Food chain represents the direction of the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem. It consists of four main components producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and decomposers. Based on the primary source of energy there are two types of food chain: Grazing and the Detritus food chain. It makes us understand the interaction among the species, the interdependence of organisms in nature, and how energy is transferred from one level to the next, sustaining life within an ecosystem.
Definition of Food Chain
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where each organism serves as a source of food for the organism at the next trophic level, demonstrating the transfer of energy and nutrient in an ecosystem.
What is Food Chain?
A food chain represents the flow of energy and nutrients among different organisms in an ecosystem. It tells us how energy and nutrients are transferred from one trophic level to another and how the organisms interact in an ecosystem. In a food chain, each organism represents a particular trophic level according to its food behavior.
- Producers are living organisms that produce their own food by utilizing solar energy through the photosynthesis process. For example, plants, green growth, etc.
- Consumers are living organisms that cannot produce their own food and obtain energy by consuming other organisms. For example, lions, tigers, wolves, foxes, etc.
- Decomposers are the organisms that breaks down dead organic matter and recycles nutrients back into the ecosystem. They are present at the last stage of the food chain, that breaks down waste and remains from all other trophic levels. For example, bacteria and fungi.
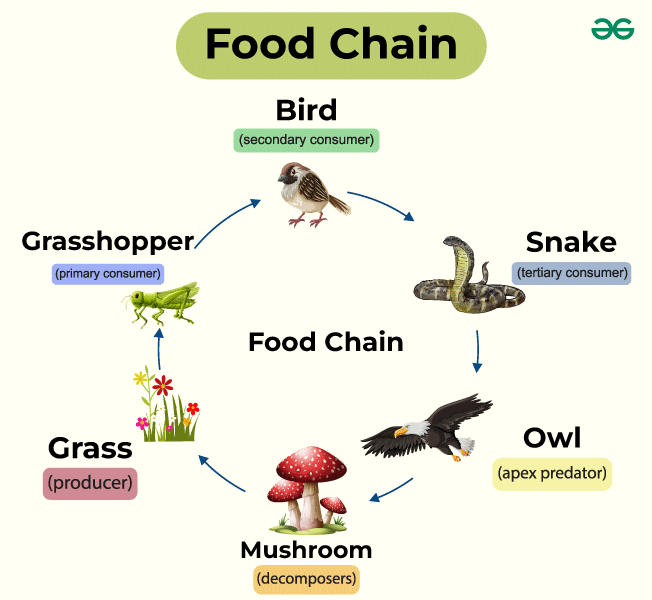
Food Chain Diagram
The diagram showing the labeled diagram of food chain is given below:
Food Web
A food web is a complex, interconnected network of multiple food chains within an ecosystem, representing the various paths through which energy and nutrients flow as organisms interact with one another. All the organisms in the trophic level, including predators, prey, and scavengers, interact within this food web, which influences the population dynamics. Decomposers break down dead matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. Each level in the food web depends on the lower level for energy and nutrients. Change in one trophic level impacts the other tropic levels or the whole food web. It shows the dependency of one trophic level on one another and the importance of biodiversity.
Types of Food Chain
Food chains are of two types on the basis of the primary energy source: Detritus and Grazing Food chain.
Detritus Food Chain
Detritus food chain is one of the types of the food chain. Detritus food chain begins with dead organisms. Dead organisms in the detritus food chain are decomposed or get mixed with soil with the help of microorganisms. Organisms or living being which feed on dead organisms is called detritivores or decomposers.

Characteristics of Detritus Food Chain
The characteristics of Detritus food chain are as follows:
- Photosynthesis does not happen in the detritus food chain.
- It has a continuous flow of energy.
- Dead organisms are the first food for the other animals.
- This type of food chain happens rarely in the presence of sunlight.
- This food chain helps in minimizing the waste and maximizing the use of waste dead content.
Uses of Detritus Food Chain
- This food chain is used to dissolve inorganic nutrients.
- Detrivores’ excreted products are used by other organisms present in the detritus food chain.
Importance of Detritus Food Chain
The Detritus food chain is essential for nutrient recycling in ecosystems, breaking down dead organic matter through decomposers, enriching soil fertility, and supporting plant growth. It plays a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem health and balance by preventing the accumulation of organic debris.
Grazing Food Chain
The grazing food chain is one of the types of food chain mentioned above. This food chain starts with plants that prepare food for themselves by the process of photosynthesis as well as for other living beings. Food prepared by the plant is eaten by herbivores(those who eat only plants), herbivores are eaten by the omnivores( those who eat both herbivores and plants), and omnivores are eaten by the carnivores( those who eat only meat like a lion).
