VAWC 2.pptx
- 1. Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004 REPUBLIC ACT 9262 GUILBERT RODINAS NOVELYN DARASIN Bachelor of Science in Social Work- 4
- 2. What is VAWC under RA 9262? It refers to any act or series of acts committed by any person against a woman who is his wife, former wife, or against a woman with whom the person has or had sexual dating relationship, or with whom he has a common child, or against her child whether legitimate or illegitimate, within or without the family abode, which result to in or is likely to result in physical, sexual, psychological harm or suffering, or economic abuse including threats of such acts, battery, assault, coercion, harassment or arbitrary deprivation of liberty.
- 3. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004 Seeks to address the prevalence of violence against women and their children (V A WC) by their intimate partners like: Husband or Ex-husband Live-in partner or former live-in partner Boyfriend/girlfriend or ex-boyfriend/ex- girlfriend Dating Partner or former dating partner Classifies VAWC as public crime
- 4. Children are those below 18 years of age or older but are incapable of taking care of themselves (as stated in RA 7610). It includes biological children of the victim and other children under her care. Dating relationship is one which has a romantic involvement. It means that a relationship existed between a woman and a partner who is abusive or has previously abused her, whether or has previously abused her, whether or not the relationship was formal. Sexual relations refer to a single sexual act which may or may not result in the bearing of a common child.
- 5. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004 VAWC includes, but not limited to the following acts: 1. PHYSICAL VIOLENCE - refers to acts that include bodily or physical harm. 2. SEXUAL VIOLENCE - refers to an act which is sexual in nature, committed against a woman or her child against a woman or her child. Boyfriend/girlfriend or ex-boyfriend/ex- girlfriend Dating Partner or former dating partner
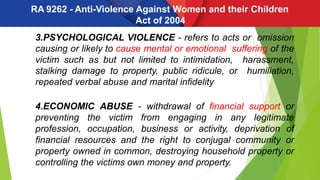
- 6. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004 3.PSYCHOLOGICAL VIOLENCE - refers to acts or omission causing or likely to cause mental or emotional suffering of the victim such as but not limited to intimidation, harassment, stalking damage to property, public ridicule, or humiliation, repeated verbal abuse and marital infidelity 4.ECONOMIC ABUSE - withdrawal of financial support or preventing the victim from engaging in any legitimate profession, occupation, business or activity, deprivation of financial resources and the right to conjugal community or property owned in common, destroying household property or controlling the victims own money and property.
- 7. Who are protected by the Anti-VAWC Act? The woman, her children, and children under her care. Children under her care are those who are not her biological children but live with her, such as her nephews or nieces, and children of her “kasambahay.” RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 8. Who are liable for VAWC? a) Husband b) Ex-husband c) The man or woman with whom she has or had a dating or sexual relationship d) The man with whom she has a child RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 9. Can a woman who is not married to the offender be protected by the Anti-VAWC? Yes, when the woman has sexual or “dating” relationship with the offender or she has a child with him. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 10. What is “dating relationship? What if there was no sexual act (just dating)? “Dating relationship” refers to a situation wherein the parties live together without marriage or when they are romantically involved with each other. It is not necessary that parties have sexual relationship, it is sufficient that they are just romantically involved over time. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 11. Can a woman who had a single sexual act with the offender file a case under the Anti-VAWC Act? Yes, a single sexual act is included in sexual relationship”. So if the offender threatens to publicly humiliate the woman after they had a one sexual act, the woman can file for a Protection Order and/or a criminal case. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 12. What acts are included in VAWC? 1. Physical violence 2. Sexual violence 3. Psychological violence 4. Economic Violence 5. Other forms of violence such as subjecting the woman to public ridicule or public humiliation RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 13. Is a husband’s infidelity a form of violence? Yes, it is a form of psychological violence. They must be married, because RA 9262 states “marital infidelity” RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 14. When the husband/ex-husband/boyfriend/ ex- boyfriend/ex-partner refuses to give sufficient support to his wife, is that an act of VAWC? Yes. For example, if he gives an insufficient amount of support even if he is financially capable. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 15. Can a husband who forces his wife to have sexual intercourse be liable under the Anti- VAWC Act? Yes, he is liable under RA 8353 (The Anti-Rape Act of 1997) for marital rape and also for sexual violence under the Anti-VAWC Act. The wife can be granted protection order to ensure her safety. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 16. The Protection Order can order the husband to: a. Leave the house b. Stay away from his wife c. Give financial support to wife and minor children. If they are not married, then only the children are entitled to the support. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 17. The Protection Orders: a. Barangay Protection Order – ordering the perpetrator to desist from committing acts of violence against the family or household members particularly women and their children (15 days valid) b. Temporary Protection Order – valid for 30 days and renewable. It is issued by the Judge before the hearings begin. The Judge can grant ex parte TPO within 24 hours from application, without notice to the respondent. c. Permanent Protection Order- issued until the hearings are finished. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 18. No, a BPO cannot order the respondent to leave the house. But the barangay officials should advise the respondent to obey the BPO or else they can file a criminal case for violation of the BPO. Violation of the BPO has a penalty of 30 days of imprisonment. Can a BPO remove respondent from the house?
