Regulation of Kidney Function Notes Class 11
Last Updated :
07 Oct, 2023
The Kidneys which are present in the human body are responsible for multiple functions in humans which include the formation of urine, water metabolism, ionic balance, and regulation of blood pressure. Therefore with the help of these kidneys, the wastes are being removed from human body. These kidneys are responsible for regulating water balance in human beings and also filtering waste and excess of these fluids from the blood.
Human Excretory System
A human excretory system consists of:
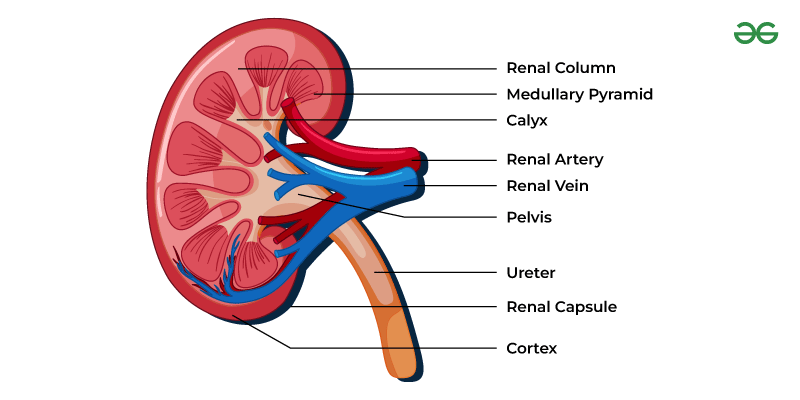
- Kidneys: Human body consists of two Kidneys which are bean-shaped structures and are reddish brown in color. They are situated between the last thoracic and lumbar vertebra. In each kidney, there consists of a notch in the inner side which is known as hilum. From this hilum, the nerves and ureter blood vessels enter.
- Ureters: They are the tube-like structure that carries out urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. There is a pair of ureters which are attached to each kidney.
- Urinary Bladder: It is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen which is a temporary storage of urine.
- Urethra: They are a normal tube-like structure that carries out the urine from the urinary bladder to outside the human body.
Regulation of Kidney Function
The Kidney function is regulated by the hormonal feedback mechanism which involves hypothalamus regulation, regulation involving Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA), and to some extent, the heart. If there is a change in blood volume, fluid volume or ionic concentration it activates the hypothalamic osmoreceptors whereas if there is excessive fluid loss or an increase in blood pressure these osmoreceptors respond by stimulating the neurohypophysis which further secrete ADH.

Main Hormones that Regulate Kidneys
The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus(JGA)
The regulation of Juxtaglomerular Apparatus(JGA) is also called the Angiotensin mechanism. Whenever the blood flow in the glomerulus decreases, renin is also released from juxtaglomerular cells. By the renal sympathetic nerves renin levels are increased through a direct action on granular cells and a decrease in the flow to the macula densa. When there is increased in renal sympathetic nerve activity it causes drop in the GFR which gradually increase the water reabsorption and proximal sodium ions. This results in reduction of fluid in the macula densa which later on helps in the renin production at high level. The Juxtaglomerular apparatus responds to decrease in blood pressure.
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
Angiotensin is an enzyme, it is located in the endothelium which is used to convert angiotensin I to angiotensin II. In the cardiovascular system angiotensin II stimulates vasoconstriction. The cardiovascular system further stimulates aldosterone production in the adrenal glands which increase the sodium reabsorption in the kidneys. The RAAS is responsible for basic regulation of blood pressure.
Hypothalamus
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) or Vasopressin
From neurohypophysis the Antidiuretic hormone or vasopressin are released if the osmoreceptors are activated. These are activated when there is a change in blood pressure or there is an excessive loss of fluids. Antidiuretic hormone stimulates the reabsorption of water from the distal parts of the tubules hence this prevents water loss and diuresis whereas when there is sufficient body fluid these osmoreceptors are switched off and therefore the release of ADH is suppressed. This ADH causes constriction of blood vessels which results in increase of blood pressure which further increases the flow of blood in the glomerulus.