Types of Grazing Food Chain
There are two type of grazing food chain that are as follows:
- Parasitic food chain: In this type, the energy and nutrients flow from plants to herbivores (primary consumers) and then to predators (secondary consumers), illustrating the consumption of herbivores by carnivores.
- Predator food chain: This type involves the direct consumption of plants (producers) by herbivores (primary consumers), showcasing the transfer of energy and nutrients without an intermediate predator level.
Characteristics of Grazing Food Chain
The characteristics of grazing food chain are as follows:
- The grazing food chain mainly depends on the sun which is the single energy source for the plants to prepare food.
- In this food chain, microscopic organisms are a part of the Grazing food chain as decomposers.
- This food chain helps the environment by adding energy to the environment by fixing inorganic nitrogen in the soil.
Uses of Grazing Food Chain
Various uses of the Grazing food chain are as follows:
- It help in understanding energy flow and nutrient dynamics in ecosystems, highlighting the relationships between plants, herbivores, and predators.
- It is essential for maintaining biodiversity, managing wildlife populations, and informing conservation strategies.
Importance of Grazing Food Chain
Importance of the Grazing food chain are as follows:
- The Grazing food chain is important for maintaining ecosystem dynamics as it regulates population sizes, maintains biodiversity.
- It facilitates the efficient transfer of energy and nutrients through trophic levels.
- It also plays a key role in shaping community structures and influencing the overall balance and stability of ecosystems.
Difference Between Food Chain and Food Web
The differences between Food Chain and Food Web are as follows:
| Features |
Food Chain |
Food Web |
| Definition |
It represents a linear sequence of organisms where each feed on the one below |
It represents the complex interconnection of multiple food chains within an ecosystem. |
| Structure |
Single direction of energy flow |
Interconnected food chain representing multiple pathways. |
| Trophic Levels |
Includes a few trophic levels. |
Includes multiple trophic levels. |
| Interactions |
Represents one feeding relationship. |
Represents multiple feeding relationships. |
| Energy Flow |
Energy flows in a single direction through levels. |
Energy flows in multiple directions. |
| Examples |
Grass → Rabbit → Fox Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Fish |
Plants → Herbivores → Carnivores → Decomposers → Multiple species interactions |
| Importance |
Helpful for understanding energy flow in a simplified manner. |
Essential for studying ecosystem stability, species relationships, etc. |
Importance of Food Chain
Some of the importace of the food chain are as follows:
- It represent the flow of energy and nutrients through different trophic level.
- It plays an important role in recycling nutrients as decomposers breaks down organic matter and return the nutrient to the soil.
- Food chains help regulate species populations by demonstrating the predator-prey relationships that prevent overpopulation and maintain ecosystem balance.
- The interconnected relationships in food chains promote biodiversity and the role played by different species in maintaining ecosystem balance.
Also Read:
FAQs on Food Chain
1. What is a Food Chain?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms representing different trophic level. It represents the flow of nutrients and energy through theses different trophic levels.
2. What are the First Organisms in a Food Chain?
Producers are the first organism in the food chain. They are also known as autotrophs and form the first trophic level. They produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis.
3. What are Animals called in a Food Chain?
Animals in the food chain are consumers as they can not produce their own food and consumes other plant and animals as their food. They form the second trophic level in the food chain.
4. What role do humans play in a food chain?
Humans play the role of omnivores in food chains.They consume both plant and animal products. Human activities can impact food chains both positively, through sustainable practices, and negatively, habitat destruction and overxploitation.
5. What do Food Chains End with?
Food chains end with decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi. They break down the remains of dead organisms and organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil, completeing the cycle. These nutrients are taken up by the plants, starting the cycle again.
Get 90% Course fee refund on completing 90% course in 90 days! Take the Three 90 Challenge today.
The next 90 Days of focus & determination can unlock your full potential. The Three 90 challenge has started and this is your chance to upskill and get 90% refund. What more motivation do you need? Start the challenge right away!
Similar Reads
What is Food Chain?
Food chain represents the direction of the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem. It consists of four main components producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and decomposers. Based on the primary source of energy there are two types of food chain: Grazing and the Detritus food
7 min read
What is Habitat?
Habitat is a natural environment where a group of plants, animals, or other organisms live and grow. In simple words, habitats are places where organisms live for food, water, and shelter to survive. There are eight major habitats on Earth. They include Grassland, Polar, Desert, Mountain, Temperate
9 min read
What is Flora and Fauna?
