Design of Microstrip Low pass filter with Defected Ground Structure
Vivek Singh Kushwah
Dept. of Electronics, Amity School of Engineering & Technology, Gwalior, India vivek_kushwah@rediffmail.com
Sarita Singh Bhadauria
Dept. of Electronics, Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior, India Saritamits61@gmail.com
Geetam Singh Tomar
Machine Intelligence Research Labs, Thatipur, Gwalior, 474011 India gstomar@ieee.org
Abstract
—
In this paper, a microstrip low pass filter hasbeen designed having circular shaped defects on ground structure (DGS). For obtaining the proposed defected ground structure, two circular shaped defected ground structure are connected by slot in the ground plane and three such defects are used for obtaining the design. The cut-off frequency of the designed filter is 1.6 GHz which is useful for the purpose of L-Band cellular communication. The highest insertion loss of the proposed filter is 31 dB and maximum return loss of 79 dB is obtained. IE3D 14.1 simulation software is used for obtaining the result.
Keywords-Microstrip Low Ppass Filters, DGS,Return loss, IE3D EM Simulation, Insertion loss
I.INTRODUCTION
Defected ground structure has turned into one of the most interesting field of research in millimeter, microwave and Radio Frequency wave applications [1], [2]. It is being used inRF and microwave circuit design such as microstrip antennas, microstrip filters,and power dividers. The minimum loss, high selectivity, high elimination and low spurious frequency band are main features of such designs. A large number of microstrip filters have been proposed and designed for obtaining the desired parameters [11]. Different types of DGS are designed by etching slot (s) onthe ground plane [7]. DGS design have good resonant character of the structure and its resonant frequency can be altered by changing the shape and size of the slot. There is an enormous development in terms of defected shapes such as L-shaped, dumbbell, periodic, fractal, circular and spiral [4], [9]. The microstrip low-pass filter with U-Shaped DGS had tried to provide compact size and to improve transition sharpness with some improvement in insertion loss by using three cascaded structure [5]. The microstrip low pass filter using double equilateral U-shaped defected ground structure has also been proposed with wide Stop band [6].Atechnique was developed for controlling the stop band of microstrip low pass filter using a new multi ring defected ground structures which has two square close-ring resonators[8]. Defected microstrip structures have also used in construction of microstrip UWB bandpass filter [13]. Such type of UWB filter consists of a cascade connection of new bandpass DMS resonators. Broadband filters had been designed by using suitably chosen impedances of transmission lines. Microstrip hairpin band pass filter had also designed using defected ground structure and open stubs [14].Stop band properties of DGS and open stubs offer broad stop band nature of filter. Microstrip filters can also be designed using slotted structures on the line having defected microstrip structures [16]. Defected microstrip structure (DMS) resonator played a very important role for realization of microstrip filter by etching an open ring in the microstrip line to eliminate the spurious response [17]. A lot of research is continuously going on in this field by employing various novel techniques in DGS or DMS, so that these techniques may also be applied in many RF or microwave applications such as microstrip antenna and filters[18],[19]. In this paper, a new circular shape DGS is proposed for the Microstrip Low Pass Filter design. The application of circular shape DGS unit is to provide sharp cut off frequency response as well as a goodperformance in the pass band and the stopband.
II.DESIGNOFMICROSTRIPLOWPASSFILTER USINGCIRCULARSHAPEDEFECTEDGROUNDSTRUCTURE
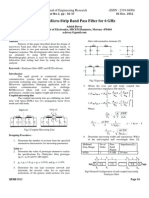
The proposed DGS unit is obtained by etching a slot between two circular shapes defected ground structure in the ground plane, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure1. A constituent of circular shaped defected ground structure and its equivalent circuit
DGS unit has slot length 10 mm, slot width 1 mm and the radius of the circular shape structure is 2 mm. The
2015 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks
978-1-5090-0076-0/15 $31.00 © 2015 IEEEDOI 10.1109/CICN.2015.1112

resonant characteristics of the circular DGS are mainly affected by its radius. Figure 1 represents proposed DGS cell and its equivalent resonant circuit.
If ω
0
is the angular resonance frequency, Z
0
is the characteristic impedance of
the microstrip transmission line and ω
c
is the 3-dB cutoff frequency. Then the corresponding resonant (L-C-R) parameters of the proposed structure are calculated as given below [2].