- 19. What are the reliefs available to the woman? 1. Apply for a Protection Order 2. File a criminal complaint – VAWC is a public crime 3. File an action for damages – a victim of VAWC is entitled to actual, compensatory, moral and exemplary damages RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 20. Who can file for a Petition for TPO and PPO? 1. The woman (survivor/victim) 2. Parent or guardian of the woman 3. Relatives within the 4th civil degree on consanguinity or affinity of the woman such as aunts, uncles, and first cousins and persons married to them 4. Social workers 5. Police officer RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 21. Who can file for a Petition for TPO and PPO? 5. Punong Barangay or Barangay Kagawad 6. Lawyers, therapist, health care provider of the woman 7. At least two (2) responsible citizens of the city or municipality where the VAWC occurred who have personal knowledge of the offense committed. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 22. What is the penalty for the violation of the Anti-VAWC Act? a. For physical violence: Parricide – life imprisonment Murder – 17 years, 4 mos amd 1 day Homicide – 17 years, 4 mos and 1 day b. For deprivation of financial support – 6 mos, 1 day to 2 years, 4 mos imprisonment c. For psychological abuse – 6 years, 1 day to 12 years of imprisonment d. For threats or physical violence : 4 mos, 1 day to 6 mos imprisonment. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 23. Until when can the woman file a criminal case for the violation of the Anti-VAWC Act? She can file the criminal case within 10 or 20 years. For deprivation of support, the wife can file a criminal case within 20 years RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 24. Jane was so scared of her live-in partner (who was beating her up for 5 years) that she only decided to file the complaint for violation of Anti-VAWC Act 3 years after his last physical violence and they separated. Can she still file the complaint? YES. Under Sections 5 (a) to 5 (f) of the Anti-VAWC Act she has twenty (20) years to file the complaint from the time the physical violence happened. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 25. What are the rights of VAWC victims under the Anti-VAWC Act? a. Treated with respect and dignity b. Avail of legal assistance from PAO of DOJ or legal assistance office of the city, municipality or provincial government (LGU) c. To be entitled to support services from DSWD and LGU d. To be entitled to all legal remedies and support as provided for in the Family Code e. To be informed of their rights and the services available to them including their right to apply for a protection order. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 26. If the father of a minor child does not give financial support, what criminal cases can be filed against him? Violation of Section 5 (e) 2 of the Anti-VAWC Act and RA No. 7610 (Anti-Child Abuse Law).
- 27. Is a husband who is depriving his wife of custody of their minor children liable under the Anti-VAWC Act? YES, depriving the wife or threatening the wife that he will deprive her of custody of their minor children is psychological abuse. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 28. Is there any liability for persons who come to the aid of the woman when they enter her house upon hearing her shouts for help? None. Any person, private individual, police officer, social worker, teacher or barangay official who helped the victim, shall not be liable for any criminal, civil or administrative liability, provided that he/she did not use violence or force greater than necessary to ensure the safety of the woman. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 29. Can the Judge advice the woman to reconcile with her husband or partner or compromise or withdraw her civil case for protection order or criminal case? No. The Judge may not do so, otherwise he may be administratively liable. RA 9262 - Anti-Violence Against Women and their Children Act of 2004
- 30. VAWC-Free Community Starts with Me Speak, or forever hold your peace. Help is just a phone call away!
- 31. THANK YOU!