Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Complementary and Supplementary Angles are the pairs of angles whose sum is 90° and 180° respectively. Complementary angles are pairs of angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees. In other words, when you have two complementary angles, the sum of their measures equals a right angle.
Supplementary angles are nothing but when the sum of two angles is equal to the straight line angle or 180 degrees. Supplementary angles are frequently encountered in various geometric shapes, such as parallelograms and straight lines.
In this article, we will learn about, supplementary angles and complementary angles, their definition and types how to find the complementary and supplementary angles along with their differences, and some practice questions on them.
Table of Content
- Definition of Angle
- Complementary Angles
- How To Find Complementary Angle?
- Supplementary Angle
- How to Find Supplementary Angle?
- Adjacent Supplementary Angles and Complementary Angles
- Complementary Angles and Supplementary Angles Theorem
- Difference Between Supplementary Angles and Complementary Angle
- Real-Life Examples of Complementary Angles and Supplementary Angles
- Example Problems on Supplementary and Complementary Angles
- Practice Questions on Complementary Angles and Supplementary Angles
Definition of Angle
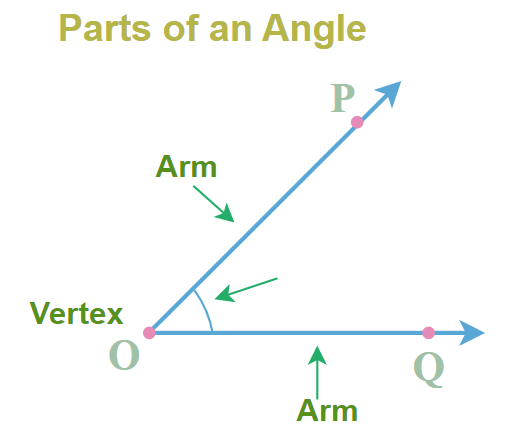
An angle is nothing but a measure of the degree of rotation around a point, line, or plane. The two lines that are joined to form the angles are called "Arms of Angle" and the point where they meet is called Vertex. The image added below shows parts of the angles,
Angle is either measured in degree or in radian.
Types of Angles
There are mainly 7 types of angles and they are as follows:
- Zero Angle: The angle whose measure is 0 degree is called Zero Angle
- Acute Angle: An acute angle is an angle that measures less than 90 degrees.
- Obtuse Angle: An obtuse angle is an angle that measures between 90 and 180 degrees.
- Right Angle: A right angle is a 90-degree angle that forms a perfect L shape.
- Straight Angle: An angle that measures 180 degrees.
- Reflex Angle: A reflex angle is an angle that measures between 180 and 360 degrees.
- Complete Angle: An angle that measures 360 degrees.
Various types of Angles are added in the image below,

Complementary Angles
Complementary angles in geometry refer to two angles that together measure 90 degrees, i.e. complementary angles sums up to a right angle.
∠A + ∠B = 90°
Different real-world entities have complementary angles. Take, for example, a door and its frame. Let's imagine the door swings open to a given angle, say 60 degrees. On the other side, the angle between the door and the door frame will be 30 degrees.
How To Find Complementary Angle?
To find the complementary angle of a given angle, you can use the fact that the sum of the measures of complementary angles is always 90 degrees. Here are the steps to find the complementary angle:
Step 1: Identify Given Angle
Start by identifying the angle for which you want to find the complementary angle. Let's call this angle "A."
Step 2: Use Complementary Angle Definition
Recall that complementary angles add up to 90 degrees. The complementary angle to angle A, let's call it "B," can be found using the equation: A+B=90∘
Step 3: Solve For Complementary Angle
Rearrange the equation to solve for the complementary angle B = 90 - A
Let us understand the concept with the help of example.
Example: Find Complementary Angle of 40°.
Suppose there is one angle given i.e. 40°.
Now use the definition of complementary angle i.e. A + B = 90°.
So the other angle will be 90 - 40 i.e. 50°.
Supplementary Angle
Supplementary angles in geometry refer to two angles that together measure 180 degrees, i.e. Supplementary angles sums up to a straight angle.
∠A + ∠B = 180°
If the sum of two angles is equal to 180 degrees or the straight line angle then it is known as the Supplementary angle. Supplementary angles are frequently encountered in various geometric shapes, such as parallelograms and straight lines.
Imagine two intersecting streets forming a straight angle. This angle ensures smooth traffic flow and optimal space utilization. Without the clear separation provided by the straight angle, chaos would ensue. Let's also consider the angle formed by the minute and hour hands of a clock at 6 o'clock. The hands are perfectly aligned, measuring a straight angle of 180 degrees. This helps us distinguish the exact time
How to Find Supplementary Angle?
To find the supplementary angle of a given angle, you can use the fact that the sum of the measures of supplementary angles is always 180 degrees. Here are the steps to find the supplementary angle:
Step 1: Identify Given Angle
Start by identifying the angle for which you want to find the supplementary angle. Let's call this angle "A."
Step 2: Use Supplementary Angle Definition
Supplementary angles add up to 180 degrees. The supplementary angle to angle A, let's call it "B," can be found using the equation: A+B=180
Step 3: Solve For Supplementary Angle
Rearrange the equation to solve for the supplementary angle (B) i.e. B = 180 - A.
Example: Find Supplementary Angle of 90°.
Let us understand the concept with the help of example.
Suppose there is one angle given i.e. 90°.
Now use the definition of supplementary angle i.e. A+B = 180°.
So the other angle will be 180 - 90 i.e. 90°.
Adjacent Supplementary Angles and Complementary Angles
Adjacent Supplementary angles are two angles that share a common vertex and a common side but do not overlap. They are placed next to each other, forming an adjacent pair and their combined measure equals 180∘.
