Expectorants (PCI syllabus, B.Pharm)
- 2. EXPECTORANT An expectorant Increases the amount of water in mucousal secretions Loosens up / thinning up of mucus Allows easy elimination of mucus on coughing CLASSIFICATION OF EXPECTORANTS Depending upon mechanism of action 1. Sedative expectorants 2. Stimulant expectorants
- 3. 1. SEDATIVE EXPECTORANTS These drugs irritate gastric mucosa and stimulate the release of Histamine and Acetylcholine (along with gastrin). The released Histamine and Ach combines with H-1 receptor and muscuranic receptor respectively in the lungs, causing bronchoconstriction and associated higher mucus production from the secretory cells that lines the bronchioles. PRINCIPLE: Indirectly acting expectorant STIMULATION OF GASTRIC REFLEX Eg: Bitter drugs such as Ipecac, Senega and Indian Squill 2. STIMULANT EXPECTORANT PRINCIPLE: Directly acting expectorants Stimulation of respiratory mucosal cells These drugs directly irritate the respiratory mucosal cells. This results in the production of more mucus which can be easily eliminated out from the lungs through coughing Eg: Ammonium Chloride, Pottasium Iodide, Sodium Citrate, Antimony Pottasium tartarate
- 4. Pottasium Iodide 2. White cubical crystals 3. Odourless 4. Saline followed by bitter taste 6. M.P. = 681°C 5. Highly soluble in water. Slightly soluble in ethanol 1. Mol. Formula: KI 1. Stimulant Expectorant: Directly irritates respiratory mucousal layer to initiate more mucus production. This results in thinning of the mucus and easier elimination of mucus from lungs through coughing. 2. As a Dietary supplement in Iodine deficiency and Cretenism. 3. Used to Iodize table salt
- 5. 3. Thyroprotective activity: To protect healthy thyroid gland cells from radioactive iodine (blocks thyroid gland cells from absorbing radioactive iodine that is used in cancer). 4. In Thyrotoxicosis (hyperthyrodism) and Grave’s disease until surgery can be performed. KI decreases the amount of thyroid hormones and reduced the amount of blood flow within the gland. In a radiation exposure emergency, such as leak out of radioactive material from a nuclear power plant or a nuclear bomb explosion, KI tablets are given to protect thyroid gland from radioactive 131I which can cause thyroid cancer. AMMONIUM CHLORIDE White Crystals Odourless Soluble in water, ethanol, methanol and glycerol Mp = 338°C Bp = 520°C
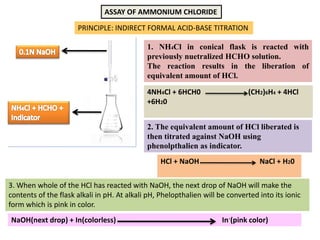
- 6. ASSAY OF AMMONIUM CHLORIDE PRINCIPLE: INDIRECT FORMAL ACID-BASE TITRATION 1. NH4Cl in conical flask is reacted with previously nuetralized HCHO solution. The reaction results in the liberation of equivalent amount of HCl. 2. The equivalent amount of HCl liberated is then titrated against NaOH using phenolpthalien as indicator. 4NH4Cl + 6HCH0 (CH2)6H4 + 4HCl +6H20 HCl + NaOH NaCl + H20 3. When whole of the HCl has reacted with NaOH, the next drop of NaOH will make the contents of the flask alkali in pH. At alkali pH, Phelopthalien will be converted into its ionic form which is pink in color. NaOH(next drop) + In(colorless) In-(pink color)
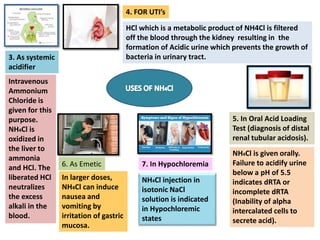
- 8. Equivalent Weight Factor Each ml of 0.1N NaOH Ξ 0.005349 g of NH4Cl 6. Calculate the percentage of NH4Cl present by putting values in the following equation MEDICINAL USES OF AMMONIUM CHLORIDE 1. As Stimulant Expectorant Irritates bronchial mucosa, thereby increasing the production of mucosal fluid. The higher volume of mucosal fluid is easier to cough up and is easier to be eliminated from Respiratory tract. 2. In hypochlorhydria and achlorhydria: Patients are administered NH4Cl so as to as to provide for the necessary acidity for the proper digestion of food.
- 9. 3. As systemic acidifier Intravenous Ammonium Chloride is given for this purpose. NH4Cl is oxidized in the liver to ammonia and HCl. The liberated HCl neutralizes the excess alkali in the blood. HCl which is a metabolic product of NH4Cl is filtered off the blood through the kidney resulting in the formation of Acidic urine which prevents the growth of bacteria in urinary tract. 4. FOR UTI’s NH4Cl is given orally. Failure to acidify urine below a pH of 5.5 indicates dRTA or incomplete dRTA (Inability of alpha intercalated cells to secrete acid). 5. In Oral Acid Loading Test (diagnosis of distal renal tubular acidosis). In larger doses, NH4Cl can induce nausea and vomiting by irritation of gastric mucosa. 6. As Emetic NH4Cl injection in isotonic NaCl solution is indicated in Hypochloremic states 7. In Hypochloremia
- 10. THANK YOU….