=
2
(
−
) ()=14(
)
()=2
1|
(
)|
−2
−1
−1 ()
The circular shaped DGS has been used for low pass filter design and spurious pass band suppression, though such structures experience slow cutoff characteristic in certain frequency bands [21].To overcome this, H-shape open stubs have been employed in single DGS cell to enhance coupling capacitance between the microstrip line and the circular DGS. Hence reduce the size of microstrip low pass filter and improve the stop band characteristics. By adding additional DGS cells for improving the out of band suppression.
III
.GENERALIE3DDESIGNLAYOUTOFDGSMICROSTRIPFILTERANDSIMULATEDRESULTS
Figure 2(a) and 2(b) represents the top and ground layer IE3D design layout of proposed microstrip low pass filter. The equivalent circuit of the proposed microstrip low pass filter is shown in Figure 2(c) with optimized dimensions based on the analysis of unit cell. The simulated result of simple microstrip low pass filter without any defected ground structure (DGS) is illustrated in Figure 3 and the simulated performance of microstrip low pass filter with three circular shaped DGS is shown in Figure 4. The length of stub is directly proportional to its parallel equivalent capacitance. While increasing the length of stub, capacitance increased. Due to such type of larger capacitance, the out of band suppression will turn into lower and the pass band to stop band attenuation slop will be converted into sharper. Microstrip filter is fabricated on an FR4 dielectric substrate having following design parameters. Dielectric constant=4.4 Substrate thickness=1.6 mm. Cut-off frequency=1.6 GHz
Top structure Dimensions of the filter:
Total length of Filter (L) = 13.5 mm. Total width of Filter (W) =8 mm.Spacing between resonators = 3.5 mm. Length of resonators=8 mm. Width of resonators= 1mm.
Characteristic impedance 50Ω line width=2.9 mm.Characteristic impedance 50Ω line length=5 mm.
Defected ground structure Dimensions of the filter
Radius of the circle shape DGS (r)= 2 mm, Slot length (l
c
) of middle DGS=3 mm, Slot length (l) of corner DGS=10 mm Slot width (s) of all three DGS=1 mm
Figure 2(a). Outer layer of the proposed microstrip low pass filter Figure 2(b). Ground layer of the proposed microstrip low pass filter
13
Figure 2(c). Equivalent RLC Circuit of the proposed low pass filter
Figure 3 and Figure 4 represent the comparison of Simple and proposed Defected Ground (DGS) design It is clear from the results obtained from simulation that DGS structure exhibits more sharp and accurate response as compared to simple design. The maximum insertion loss of the simple microstrip filter is 20 dB and maximum return loss is 72 dB as shown in Figure 3 whereas the highest insertion loss of the proposed microstrip filter using DGS structure is 31 dB and maximum return loss is 79 dB as shown in Figure 4.Hence it is clearly distinguished that DGS design is much better as compared to simple design. Figure 5 exhibits the phase response of the proposed DGS design which shows the phase or group delay properties of the DGS design. Smith Chart of the proposed DGS filter design is shown in Figure 6 which shows the impedance matching properties of the proposed DGS microstrip lowpass filter.
Figure 3.Simulated result of simple microstrip low pass filter without DGS Figure 4.Simulated result of the proposed microstrip low pass filter with DGS
.
Figure 5.Phase Response of the proposed microstrip low pass filter Figure 6.Smith Chart of the proposed microstrip low pass filter
IV.CONCLUSION
It is obvious from the performance graph of the proposed design of microstrip filter that the half power cut-
14
off frequency is obtained at 1.6 GHz which is applicable for L-band applications such as cellular mobile communication, satellite communication and satellite navigation. The defected ground plane structure is used for significantly improving the low pass filter characteristics and an improved 79 dB rejection stopband is achieved with the proposed DGS filter. Microstrip filter is fabricated and analyzed using the proposed structure dimensions parameters. The proposed microstrip filter has very compact size. It has very low return loss, sharp cutoff, high insertion loss in the stopband and high return loss,low insertion loss in the pass band which is the desired characteristics of an ideal microstrip low pass filter.
References
[1] Jia-
Shen G.Hong & M.J.Lancaster, “Microstrip Filters fo
r RF/
Microwave Applications,” John Wiley & Sons Inc., 2001.