Adjacent Complementary angles are two angles that share a common vertex and a common side. They are placed next to each other, forming an adjacent pair and their combined measure equals 90∘.
Complementary Angles and Supplementary Angles Theorem
Complementary and Supplementary Angles theorem are added below,
Complementary Angle Theorem
Complementary Angle Theorem states that if the sum of the measures of two angles is 90 degrees, then the angles are complementary.
Proof:
- Let ∠x and ∠y be two angles such that ∠x + ∠y = 90°.
- By definition, complementary angles are two angles whose sum is 90°. Therefore, if ∠x + ∠y = 90°, it follows that ∠x and ∠y are complementary.
Thus, we have shown that if the sum of two angles is 90 degrees, then those two angles are complementary, which proves the Complementary Angle Theorem.
Supplementary Angle Theorem
Supplementary angle theorem states that if two angles are supplementary to the same angle, then the two angles are said to be congruent.
Proof:
If ∠x and ∠y are two angles that are supplementary to a third angle ∠z, then,
∠x + ∠z = 180 ……. (1)
∠y + ∠z = 180 ……. (2)
Then, from the above equations, we can conclude,
∠x = ∠y
Hence Proved
Difference Between Supplementary Angles and Complementary Angle
Difference between complementary and supplementary angles are added in the table added below,
Feature | Complementary Angles | Supplementary Angles |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Pairs of angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees. | Pairs of angles whose measures add up to 180 degrees. |
Sum of Measures | Sum of measures adds up to 90 degrees. | Sum of measures adds up to 180 degrees. |
Symbolic Representation | ∠A + ∠B = 90° | ∠A + ∠B = 180° |
Common Use | Useful in solving problems involving right angles or perpendicular lines. | Used to solve problems involving straight lines or forming a half-circle. |
Real-Life Examples of Complementary Angles and Supplementary Angles
Various examples of Complementary and Supplementary Angles are added below,
- Straight Line Segment: A straight-line segment can be considered as having two pairs of complementary angles because any two adjacent angles formed by a line segment and a line can be complementary as they add up to 90 degrees.
- Right Triangle: In a right triangle, the two angles adjacent to the right angle are complementary. This is because the sum of the two acute angles in a right triangle is always 90 degrees.
- Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has three pairs of complementary angles. Each pair consists of three internal angles that add up to 180 degrees, making them supplementary to each other.
- Rectangle: In a rectangle, two pairs of complementary angles can be found, where opposite sides are parallel. This is because the adjacent angles formed by intersecting lines, such as the diagonals of a rectangle, are complementary.
Read More,
Example Problems on Supplementary and Complementary Angles
Example 1: If Angle P is 35 degrees, what is the measure of its complementary angle.
Solution:
Angle P + Angle Q = 90°
Given,
- ∠P = 35°
So, 90° - 35° = 55°
Example 2: In a right-angled triangle, one angle measures 60 degrees. What is the measure of the other angle, which is complementary to the given angle?
Solution:
Angle P + Angle Q = 90
Given,
- ∠P = 60°
So 90 - 60 = 30°
Example 3: If Angle X is 110 degrees, what is the measure of its supplementary angle?
Solution:
Angle X + Angle Y = 180
Given,
- ∠X = 110°
So, 180 - 110 = 70°
Example 4: In a straight line, one angle measures 75 degrees. What is the measure of the other angle, which is supplementary to the given angle?
Solution:
Angle X + Angle Y = 180
Given,
- ∠X = 75°
So 180 - 75 = 105°
Example 5: If the measure of an angle is 1/3 of its complementary angle, find the measures of both angles.
Solution:
Let the measure of the angle be x.
According to given information, measure of complementary angle would be 3x because it's three times measure of angle.
Sum of measures of complementary angles is 90 degree:
x + 3x = 90
4x = 90
So, x = 22.5
So, measure of angle is 22.5 and measure of its complementary angle is 3 x 22.5 = 67.5 degree.
Practice Questions on Complementary Angles and Supplementary Angles
Q1. If Angle X is 50 degrees, find the measure of its complementary angle.
Q2. In a right-angled triangle, one angle measures 35 degrees. Determine the measure of its complementary angle.
Q3. If Angle P is 130 degrees, what is the measure of its supplementary angle?
Q4. In a straight line, one angle measures 85 degrees. What is the measure of the other angle, which is supplementary to the given angle?
Q5. If Angle Y is complementary to Angle Z, and the measure of Angle Y is 25 degrees, what is the measure of Angle Z?
Answers to Practice Questions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ans 1. 40° | Ans 2. 55° | Ans 3. 50° | Ans 4. 95° | Ans 5. 65° |
Complementary and Supplementary Angles - FAQs
What are Complementary Angles?
Complementary angles are pairs of angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees. In other words, when you have two angles that are complementary, the sum of their measures equals a right angle (90 degrees).
What are Supplementary Angles?
Supplementary angles are pairs of angles whose measures add up to 180 degrees. When two angles are supplementary, their combined measures equal a straight line (180 degrees).
How do you Find the Complementary Angle of a Given Angle?
To find complementary angle of a given angle, subtract the given angle's measure from 90 degrees. The result is the measure of the complementary angle.
How do you Find the Supplementary Angle of a Given Angle?
To find supplementary angle of a given angle, subtract the given angle's measure from 180 degrees. The result is the measure of the supplementary angle.
Which Angle is Supplementary?
Two angles are supplementary if the sum of their measures is 180 degrees.
What are Complementary Angles for Kids?
Complementary angles are pairs of angles that add up to 90 degrees.
What is the Complementary Angle of 55 degrees?
Complementary Angle of 55 degrees is 35 degrees.




