Which of the following is a characteristic of monocotyledons?
Two cotyledons
Vascular bundles in a ring
Parallel leaf venation
Flower parts in multiples of four or five

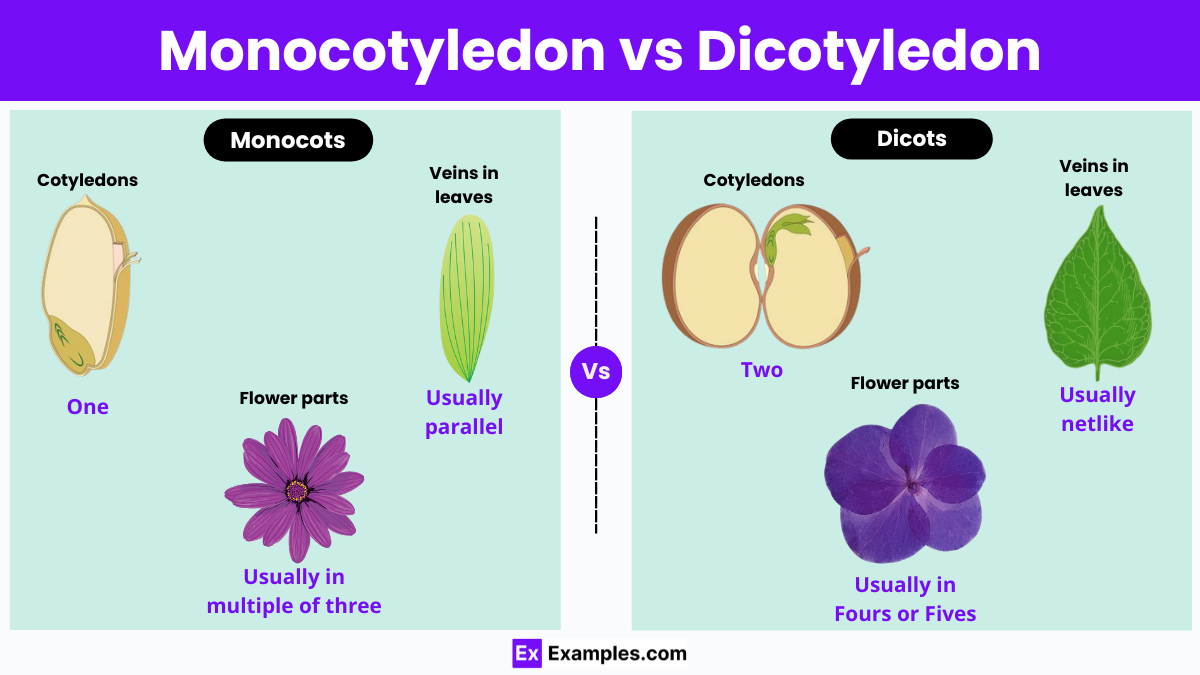
Flowering plants, or angiosperms, are the most diverse group in the plant kingdom, predominantly categorized into monocots and dicots. This classification stems from the number of cotyledons, or seed leaves, present in the embryo—monocots have one, while dicots have two. This initial difference influences their entire structure and development, affecting roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. In this article, we will explore these distinctions and their implications for the plants’ growth and ecological roles.
Monocotyledons, commonly referred to as monocots, are plants that start their life with a single seed leaf known as a cotyledon. This characteristic shapes their growth, resulting in unique features such as fibrous root systems that spread horizontally, providing stability and efficient nutrient absorption in surface soil layers. Monocots also have vascular tissues scattered throughout their typically hollow and flexible stems, which contribute to their ability to thrive in various environmental conditions. Additionally, their leaves feature parallel veins that facilitate rapid growth and effective water transport. Flower structures in monocots are distinctive, usually having petals that appear in multiples of three, which is essential for specific pollination strategies.
Dicotyledons, or dicots, begin their development with two seed leaves, leading to a different set of structural characteristics. These plants usually develop a taproot system with a main, deep-penetrating root that helps in stabilizing the plant and accessing water from deeper layers of the soil. Smaller lateral roots complement this, enhancing nutrient uptake. In dicots, the stem organizes the vascular tissues in a ring, providing robust support for larger plant structures such as branches and broad leaves with branching veins. This vein arrangement supports a wider leaf area, optimizing photosynthesis. Dicots typically produce flowers with petals in groups of four or five, aiding in their identification and reproductive processes. The understanding of these differences is crucial in agriculture and horticulture, influencing everything from the selection of herbicides to the choice of plants for specific environmental conditions.

| Feature | Monocotyledon (Monocots) | Dicotyledon (Dicots) |
|---|---|---|
| Seed | One cotyledon (seed leaf) | Two cotyledons |
| Leaf Veins | Parallel veins | Net-like, branched veins |
| Root System | Fibrous root system (many thin roots) | Taproot system (main root with smaller offshoots) |
| Floral Parts | Floral organs usually in multiples of 3 | Floral organs usually in multiples of 4 or 5 |
| Vascular Bundles | Scattered throughout the stem | Arranged in a ring around the stem |
| Pollen Structure | Single furrow or pore | Three furrows or pores |
| Stem Growth | Primary growth only; typically no secondary growth | Both primary and secondary growth |
| Leaf Shape | Generally narrow and elongated | Wide variety of shapes |
| Wood Formation | Absence of true wood | Presence of true wood, formed by secondary growth |
| Stem Type | Generally soft and herbaceous | Can be woody or herbaceous |
| Germination | Cotyledon usually stays underground | Cotyledons emerge above the ground |
| Photosynthesis | Mostly in leaves | In leaves, stems, and sometimes cotyledons |
Monocotyledons have one seed leaf, while dicotyledons have two, affecting root, stem, and leaf development.
Identify a monocot by its single seed leaf, parallel leaf venation, and fibrous root system.
Grass is a monocot, characterized by its parallel leaf venation and fibrous roots.
Banana is a monocot, noted for its single cotyledon, parallel leaf veins, and clustered flower structure.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is a characteristic of monocotyledons?
Two cotyledons
Vascular bundles in a ring
Parallel leaf venation
Flower parts in multiples of four or five
Which type of plant has a taproot system?
Monocotyledon
Dicotyledon
Both monocotyledon and dicotyledon
Neither
Which of the following plants is a monocot?
Rose
Sunflower
Corn
Maple
How are the vascular bundles arranged in the stem of a dicotyledon?
Scattered throughout the stem
In a ring
Randomly
None of the above
What type of leaf venation is found in dicotyledons?
Parallel
Spiral
Reticulate (net-like)
None
Which of the following is NOT a feature of dicotyledons?
Two cotyledons
Flower parts in multiples of three
Reticulate venation
Vascular bundles in a ring
Which plant part is most indicative of monocotyledon classification?
Root system
Leaf venation
Number of cotyledons
Type of flowers
Which of the following trees is a dicotyledon?
Palm tree
Bamboo
Oak tree
Sugarcane
In monocotyledons, the vascular bundles in the stem are:
Arranged in a ring
Scattered throughout
Absent
Arranged in rows
The flowers of monocotyledons typically have parts in multiples of:
Two
Four
Five
Three
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

