
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
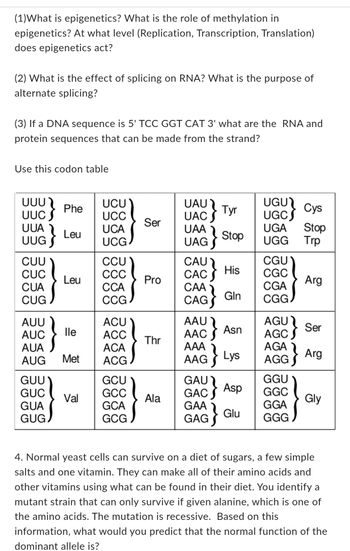
Transcribed Image Text:**Section on Epigenetics, RNA Splicing, and Genetic Translation**
**1. Understanding Epigenetics**
- **Definition:** Epigenetics involves the study of changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the underlying DNA sequence. These changes can affect how cells read genes.
- **Role of Methylation:** Methylation is a key epigenetic mechanism where methyl groups are added to DNA. This often modifies the expression of genes and can turn genes on or off.
- **Level of Action:** Epigenetics primarily acts at the level of transcription, influencing whether a gene is expressed or silenced.
**2. Impact of Splicing on RNA**
- **Function of Splicing:** Splicing is a process during RNA processing where introns (non-coding regions) are removed, and exons (coding sequences) are joined.
- **Purpose of Alternate Splicing:** Alternate splicing enables a single gene to code for multiple proteins by varying the combination of exons in the final mRNA.
**3. Translating DNA to Proteins**
- **Given DNA Sequence:** 5' TCC GGT CAT 3'
- **RNA and Protein Sequences:**
- **RNA Transcription:** The sequence is transcribed to 3' AGG CCA GUA 5' (RNA: AGG CCA GUA).
- **Using the Codon Table:**
- **Codons:**
- AGG - Arg (Arginine)
- CCA - Pro (Proline)
- GUA - Val (Valine)
**Codon Table Explanation**
- The table is a visual representation of the genetic code, showing which triplets of RNA bases (codons) correspond to which amino acids or functions (e.g., start, stop).
- Codons are grouped into categories based on the first base of the triplet, and each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, listed using standard abbreviations (e.g., Phe for Phenylalanine, Leu for Leucine).
**4. Yeast Mutation Analysis**
- **Scenario Overview:** Normal yeast can synthesize all necessary amino acids and vitamins from a basic diet. A discovered mutant strain requires external alanine supplementation due to a recessive mutation.
- **Predicting the Function of the Dominant Allele:** Given the mutant's reliance on external alanine, the dominant allele likely codes for an enzyme required for
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the function of RAG1? What will happen if RAG1's function is lost due to mutations?arrow_forwardWhat are the Results of tra splicing when Sxl protein is present?arrow_forwardIn the early 1960's scientists knew the structure of DNA, however they didn't know how it coded for the expression of proteins. To find out, American Biochemist, Marshall Nirenberg did an experiment and figured out the first codon! To begin he made a solution of Uracil (U), and linked the nucleotides together to form a synthetic RNA molecule which read-UUUUUUU... etc. Therefore, no matter where the message started or stopped, the codon triplets always read UUU, UUU, UUU. Next, he added the poly-U chain to a solution of ribosomes and other ingredients needed for polypeptide synthesis. The result was a polypeptide containing the amino acid phenylalanine. Thus, Niernberg learned that the RNA codon UUU specifies the amino acid phenylalanine. What is the central theme of molecular genetics? Now let's look at the entire process of taking DNA and creating Proteins from that code: Say we have the following nucleotide chain in DNA: T-A-C-T-A-G-C-G-G-A-T-A-G-C-A-T-C-C-C-G-G-G-A-T-A-T-T DNA What…arrow_forward
- Which DNA strand will serve as the template strand during the transcription of the RNA-coding sequence?arrow_forwardRNA polymerases generally require a primer to begin transcription. (T) (F) The Death Cap Mushroom Amanita phalloides is toxic because of its ability to produce alpha-amanitin, which is an inhibitor of RNA Polymerases I and III. (T) (F) In bacteria, transcription and translation can occur simultaneously. (T) (F) In eukaryotes, transcription and translation can occur simultaneously (T) (F) RNA polymerase II has no form of proofreading activity. (T) (F) Sigma factors specify binding of bacterial RNA Polymerases to specific promoters (T) (F) An E. coli strain with mutations in genes encoding both the dam methylase and the RecA protein would likely be inviable (dead) (T) (F) An E. coli culture grown in a pure (100%) N2 atmosphere would likely have a lower rate of mutations than a culture grown under normal conditions (~30% O2 and 70% N2) (T) (F) Non-homologous end joining repairs double strand DNA breaks with no loss of information, restoring the original…arrow_forwardWhat percent of the transcription in a human cell makes protein-coding RNA, and what percent of transcription makes non-coding RNA?arrow_forward
- Which is the expected outcome following the deacetylation of histones? a) Coiling of chromatin, preventing it from being accessed by transcriptional machinery b) Coiling of chromatin, allowing it to be accessed by transcriptional machinery c) Uncoiling of chromatin, preventing it from being accessed by transcriptional machinery d) Uncoiling of chromatin, allowing it to be accessed by transcriptional machineryarrow_forwardConsider the mechanism of the enzyme RNase: What would happen to the Km (i.e., would it increase, decrease, or stay the same) if the his12 was mutated to a lysine? Explain. What would happen to the Kcat (i.e., would it increase, decrease, or stay the same) if the his12 was mutated to a valine? Explain.arrow_forwardUsing the transcription unit diagrammed below, in which exons are represented by blue boxes and introns are represented by the connecting lines. You discover a single base deletion in region E of this DNA sequence. Regarding transcription, this mutation will likely: 1.) Result in an alteration to the mRNA sequence. 2.)Have no effect on transcription or the mRNA sequence 3.)Prevent transcription at the TATAA box 4.) Result in an increase or decrease in the amount of mRNA transcribedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education