Artificial Reproductive Technology
- 1. PRESENTED BY: Mr.Abrar Rashid Wani 4th Year Bsc(N) RajaRajeswari College Of Nursing, Bangalore
- 2. Assisted Reproductive technology is defined as the technology used to achieve pregnancy in procedures such as artificial insemination, in vitro fertilization and surrogacy.
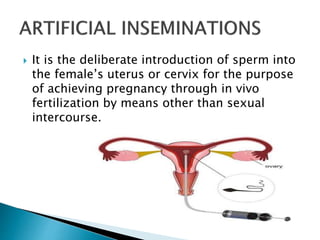
- 4. It is the deliberate introduction of sperm into the female’s uterus or cervix for the purpose of achieving pregnancy through in vivo fertilization by means other than sexual intercourse.
- 5. Intracervical insemination Intrauterine insemination Intratubal insemination
- 6. The seminal vesicle is prepared in the laboratory (washed with special media). Injected inside the uterus with catheter after stimulating the ovaries to produce more eggs per cycle. The catheter used here is known as ‘TOM CAT’
- 7. It involves injection of unwashed or raw semen into the cervix with the needleless syringe. A vaginal speculum is used to hold open the vagina so that cervix may be observed and then syringe is inserted ,the plunger is pushed forward and semen is emptied deep in the vagina.
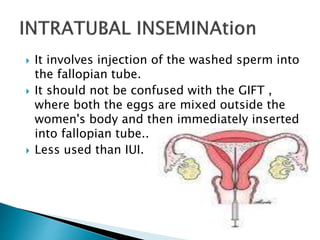
- 8. It involves injection of the washed sperm into the fallopian tube. It should not be confused with the GIFT , where both the eggs are mixed outside the women's body and then immediately inserted into fallopian tube.. Less used than IUI.
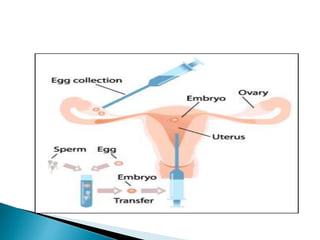
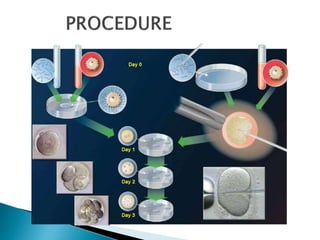
- 10. In Vitro Fertilization is the uniting of egg and sperm in vitro(in the lab).Subsequently the embryos are transferred into the uterus through the cervix and pregnancy is allowed to begin. It is the technique of letting fertilization of male and female gametes occur outside the female body.
- 11. Most commonly used are: 1. Transvaginal ovum retrieval (OCR)fallopian 2. Embryo Transfer 3. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection 4. Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer 5. Gamet Intrafallopian Transfer 6. Surrogacy
- 12. Less commonly used are: 1. Cytoplasmic Transfer 2. Assisted Zona Hatching 3. Egg Donors 4. Sperm donation 5. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis 6. Embryo Splitting 7. Cryopreservation
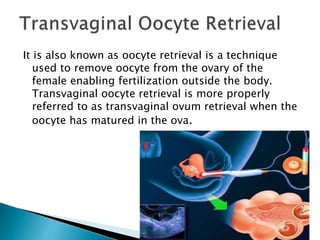
- 13. It is also known as oocyte retrieval is a technique used to remove oocyte from the ovary of the female enabling fertilization outside the body. Transvaginal oocyte retrieval is more properly referred to as transvaginal ovum retrieval when the oocyte has matured in the ova.
- 14. Under ultrasound guidance, the operator inserts a needle through the vaginal wall and into an ovarian follicle, taking care not to injure organs located between the vaginal wall and the ovary. The other end of the needle is attached to a suction device. Then the follicular fluid and cellular material is suctioned with the needle. The procedure usually lasts 10-20 minutes
- 15. It is an in vitro fertilization procedure in which a single sperm is injected directly into an egg. It is beneficial in the case of male factor infertility where sperm counts are very low. The first child borne from gamete micromanipulation was a child in Singapore born in April of 1989. The first activated embryo by ICSI was produced in1990, but the first successful birth by ICSI took place on January 14, 1992.
