| Error code | Error no | Description |
|---|
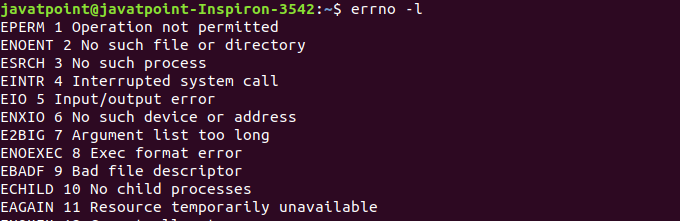
| EPERM | 1 | It is displayed if the operation is not permitted. |
| ENOENT | 2 | It is displayed if there is no such file or directory exists. |
| ESRCH | 3 | It is displayed if there is no such process exists. |
| EINTR | 4 | It is displayed for Interrupted system call |
| EIO | 5 | It is displayed for input/output error. |
| ENXIO | 6 | It is displayed if there is no such device or address exists. |
| E2BIG | 7 | It is displayed if argument list is too long. |
| ENOEXEC | 8 | It is displayed if there is an exec format error |
| EBADF | 9 | It is displayed in case of bad file descriptor. |
| ECHILD | 10 | It is displayed if there is no child process exists. |
| EAGAIN | 11 | It is displayed if resource is temporarily unavailable. |
| ENOMEM | 12 | It is displayed if the system cannot allocate memory. |
| EACCES | 13 | It is displayed if permission is denied. |
| EFAULT | 14 | It is displayed if there is a bad address. |
| ENOTBLK | 15 | It is displayed if Block device is required. |
| EBUSY | 16 | It is displayed if device or resource is busy. |
| EEXIST | 17 | It is displayed if file already exists. |
| EXDEV | 18 | It is displayed if there is invalid cross-device link. |
| ENODEV | 19 | It is displayed if there is no such device. |
| ENOTDIR | 20 | It is displayed if there is not a directory. |
| EISDIR | 21 | It is displayed if there is a directory. |
| EINVAL | 22 | It is displayed if there is an invalid argument. |
| ENFILE | 23 | It is displayed if there are too many open files in system. |
| EMFILE | 24 | It is displayed if there are too many open files. |
| ENOTTY | 25 | It is displayed if there is an inappropriate ioctl for device. |
| ETXTBSY | 26 | It is displayed if text file is busy. |
| EFBIG | 27 | It is displayed if the file is too large. |
| ENOSPC | 28 | It is displayed if there is no space left on device. |
| ESPIPE | 29 | It is displayed in case of illegal seek. |
| EROFS | 30 | It is displayed in case of read-only file system. |
| EMLINK | 31 | It is displayed if there are too many links. |
| EPIPE | 32 | It is displayed in case of broken pipe. |
| EDOM | 33 | It is displayed if numerical argument is out of domain. |
| ERANGE | 34 | It is displayed if numerical result is out of range. |
| EDEADLK | 35 | It is displayed if resource deadlock is avoided. |
| ENAMETOOLONG | 36 | It is displayed if file name is too long. |
| ENOLCK | 37 | It is displayed if no locks are available. |
| ENOSYS | 38 | It is displayed if function is not implemented. |
| ENOTEMPTY | 39 | It is displayed if directory is not empty. |
| ELOOP | 40 | It is displayed if there are too many levels of symbolic links. |
| ENOMSG | 42 | It is displayed if there is no message of desired type. |
| EIDRM | 43 | It is displayed if identifier is removed. |
| ECHRNG | 44 | It is displayed if channel number is out of range. |
| EL2NSYNC | 45 | It is displayed if level 2 is not synchronized. |
| EL3HLT | 46 | It is displayed if Level 3 is halted. |
| EL3RST | 47 | It is displayed if Level 3 is reset. |
| ELNRNG | 48 | It is displayed if the link number is out of range. |
| EUNATCH | 49 | It is displayed if protocol driver is not attached. |
| ENOCSI | 50 | It is displayed if there is no CSI structure available. |
| EL2HLT | 51 | It is displayed if Level 2 is halted. |
| EBADE | 52 | It is displayed in case of invalid exchange. |
| EBADR | 53 | It is displayed in case of invalid request descriptor. |
| EXFULL | 54 | It is displayed if exchange is full. |
| ENOANO | 55 | It is displayed in case of No anode. |
| EBADRQC | 56 | It is displayed for invalid request code. |
| EBADSLT | 57 | It is displayed for invalid slot. |
| EBFONT | 59 | It is displayed if there is bad font file format. |
| ENOSTR | 60 | It is displayed if device is not a stream. |
| ENODATA | 61 | It is displayed if there is no data available. |
| ETIME | 62 | It is displayed in case of timer is expired. |
| ENOSR | 63 | It is displayed in case of out of streams resources. |
| ENONET | 64 | It is displayed if machine is not on the network. |
| ENOPKG | 65 | It is displayed if package is not installed. |
| EREMOTE | 66 | It is displayed if object is remote. |
| ENOLINK | 67 | It is displayed if the link has been severed. |
| EADV | 68 | It is displayed for advertise error. |
| ESRMNT | 69 | It is displayed for Srmount error. |
| ECOMM | 70 | It is displayed if there is communication error on send. |
| EPROTO | 71 | It is displayed for protocol error. |
