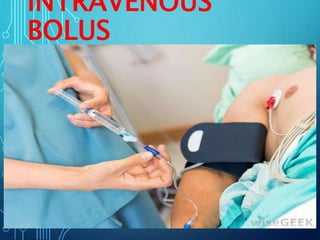
Intravenous Bolus Procedure
- 2. INTRODUCTION • A relatively large dose of medications are administered into the vein in a short period usually 1 to 30 minutes • The IV bolus is not used for patients who have decreased cardiac output or systemic edema • The IV bolus is commonly used when rapid administration is needed
- 3. DEFINITION • An IV bolus involves introducing a concentrated dose of a drug directly into the systemic circulation • IV bolus may be given directly into a vein into an existing IV line through an injection port or through a saline or heparin lock
- 4. INDICATIONS • It provides control of over dosage • For quick administration of medication • For patients who DO NOT like to take medications orally • For quick absorption of medication
- 5. CONTRAINDICATION • An iv bolus should never be given if the insertion site appears puffy or edematous • If the fluid from the connecting iv line cannot flow at a proper rate • When the iv line is not in place • When the medication is oilly or thick in substance it should not be given through push
- 6. PREPARARTION OF ARTICLE, NURSE, ENVIRONMENT AND PATIENTPREPARATION OF ARTICLES .Syringe 10 ml .Iv push existing line .Vial or ampule of medication .Sterile needle (21 or 25 G) .Alcohol swab (wet cotton) .Clean gloves .Paper bag .Kidney tray .Medication card .Syringe tray .Label for medication .Posiflush
- 8. PREPARATION OF NURSE CONTINUED… • CHECK DOCTORS ORDER. • COLLECT ALL THE ARTICLES FOR THR PROCEDURE. • PERFORM HAND HYGIENE.
- 10. PREPARATION OF PATIENT CONTINUED • EXPLAIN THE PROCEDURE TO THE PATIENT. • PROVIDE COMFORTABLE POSITION. • PROVIDE MORAL SUPPORT.
- 12. PREPARATION OF ENVIRONMENT CONTINUED • ENSURE ADEQUATE LIGHT AND VENTILATION. • PROVIDE PRIVACY. • KEEP THE UNIT CLEAN. • KEEP THE CARDIAC TABLE NEAR TO THE PATIENTS BEDSIDE FOR EASY ACCESS.
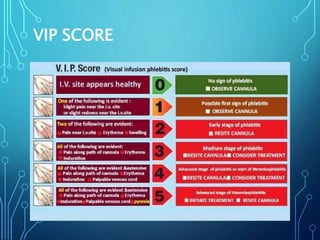
- 13. VIP SCORE
- 14. COMPLICATION • Local : infiltration extravarationt/ thrombosis • Systemic : embolism of air hematoma systemic infection circulatory overload allergic reaction