Ependymoma
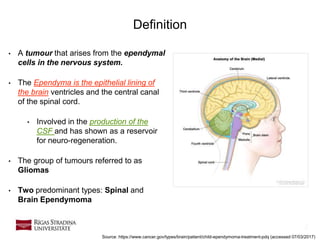
- 2. 2 • A tumour that arises from the ependymal cells in the nervous system. • The Ependyma is the epithelial lining of the brain ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord. • Involved in the production of the CSF and has shown as a reservoir for neuro-regeneration. • The group of tumours referred to as Gliomas • Two predominant types: Spinal and Brain Ependymoma Definition Source: https://www.cancer.gov/types/brain/patient/child-ependymoma-treatment-pdq (accessed 07/03/2017)
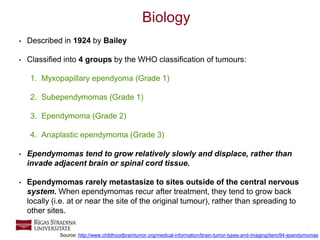
- 3. 3 Biology • Described in 1924 by Bailey • Classified into 4 groups by the WHO classification of tumours: 1. Myxopapillary ependyoma (Grade 1) 2. Subependymomas (Grade 1) 3. Ependymoma (Grade 2) 4. Anaplastic ependymoma (Grade 3) • Ependymomas tend to grow relatively slowly and displace, rather than invade adjacent brain or spinal cord tissue. • Ependymomas rarely metastasize to sites outside of the central nervous system. When ependymomas recur after treatment, they tend to grow back locally (i.e. at or near the site of the original tumour), rather than spreading to other sites. Source: http://www.childhoodbraintumor.org/medical-information/brain-tumor-types-and-imaging/item/84-ependymomas
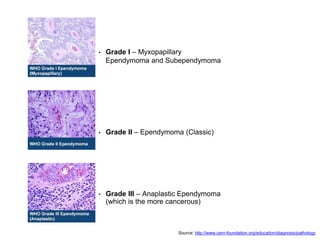
- 4. • Grade I – Myxopapillary Ependymoma and Subependymoma • Grade II – Ependymoma (Classic) • Grade III – Anaplastic Ependymoma (which is the more cancerous) Source: http://www.cern-foundation.org/education/diagnosis/pathology
- 5. 5 • Intracranial ependymomas represent 6-9% of primary CNS neoplasms and account for 30% of primary CNS neoplasms in children younger than 3 years. • The incidence of ependymoma is approximately equal in males and females. • Ependymomas generally present in young children with a mean age of diagnosis of 4 years, yet 25-40% of patients are younger than 2 years. • Spinal ependymomas are most common in patients aged 15-40 years, most of which are of a myxopapillary subtype. Epidemiology
- 6. 6 • Symptoms are dependant on the location of the tumour, typically found in three major locations: • The posterior fossa (below the tentorium, containing the cerebellum and the brainstem), • The supratentorium (above the tentorium containing the cerebral hemispheres), • The spinal cord In adults, >75% of ependymomas arise within the spinal canal, but in children, about 90% arise within the brain in the posterior fossa, in or around the fourth ventricle and only 10% arise within the spinal cord. Presentation/Symptoms Source: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/ependymoma
- 7. 7 • (60%) are located in the posterior fossa (infratentorial), usually arising from the floor of the fourth ventricle. This is especially true in children. • The remainder (40%) are located supratentorially and up to half of these are intraparenchymal. • Posterior fossa ependymomas has the propensity to grow out of the - Foramina of Luschka into the Cerebellopontine angle into the Foramen of Magendi hence the term plastic ependymoma. From here it can spread into the spine. • Ependymomas are typically heterogeneous masses with areas of necrosis, calcification, cystic change and haemorrhage frequently seen. General radiographic features
- 8. 8 Imaging modalities • X-ray • CT • MRI • Nuclear medicine
- 9. 9 X-ray • Primarily of historical interest since the onset of CT in 1974 • Was useful for detecting increased intra- cranial pressure and intracranial calcification.
