Algorithm and Flowchart for Quick Sort with implementation in Java
[20325 views]
What is Quick Sort Algorithm?
It is an algorithm of the type Divide & Conquer.
Divide stands for : Rearranging the elements and split arrays into two sub-arrays and an element in between search that each element in left sub array is less than or equal to the average element and each element in the right sub- array is larger than the middle element.
Conquer stands for : Recursively, sorting two sub arrays.
Combine stands for: Combining the already sorted array.
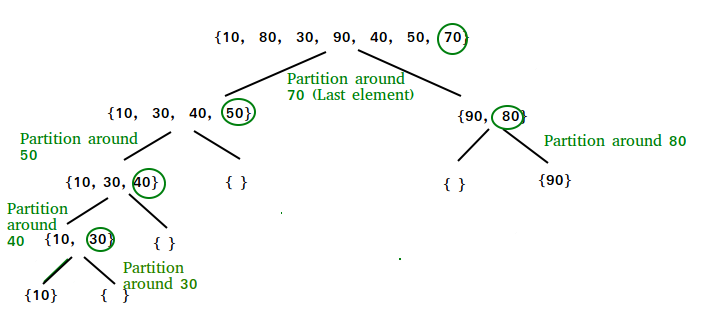
Image Reference: Geeks for Geeks
Quick Sort Flowchart:

Image Reference: Geeks for Geeks
Quick Sort PseudoCode:
Partition Pseudocode below rearranges the sub arrays in a place.
Quick Sort Implementation in Java:
Output:
Want to Learn How to write own Algorithm and Flowcharts
Want to test your logical skills in Algorithms?
AI Powered Search Engine:
Comments
Search Anything:
Interesting Technical Quizzes:
Search Tags
Quick Sort algorithm explanation
Java Program for Quick Sort Algorithm
Flowchart for Quick Sort
You Might Also Like
- Algorithm and flowchart to check whether two numbers are coprime or not
- Algorithm and Flowchart for Armstrong Number
- Algorithm and Flowchart to check whether an array is mirror inverse or not
- Algorithm and Flowchart to Count no. of Vowels, Consonants and Special Character in a string
- Algorithm and Flowchart to find the power of 2
 6 Upvotes
6 Upvotes 4 Downvotes
4 Downvotes