, Gell-Mann (Photon) (Weak Nuclear Force)

Decreasing Size The Structure of Physics Increasing Speed Large Size >> Atomic Size Small Size < ~ Atomic Size In this course, our focus will be here! Low Speed High Speed v << c Classical Mechanics v<~c Special Relativity (Newton, Hamilton, Lagrange) (Einstein) Quantum Mechanics Relativistic Quantum (Schrodinger, Heisenberg) Mechanics (Dirac) Atomic Physics Quantum Field Quantum Theory Electrodynamics Molecular (Chemical) Physics Solid State Physics Nuclear & Particle Physics (Gluons, Quarks, Leptons, Strong Nuclear Force) Quantum Chromodynamics Feynman, Schwinger, Gell-Mann (Photon) (Weak Nuclear Force)

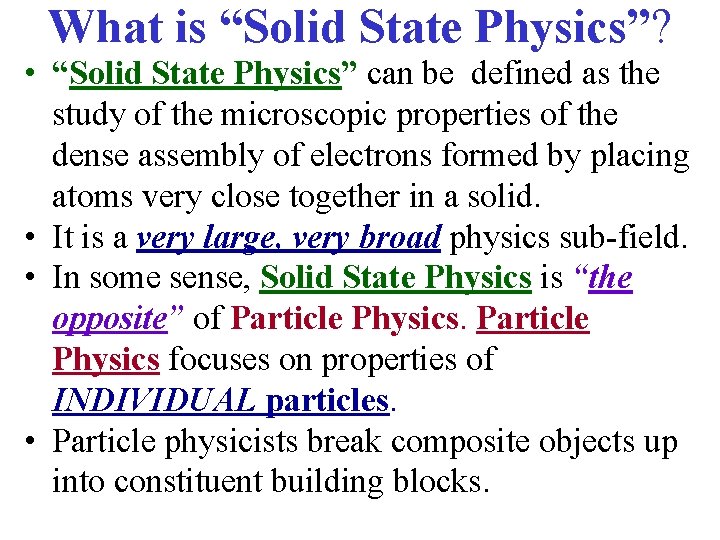
What is “Solid State Physics”? • “Solid State Physics” can be defined as the study of the microscopic properties of the dense assembly of electrons formed by placing atoms very close together in a solid. • It is a very large, very broad physics sub-field. • In some sense, Solid State Physics is “the opposite” of Particle Physics focuses on properties of INDIVIDUAL particles. • Particle physicists break composite objects up into constituent building blocks.

What is “Solid State Physics”? • Solid State Physics deals with the microscopic properties of large COLLECTIONS of particles. • Solid State physicists are interested in what fundamentally NEW PROPERTIES emerge when these building blocks are grouped together in various ways.

Motivations for the Study of Solid State Physics • There are Technological & Basic Physics motivations to study Solid State Physics. Technological Motivations • A very important motivation is that the microscopic properties Solid State Physics deals with are responsible for the majority of modern technology.

Motivations for the Study of Solid State Physics Technological Motivations • A very important motivation is that the microscopic properties Solid State Physics deals with are responsible for the majority of modern technology. • These properties determine the mechanical strength of materials, how they interact with light, how they conduct electricity, etc. • So, Solid State Physics is important for technology, because it gives guidance on the design of circuits needed for modern electronic devices. This field gave us the transistor & the semiconductor chip!

Technological Motivations This field gave us the transistor & the semiconductor chip! • So, Solid State Physics is traditionally linked to materials science, chemistry & engineering. • Recently, it has developed overlaps with biology, biochemistry, biotechnology & medicine. • So, many current research questions in Solid State Physics are still at the frontiers of applied science & next-generation technologies.

Basic Physics Motivations • A very important motivation to study Solid State Physics is that the fundamental physics needed to understand the microscopic properties of solids is very interesting. • To understand these properties, the ideas & methods of quantum mechanics must be used. The physics of solids is VERY deeply quantum mechanical.

Basic Physics Motivations • The physics of solids is VERY deeply quantum mechanical. • Solid State Physics has sometimes been called the best “laboratory” for studying subtle quantum mechanical effects. • This course may be a first chance for students to see quantum mechanical ideas & methods applied to cases where their technological consequences are so important.

• 2 examples (of MANY!) in which Solid State Physics discoveries have revealed very interesting, fundamental physics are the observations/explanations of 1. Superconductivity 2. The Fractional Quantum Hall Effect

1. Superconductivity 2. The Fractional Quantum Hall Effect • Both have exotic quantum mechanical explanations. • A very strong indicator that Solid State Physics has led (& continues to lead!) to the understanding of many very interesting basic physics phenomena is the fact that: More than 40% of Physics Nobel Prizes in the past 40 years & 50% of those in the past 10 years have been for work in Solid State Physics!!!!

 Solid physics
Solid physics Magnetism in solid state physics
Magnetism in solid state physics Philip hofmann solid state physics
Philip hofmann solid state physics Philip hofmann solid state physics
Philip hofmann solid state physics Solid
Solid Crystalline solid
Crystalline solid Solid state physics
Solid state physics Solid state physics
Solid state physics Drude model solid state physics
Drude model solid state physics Solid state physics
Solid state physics Solid
Solid Simulations for solid state physics
Simulations for solid state physics Understanding solid state physics
Understanding solid state physics Philip hofmann solid state physics
Philip hofmann solid state physics Crystalline solid and amorphous solid
Crystalline solid and amorphous solid