- 10. 10 • Most intracranial neoplasms are visible on CT • Tumours may be hypodense, isodense or hypotense on a non-contrast CT depending on tumour histology and location. • Small tumours or isodense tumours may be missed on non-contrast CT but highlight after contrast administration • CT is preferred for visualising tumour calcification or haemorrhage. CT
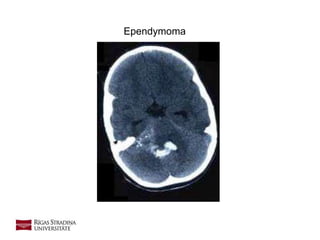
- 11. Ependymoma
- 12. 12 MRI • MRI is the diagnostic modality of choice in the workup and follow-up observation of intracranial neoplasms, including ependymoma. • MRI exploits the use of increased water content of many neoplasms. This water concentration shows up as increased signal on T2 weighted images and decreased signal on T1 images • MRI is used to monitor ongoing treatment and to search for recurrence. • Final diagnosis is achieved through biopsy with histopathologic analysis.
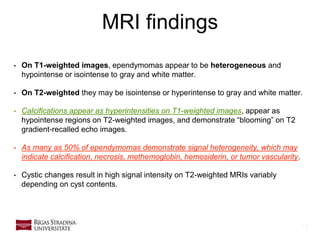
- 13. 13 MRI findings • On T1-weighted images, ependymomas appear to be heterogeneous and hypointense or isointense to gray and white matter. • On T2-weighted they may be isointense or hyperintense to gray and white matter. • Calcifications appear as hyperintensities on T1-weighted images, appear as hypointense regions on T2-weighted images, and demonstrate “blooming” on T2 gradient-recalled echo images. • As many as 50% of ependymomas demonstrate signal heterogeneity, which may indicate calcification, necrosis, methemoglobin, hemosiderin, or tumor vascularity. • Cystic changes result in high signal intensity on T2-weighted MRIs variably depending on cyst contents.
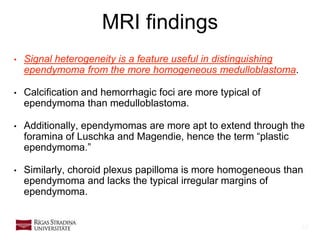
- 14. 14 • Signal heterogeneity is a feature useful in distinguishing ependymoma from the more homogeneous medulloblastoma. • Calcification and hemorrhagic foci are more typical of ependymoma than medulloblastoma. • Additionally, ependymomas are more apt to extend through the foramina of Luschka and Magendie, hence the term “plastic ependymoma.” • Similarly, choroid plexus papilloma is more homogeneous than ependymoma and lacks the typical irregular margins of ependymoma. MRI findings
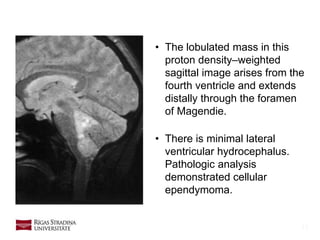
- 15. 15 • The lobulated mass in this proton density–weighted sagittal image arises from the fourth ventricle and extends distally through the foramen of Magendie. • There is minimal lateral ventricular hydrocephalus. Pathologic analysis demonstrated cellular ependymoma.
- 16. 16 MRI Gadolinium • Contrast (often gadolinium I/V) helps visualise small tumours that don't cause much oedema. • Enhancement with IV gadolinium is useful in differentiating tumour from adjacent vasogenic oedema and normal brain parenchyma. • Without intravenous contrast enhancement, T2-weighted images are more reliable in differentiating tumour margins than are T1-weighted images.
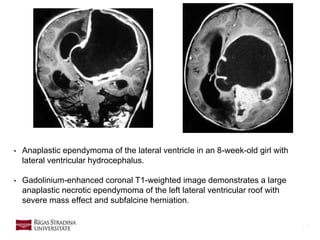
- 17. 17 • Anaplastic ependymoma of the lateral ventricle in an 8-week-old girl with lateral ventricular hydrocephalus. • Gadolinium-enhanced coronal T1-weighted image demonstrates a large anaplastic necrotic ependymoma of the left lateral ventricular roof with severe mass effect and subfalcine herniation.