- 17. Low sperm count Poor sperm motility Abnormally high amount of morphologically atypical sperm Obstruction in the epididymus due to past inflammation retrograde ejaculation Immunological factors
- 18. It refers to a step in the process of assisted reproduction in which embryos are placed in the uterus of the female to establish the pregnancy In embryo transfer the embryos are placed in a woman’s uterus. The goal is to create a pregnancy. The embryos can be either fresh or frozen. if they are frozen, they can thawed right before they are transferred. It is the last step in a type of fertility treatment.
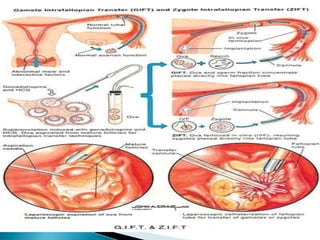
- 21. It is an infertility treatment used when a blockage in the fallopian tubes prevents the normal binding of sperm to the egg. Egg cells are removed from a woman’s ovaries, and in vitro fertilized. The resulting zygote is placed into the fallopian tube by the use of laparoscopy. It has the success rate of 64.8% in all the cases.
- 24. It is a tool of assisted reproductive technology against infertility. Eggs are removed from a woman’s ovaries , and placed in one of fallopian tubes , along with the man’s sperm. The first attempt was made by Steptoe and Edwards. It takes on average four to six weeks to complete the cycle of GIFT.
- 25. Steps: 1. The woman must take a fertility drug to stimulate egg production in the ovaries. 2. Monitoring the growth of the ovarian follicles. 3. Once they are mature, the woman will be injected the hCG. 4. After 36 hours, the eggs will be harvested mixed with the man’s sperm and placed back into the woman’s fallopian tubes using a laparoscope.
- 27. Surrogacy is when another woman carries and gives birth to a baby for the couple who want to have a child. It is the carrying of a pregnancy for intended parents. In this a woman agrees to became pregnant and deliver a child for a contracted party.
- 28. 1. Traditional surrogacy: It is the simplest and least expensive form of surrogacy and is also known as artificial insemination. The surrogate mother uses an insemination kit to became pregnant using an intended father’s semen. 2. Gestational surrogacy: It is physically more complicated and more expensive. Here both the eggs and sperm are taken from intended father and mother.
- 29. Three Steps: 1. Egg Donation 2. Fertilization 3. Transfer
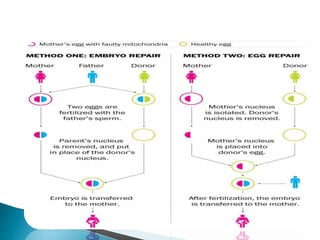
- 30. Cytoplasmic transfer: It is the technique in which the contents of a fertile egg from a donor are injected into the infertile of the patient along with the sperm. Assisted zona hatching: It is performed shortly before the embryo is transferred to the uterus . A small opening is made in the zona pellucida using a micromanipilator , thereby facilitating zona hatching to occur
- 31. Egg Donors: In egg donors eggs are retrieved from a donors ovaries, fertilized in laboratory with the sperm from recipients partner and resulting healthy embryos are returned to recipients uterus. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: It helps in identify genetically abnormal embryos and improve healthy outcomes. Embryo Splitting: It can be used for twinning to increase the number of available embryos.
- 32. Assisted Reproductive Technology involves in vitro fertilization , GIFT, ZIFT, artificial insemination and frozen embryo transfer.. These techniques can also apply to oocyte donation and gestational carriers. IVF has helped many couples to conceive successfully Surrogacy is when another woman carries and gives birth to a baby for the couple who want to have a child.