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide is a 28 amino acid peptide hormone which are located in the granules in atrial myocytes. ANP is released when there is increased blood flow in the atria of the heart. Renal tubules are inhibited from reabsorbing water and salt. The reduced sodium ion and the water level enhance the urine result, allowing the blood volume to become normal. ANP exerts moderate effects in vasodilatory which results in low blood pressure but increase in capillary pressure.
Micturition
Micturition is defined as a process where urine is expelled out (passed out) from the human body. The urine which are formed in the nephron is stored in the urinary bladder until a voluntary signal is given by the CNS which involves contraction of soft muscles of the urinary bladder and relaxation of urethral sphincter which causes release in urine.
Disorders of Excretory System
Some of the disorders which are related to excretory system are mentioned below:
- Uremia: It is a type of disorder in which urea is accumulated in the blood due to malfunctioning of kidneys which can lead to kidney failures. Through the process of hemodialysis this disorder is being treated.
- Renal failure: In this condition the glomerular filtration and both the kidneys stops working. Kidney transplant is the only treatment available in this disorder.
- Renal Calculi: It is a condition in which stones salts are formed in the kidney. By operation this disorder can be cured.
- Glomerulonephritis: In this condition there is an inflammation of glomeruli happens which occurs due to the entry of protein and RBCs.
FAQs on Regulation of Kidney
1. What do you mean by Kidneys ?
Answer:
There are two Kidneys in a human body which are located in the either side of the spine below the rib cage which are used to filter the waste materials out of the blood and then pass them out of the body in the form of urine.
2. What is the role of Hypothalamus in the regulation kidney function?
Answer:
Whenever there is the change in the volume of blood or in the ionic concentration or if there is loss of excessive fluids the hypothalamus is activated and releases ADH which further stimulates reabsorption of water.
3. Which hormones are used for the regulation of Kidneys function ?
Answer:
The regulation is done by some hormones such as - the hypothalamus regulation which includes ADH and ANP, the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) and to some extent, the heart.
4. What is the role of Renin-Angiotensin mechanism in kidney function ?
Answer:
Whenever the blood flow in the glomerulus decreases, renin is released from the juxtaglomerular cells which causes increase in the glomerular blood pressure of GFR. Therefore, the regulation of Juxtaglomerular Apparatus is called as Renin-Angiotensin mechanism.
5. What is the role of kidney in excretion ?
Answer:
Kidneys are the excretory organs in human body which are used for the excretion of urea in the form of urine. The function of kidneys are monitored and regulated by feedback mechanism.
6. What are the main hormone which controls the kidney ?
Answer:
The three main hormones which controls the kidney are- Antidiuretic hormone, Atrial natriuretic peptide and the renin aldosterone.
Similar Reads
Regulation of Kidney Function Notes Class 11
The Kidneys which are present in the human body are responsible for multiple functions in humans which include the formation of urine, water metabolism, ionic balance, and regulation of blood pressure. Therefore with the help of these kidneys, the wastes are being removed from human body. These kidn
6 min read
What is the Function of Regulating Hormones?
