INNDIIAANN ASSSSOOCCIIAATIIONN OFF PPHYYSICSS TTEEACCHEER SS
NATIONAL STANDARD EXAMINATION IN PHYSICS 2012-2013
Date of Examination : 24
th
November 2012 Time 09.30 to 11.30 hrs Total time : 120 minutes (A-1, A-2 & B)
[Q.P. CODE NO.
: 1-1-6] PART-A (Total Marks : 180)
SUB-PART A-1 : ONLY ONE OUT OF FOUR OPTIONS IS CORRECT N.B. Physical constants are given at the end SUB-PART A-1
1.
Two thermally insulated compartments 1 and 2 are filled with a perfect gas and are connected by a short tube having a valve which is closed. The pressures, volumes and absolute temperatures of the two compartments are respectively (p
1
, V
1
,
T
1
) and (p
2
, V
2
,
T
2
). After opening the valve, the temperature and the pressure of both the compartments respectively are - (a)
212211
222111
221121
VVV pV p
,)TV pTV p(
)V pV p(TT
(b)
212211
21
VVV pV p
,TT
(c)
2211
222111
222111
221121
TVTV
TV pTV p
,)TV pTV p(
)V pV p(TT
(d)
21221121
VVV pV p
,2TT
Ans. [Bonus] Sol.
*Internal energy before connection R ' pCR V pCR V pC
V22V11V
[V
1
+ V
2
]
212211
VVV pV p
' p
n
1
+ n
2
=
'2'1
nn
*Law of mole conservation 'RT'RT
V' pV' p
RTV pRTV p
21222111
T ' = )TV pTV p(
)V pV p(TT
122211
221121
Comment :
No option is matching so question is bonus.
www.examrace.com

2.
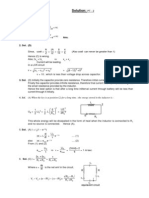
An inductance coil is connected to an ac source through a 60 ohm resistance in series. The source voltage, voltage across the coil and voltage across the resistance are found to be 33 V, 27 V and 12 respectively. Therefore, the resistance of the coil is - (a) 30 ohm (b) 45 ohm (c) 105 ohm (d) 75 ohm
Ans. [b] Sol.
L,R 60
27V12V
~
V
S
= 33
I = 516012
260R 2L2S
)VV(VV
26060R 2R 2L2S
VVV2VVV
(33)
2
= (27)
2
+ 2V
R
(12) + (12)
2
1089 = 729 + 24V
R
+ 144 24V
R
= 216 V
R
= 24216= 9 IR = 9 R = 5/19I9
= 45
3.
An ideal inductance coil is connected to a parallel plate capacitor. Electrical oscillation with energy W are set up in this circuit. The capacitor plates are slowly drawn apart till the frequency of oscillations is doubled. The work done in this process will be - (a) W (b) 2W (c) 3W (d) 4W
Ans. [c] Sol.
f = LC21
frequency is doubled when capacitance is th41 energy
U
1
= WC2Q
2
www.examrace.com
energy after shifting U
2
= 4C2Q
2
= 4W Work done = U
2
– U
1
= 4W – W = 3W
4.
Two equal masses are connected by a spring satisfying Hooke's law and are placed on a frictionless table. The spring is elongated a little and allowed to go. Let the angular frequency of oscillations be
. Now one of the masses is stopped. The square of the new angular frequency is - (a)
2
(b) 2
2
(c) 3
2
(d) 2
2
Ans. [b] Sol.
mM
= 2m
2
=
k = mk 2 When one block is stopped
12
= mk = 2
2
5.
When a particle oscillates in simple harmonic motion, both its potential energy and kinetic energy vary sinusoidally with time. If
be the frequency of the motion of the particle, the frequency associated with the kinetic energy is - (a) 4
(b) 2
(c)
(d) 2
Ans. [b] Sol.
x = A sin
t frequency is
v =
A cos
t KE = 21 mv
2
= 21 m
2
A
2
cos
2
t = 21KA
2
cos
2
t = 21KA
2
2
KA412t2cos1
(1 + cos 2
t) so, the frequency of energy is doubled
2
www.examrace.com
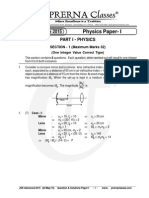
6.
A gas expands from i to f along the three paths indicated. The work done along the three paths denoted by W
1
, W
2
and W
3
have the relationship -
i13f 2VP 4 3 2 1 123456
(a) W
1
< W
2
< W
3
(b) W
2
< W
1
= W
3
(c) W
2
< W
1
< W
3
(d) W
1
> W
2
> W
3
Ans. [a] Sol.
We know W =
dV.P area under PV curve (Area)
3
> (Area)
2
> (Area)
1
W
3
> W
2
> W
1
7.
An ideal gas at 30ºC enclosed in cylinder with perfectly non conducting side and a piston moving without friction in it. The base of the cylinder is perfectly conducting. Cylinder is first placed on a heat source till the gas is heated to 100ºC and the piston raised by 20 cm and the atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. The piston is then held in final position and cylinder is placed on the heat sink to cool the gas to 30ºC. Denoting
Q
1
as the heat supplied during heating and
Q
2
as the heat lost during the cooling then [
Q
1
~
Q
2
] would be equal to (a) 436 J (b) 336 J (c) 236 J (d) 136 J
Ans. [Bonus] Sol.
Comment :
Either
cross sectional area should be given or number of moles of gas should be given in this questions
question is bonus.
Q
1
= nC
p
T – nC
v
T
n(C
p
– C
v
)
T
nR
T = PdV = P(Adx)
Not given Not given
8.
Equal amount liquid helium and water at their respective boiling points are boiled by supplying the heat from identical heaters in time t
He
and t
w
. The latent heats of vaporization of He and Water are 2.09 × 10
4
J /kg and 540 kcal/kg, then t
He
is - (a) about 0.1 t
w
(b) about 0.05 t
w
(c) just greater than 0.01 t
w
(d) just less than 0.01 t
w
Ans. [d]
www.examrace.com