Life in Temperate grasslands is described as having grasses as the prevailing vegetation. Trees and huge bushes are missing. Temperatures differ more from summer to winter, and how much precipitation is less in calm prairies Temperate grasslands have sweltering summers and cold winters. Precipitatio
4 min read
What is Food Security?
Food security, as characterized by the United Nations' Committee on World Food Security, implies that all individuals, consistently, have physical, social, and financial admittance to adequate, safe, and nutritious food that meets their food inclinations and dietary requirements for a functioning an
5 min read
Food Chains and Food Webs
Food Chain and Food Web both show the direction of the flow of energy and nutrients in the ecosystem. The food chain is a linear representation of organisms along the trophic level, while the food web is multiple interconnected food chains. The food chain and food web make us understand the interact
8 min read
Overview of Grazing Food Chain
A grazing food chain is a type of food chain that involves the transfer of energy between autotrophic plants and herbivores. In a food chain, nutrients and energy flow from one organism to another at different trophic levels. The grazing food chain starts with producers. Green plants (producers) use
8 min read
What are Protists?
Based on their body's form and function, all living organisms are recognized and categorized. Several traits are likely to make more substantial physical modifications than those of others. Time has a function in additionally this, thus, once a particular body type comes into being, it will influenc
7 min read
Diagram of Food Chain
The diagram of food chain shows the flow of energy and nutrients through various organisms in an ecosystem in a linear fashion. The food chain starts with producers and ends with decomposers. A food chain diagram shows how energy passes within an ecosystem through organisms eating and being eaten. T
3 min read
What is Nutrient Cycling?
To survive, organisms need nutrients. The natural recycling process is called the nutrient cycle. From one organism to the next, an element travels in a circular pattern. Recycling is the ecological process that supports and makes additional contributions to human welfare. Nutrient CycleThe term "nu
7 min read
Diagram of Food Web
The diagram of the food web explains the network of food chains. In the food web, the food networks are interconnected. A food chain is a particular sequence where each member of the web is eaten by the other. The food web consists of producers, consumers, and the decomposers. The food web generally
5 min read
What is Seasonal Hunger?
The existence of the poor in country India is firmly administered by the repeating idea of occasional changes. This relationship turns out as expected in every agrarian local area, yet the effects are a lot more critical in the low-pay agricultural nations, where the rustic economy is still, general
3 min read
What is a Natural Ecosystem?
Natural ecosystems are self-sustaining and do not require human intervention. Natural Ecosystems are the outcome of interactions between living things and their surroundings. A few examples are lakes, woods, oceans, and deserts. A natural ecosystem is a big, interconnected community where plants, an
6 min read
Agriculture and Food Security
Food security entails ensuring that food is available, accessible, and affordable to all people at all times. When there is difficulty with food crop production or distribution, disadvantaged households are more prone to food insecurity. When food security is threatened, it is dependent on the Publi
5 min read
Digestion Of Food
Food is a substance taken from outside that nourishes the body, builds tissues, and supplies energy. Essential components of our food are mainly carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Vitamins and minerals are also needed in small quantities. Water plays a crucial role in metabolic processes and also pr
11 min read
Food Security in India
Food Security in India: Food Security and its implementation is an important aspect of the Government of India for attaining food security for all its citizens. The article gives us an idea about food subsidies, Public Distribution systems, and the challenges faced in ensuring food security for all
8 min read
Difference Between Food Chain and Food Web
The difference between a food chain and a food web lies in their complexity and structure. The Food chain and food web both represent the flow of energy and nutrients through ecosystems. A food chain represents a linear sequence of organisms where each is eaten by the next, while a food web depicts
7 min read
Digestion and Absorption
We require food on a daily basis. Food provides us with nutrients that help in growth, repair and immunity. The major nutrients of food are Proteins, Carbohydrates, Fats, Vitamins and Minerals. We cannot use food as it is. It needs to be broken down into simpler substances to make it available for u
11 min read
Facts About Animals
Facts About Animals: Animals are creatures that inhabit our planet, showcasing a remarkable diversity of shapes, sizes, and behaviours. From tiny insects to majestic mammals, the animal kingdom is full of fascinating species. In this article, we will cover some interesting facts about animals. Table
4 min read
What is Agroforestry? Types and Benefits
Agroforestry is an integrated and sustainable strategy for land management that blends traditional agricultural methods with tree cultivation, resulting in a balanced ecosystem where trees, crops, and cattle coexist for mutual benefit. Several environmental, financial, and social advantages can be d
9 min read