| EMULTIHOP | 72 | It is displayed for Multihop attempted. |
| EDOTDOT | 73 | It is displayed for RFS specific error. |
| EBADMSG | 74 | It is displayed for Bad message. |
| EOVERFLOW | 75 | It is displayed if value is too large for defined data type. |
| ENOTUNIQ | 76 | It is displayed if name is not unique on network. |
| EBADFD | 77 | It is displayed if file descriptor is in bad state. |
| EREMCHG | 78 | It is displayed if remote address is changed. |
| ELIBACC | 79 | It is displayed if we cannot access a needed shared library. |
| ELIBBAD | 80 | It is displayed in case of accessing a corrupted shared library. |
| ELIBSCN | 81 | It is displayed if there is .lib section in a.out is corrupted. |
| ELIBMAX | 82 | It is displayed if we are attempting to link in too many shared libraries. |
| ELIBEXEC | 83 | It is displayed if we cannot exec a shared library directly. |
| EILSEQ | 84 | It is displayed for an invalid or incomplete multibyte or wide character |
| ERESTART | 85 | It is displayed to inform that interrupted system call should be restarted. |
| ESTRPIPE | 86 | It is displayed if there is streams pipe error. |
| EUSERS | 87 | It is displayed for too many users. |
| ENOTSOCK | 88 | It is displayed for socket operation on non-socket. |
| EDESTADDRREQ | 89 | It is displayed if the destination address is required. |
| EMSGSIZE | 90 | It is displayed if message is too long. |
| EPROTOTYPE | 91 | It is displayed if the protocol is wrong type for socket. |
| ENOPROTOOPT | 92 | It is displayed if the protocol is not available. |
| EPROTONOSUPPORT | 93 | It is displayed if protocol is not supported. |
| ESOCKTNOSUPPORT | 94 | It is displayed if the Socket type is not supported. |
| EOPNOTSUPP | 95 | It is displayed if the Operation is not supported. |
| EPFNOSUPPORT | 96 | It is displayed if the protocol family is not supported. |
| EAFNOSUPPORT | 97 | It is displayed if the address family is not supported by protocol. |
| EADDRINUSE | 98 | It is displayed if the address is already in use. |
| EADDRNOTAVAIL | 99 | It is displayed if the system cannot assign requested address. |
| ENETDOWN | 100 | It is displayed if network is down. |
| ENETUNREACH | 101 | It is displayed if network is unreachable. |
| ENETRESET | 102 | It is displayed if network has dropped connection on reset. |
| ECONNABORTED | 103 | It is displayed if software caused connection abort. |
| ECONNRESET | 104 | It is displayed if connection is reset by peer. |
| ENOBUFS | 105 | It is displayed if there is no buffer space available. |
| EISCONN | 106 | It is displayed if the transport endpoint is already connected. |
| ENOTCONN | 107 | It is displayed if the transport endpoint is not connected. |
| ESHUTDOWN | 108 | It is displayed if the system cannot send after transport endpoint shutdown. |
| ETOOMANYREFS | 109 | It is displayed if there are too many references: cannot splice. |
| ETIMEDOUT | 110 | It is displayed if connection is timed out. |
| ECONNREFUSED | 111 | It is displayed if connection is refused. |
| EHOSTDOWN | 112 | It is displayed if the Host is down. |
| EHOSTUNREACH | 113 | It is displayed if there is no route to host. |
| EALREADY | 114 | It is displayed if operation is already in progress. |
| EINPROGRESS | 115 | It is displayed if the operation is now in progress. |
| ESTALE | 116 | It is displayed for Stale file handle. |
| EUCLEAN | 117 | It is displayed if structure needs cleaning. |
| ENOTNAM | 118 | It is displayed for not a XENIX named type file. |
| ENAVAIL | 119 | It is displayed if there are no XENIX semaphores are available. |
| EISNAM | 120 | It is displayed if there is a named type file. |
| EREMOTEIO | 121 | It is displayed for Remote I/O error. |
| EDQUOT | 122 | It is displayed if disk quota is exceeded. |
| ENOMEDIUM | 123 | It is displayed if there is no medium found. |
| EMEDIUMTYPE | 124 | It is displayed if there is wrong medium type. |
| ECANCELED | 125 | It is displayed if operation is cancelled. |
| ENOKEY | 126 | It is displayed if required key is not available. |
| EKEYEXPIRED | 127 | It is displayed if the key has expired. |
| EKEYREVOKED | 128 | It is displayed if the key has been revoked. |
| EKEYREJECTED | 129 | It is displayed if the key was rejected by service. |
| EOWNERDEAD | 130 | It is displayed if the Owner is died. |
| ENOTRECOVERABLE | 131 | It is displayed for no recoverable state. |
| ERFKILL | 132 | It is displayed if the operation is not possible due to RF-kill. |
| EHWPOISON | 133 | It is displayed if the memory page has hardware error. |