Regulating hormones, also known as regulatory hormones, play important roles in maintaining the body's homeostasis by controlling and coordinating various physiological processes. Here are the key functions of regulating hormones: Growth and Development: Hormones like growth hormone (GH) and thyroid
2 min read
Regulation of Cardiac Activity
Different fluids make up the majority of our bodies. Body fluids are crucial for the normal operation of our tissues and perform the crucial tasks of supplying nutrients to live cells and removing toxic toxins created by our systems. Other techniques for facilitating these activities have been creat
7 min read
Osmoregulation - Definition, Types, & Importance
Osmoregulation is the physiological process that regulates the osmotic pressure in the organism through the osmoreceptors. It helps in maintaining the fluid balance of the body and electrolyte concentration. In this article, we will study the definition of osmoregulation, types of osmoregulation, Os
6 min read
Hormonal Regulation of Food Intake
The human body is a complex combination of different organs. Some organs help to gain energy; some organs help to distribute that energy. There are also some organs present that help to command the overall human body. If the human body is considered a special complex machine, then there should be a
15+ min read
Reabsorption in Kidney
The kidney is the organ that helps to eliminate harmful substances from the body. The process that helps to eliminate those substances is known as the excretion process. So, the kidney is an excretory organ. This organ helps to balance the substances in the body. The human body also has a kidney. In
13 min read
Various Modes of Excretion: Functions and Importance
Excretion is a vital natural process that enables living organisms to exclude waste products from their bodies. The process of excretion helps to maintain the internal terrain of the body by removing poisonous substances that could harm the body. The excretory system is responsible for removing wast
9 min read
Function of Lungs in Respiratory System
The function of the lung is to move oxygen from the air into the bloodstream and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. It plays a vital role in maintaining the body's oxygen levels and supporting cellular function. Additionally, the lungs function to help regulate pH levels in the blood by adjusting
8 min read
Urine Formation And Osmoregulation
Urine formation and osmoregulation are important processes that maintain the body's water and electrolyte balance. In the kidneys, filtration of blood occurs in the glomerulus, followed by reabsorption of essential substances in the renal tubules. Excess waste products and ions, along with water, ar
6 min read
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) - Functions, Regulations, Disorders and Levels
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin, is a hormone that regulates water balance in the body by controlling the amount of water reabsorbed by the kidneys. Understanding antidiuretic hormone function and secretion helps in managing water balance in the body, which is crucial for maint
7 min read
Exchange Of Gases Notes CBSE Class 11
The exchange of gases refers to the process that happens between carbon dioxide and oxygen. Gas exchange takes place between the capillaries and alveoli. The rate of diffusion depends on the solubility and thickness of the membrane which are involved in the exchange of gases. Oxygen is transferred f
4 min read
How Does a Cell Regulate Osmosis and Diffusion?
Cells regulate osmosis and diffusion through several mechanisms that ensure proper balance and function. Osmosis is the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane, while diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. How
2 min read
Structure and Functions of Heart
The human heart is life for humans because without a heart they cannot even live. Blood transportation over the body is done by the heart itself and also air transportation from the environment to the lungs is done by the heart. The average heartbeat in a day is 100,000 times. Male heart weight is a
9 min read
NCERT Solutions Class 11- Biology
Class 11 NCERT Biology Solutions are designed to help students easily understand the concept of Biology and every topic of the class 11 textbook. The NCERT Biology Solutions provided here give detailed information about NCERT textbooks. By studying these Solutions you will be able to understand the
8 min read
NCERT Notes Class 10 Control and Coordination
NCERT Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 6: Control and Coordination in the living organism mean the ability to control and coordinate different body functions to complement each other. Separately control means the ability of our body to have power of regulation over any mechanism whereas coordination m
15+ min read
Types and Functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum
The types and functions of the Endoplasmic Reticulum include the Rough ER, which synthesizes proteins, and the Smooth ER, which is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification. The Endoplasmic Reticulum diagram shows the cell organelle location within the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic Reticulum discovere
6 min read
NCERT Notes of Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
Notes on NCERT for Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals: Structural organization in animals refers to the arrangement of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems that work together through the division of labour and ensure the survival of the whole body. In this article, yo
8 min read
Mechanism of Muscle Contraction - CBSE Class 11
The mechanism of muscle contraction refers to the process by which muscles generate force and produce movement. Muscle contraction involves a complex interplay of biochemical and physiological events within the muscle fibers. When a nerve signal reaches a muscle, it triggers the release of calcium i
6 min read
Levels of Organization in Animals
The levels of organization in animals are arranged hierarchically, starting with cells, the basic unit of life. Groups of similar cells form tissues, which perform specific functions. Tissues combine to create organs, each with distinct roles in the body. Organs work together within organ systems to
8 min read