[2]
D.Ahn, J.S. Park, C.S. Kim, J. Kim, Y. Qian, and T. Itoh, “A design of
the low-pas filter using the novel microstrip defected ground structure
,”
IEEE Transaction on Microwave Theory & Techniques, pp. 86
–
93, 2001. [3]H-W. Liu, Z-F. Li, X.-W. Sun and J-
F Mao, “An improved 1
-D periodic defected ground structure for micro-strip line,
”
IEEE Microwave and Wireless Component Letters, vol. 14, pp. 180-182, April 2004. [4
] S. W. Ting, K.W. Tam, and R. P. Martins, “Miniaturized Microstrip
Lowpass Filter With Wide Stopband Using Double Equilateral U-Shaped Defected Ground Structure
,”
IEEE Microwave And wireless component Letters, vol. 16, No.5, pp.1309-1531, May 2006. [5]Boutejdar, A. Rama
dan, M. Makkey and A. S. Omar, “
Design of Compact Microstrip Lowpass Filters Using U-Shaped Defected Ground
Structure and Compensated Microstrip Line”, IEEE 36th Europian
Microwave Conference, pp. 267-270, 2006. [6]Sio-Weng T., Kam-Weng Tam
and R.P. Martins, “
Miniaturized Microstrip Lowpass Filter with Wide Stopband using Double Equilateral U-
Shaped Defected Ground Structure,” IEEE Microwave and wireless
components letters, Vol.16, No.5, pp.240-242, 2006. [7
] B. Wu, B. Li, and C. Liang, “Design of lowpass filter using novel split
-
ring resonator defected ground structure,”
Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, Vol. 49, pp.288
–
291, 2007. [8] Boutejdar, A. Batmanov, A. Elsher
bini, A. Omar and E. P. Burte, “
A Simple Method to Control the Reject Band of Microstrip Low Pass Filter Using a New Multi-
Ring Defected Ground Structures,” IEEE International
Symposium on Antennas and Propagation Society, pp.1-4, 2008. [9]
Piscarreta,D. and S. W. Ting, “Microstrip parallel coupled
line
bandpass filter with selectivity improvement using
U-shaped defected g
round structure,”
Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, Vol. 50, No. 4,pp.911
–
915,2008. [10]
Boutejda, A. Elsherbini,and A. Ornar, “Design of a novel ultra
-wide
stopband lowpass filter using h
-
defected ground structure,”
Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, Vol. 50,No. 3,pp.771
–
775, 2008. [11]Wei, F., Li, B., Shi, X.W.
, Huang, Q.L., and Wang, X.H.: “
Design of an compact microstrip low-pass filter using defected ground structure,
”
Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, Vol. 50, issue 12, pp. 3157
–
3160, 2008. [12]
X. Q. Chen, R. Li, S. J. Shi, Q. Wang, L. Xu, andX. W. Shi, “A novel low pass filter using elliptic shape defected ground structure,” Progress In
Electromagnetic Research,Vol.9, pp. 117
–
126, 2008. [13]
S. Fallahzadeh and M. Tayarani, “A
New Microstrip UWB Bandpass
Filter Using Defected Microstrip Structures,” International Journal of
Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, Taylor & Francis, Vol. 24, pp. 893
–
902, 2010. [14]
K. Vidhya and T.Jayanthy, “
Design of Microstrip Hairpin Bandpass
Filter Using Defected Ground Structure and Open Stubs,” International
Conference on Information and Electronics Engineering IPCSIT vol.6, pp. 268-272, 2011. [15] Abraham Ortega, Leonardo R.A.X. de Menezes, A.J. Martins Soares
and Humberto Abdalla Jr., “
Design of low-pass microstrip filters based on defected ground structure
,” IEEE international conference on Microwave
and optoelectronics, pp.69-74,2011.[16] D. Cheng, H.-C. Yin and H.-
X. Zheng, “
Investigation on a Defected Microstrip Structure and Applic
ations in Designing Microstrip Filters,”
International Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, Taylor & Francis, Vol. 26, No. 10, pp.1332-1340, 2012. [17] S. Fallahzadeh
, A. Akbarzadeh & M. Tayarani, “
Spurious Response Suppression in Microstrip Bandpass Filters using Defected Microstrip
Structures” Taylors and Francis; International Journal of Electronics, Vol.
100, pp.389-400, 2013 [18]
G. M. Rafiquzzaman, Abu Talha Sadi, and Md. Nurunnabi Mollah, “
Anew approach to design microstrip low pass filter using novel defected ground structure
,” IEEE Interna
tional Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (ICECE), pp. 568-571,2014. [19]Vivek Singh Kushwah, Shivani Jain, Gaurav Saxena,
“Design of
Microstrip Patch
Antenna using Defected Microstrip Structure,” 5th IEEE
International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, pp. 37-40, 2015. [20] Chen
iaoqun
ang Lingxia
eng Lihong
“
Compact low pass filter using novel elliptical shape DGS.Journal of Mirowaveand OpticalTechnologyLetters
Vol.51, Issue 4, pp.1088-1091, 2009.
15