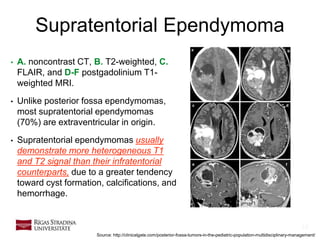
- 18. 18 Supratentorial Ependymoma • A. noncontrast CT, B. T2-weighted, C. FLAIR, and D-F postgadolinium T1- weighted MRI. • Unlike posterior fossa ependymomas, most supratentorial ependymomas (70%) are extraventricular in origin. • Supratentorial ependymomas usually demonstrate more heterogeneous T1 and T2 signal than their infratentorial counterparts, due to a greater tendency toward cyst formation, calcifications, and hemorrhage. Source: http://clinicalgate.com/posterior-fossa-tumors-in-the-pediatric-population-multidisciplinary-management/
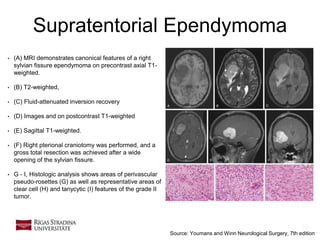
- 19. 19 Supratentorial Ependymoma • (A) MRI demonstrates canonical features of a right sylvian fissure ependymoma on precontrast axial T1- weighted. • (B) T2-weighted, • (C) Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery • (D) Images and on postcontrast T1-weighted • (E) Sagittal T1-weighted. • (F) Right pterional craniotomy was performed, and a gross total resection was achieved after a wide opening of the sylvian fissure. • G - I, Histologic analysis shows areas of perivascular pseudo-rosettes (G) as well as representative areas of clear cell (H) and tanycytic (I) features of the grade II tumor. Source: Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery, 7th edition
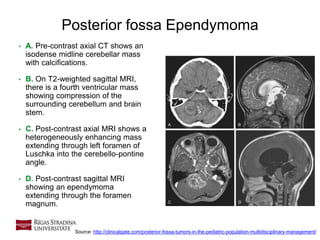
- 20. 20 Posterior fossa Ependymoma • A. Pre-contrast axial CT shows an isodense midline cerebellar mass with calcifications. • B. On T2-weighted sagittal MRI, there is a fourth ventricular mass showing compression of the surrounding cerebellum and brain stem. • C. Post-contrast axial MRI shows a heterogeneously enhancing mass extending through left foramen of Luschka into the cerebello-pontine angle. • D. Post-contrast sagittal MRI showing an ependymoma extending through the foramen magnum. Source: http://clinicalgate.com/posterior-fossa-tumors-in-the-pediatric-population-multidisciplinary-management/
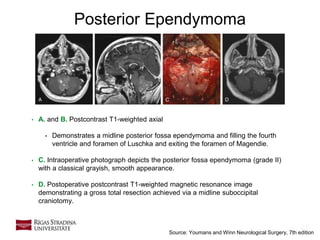
- 21. 21 Posterior Ependymoma • A. and B. Postcontrast T1-weighted axial • Demonstrates a midline posterior fossa ependymoma and filling the fourth ventricle and foramen of Luschka and exiting the foramen of Magendie. • C. Intraoperative photograph depicts the posterior fossa ependymoma (grade II) with a classical grayish, smooth appearance. • D. Postoperative postcontrast T1-weighted magnetic resonance image demonstrating a gross total resection achieved via a midline suboccipital craniotomy. Source: Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery, 7th edition
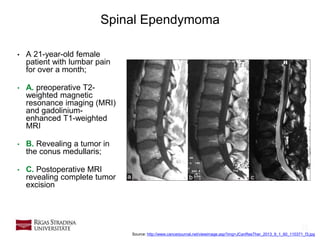
- 22. 22 Spinal Ependymoma • A 21-year-old female patient with lumbar pain for over a month; • A. preoperative T2- weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and gadolinium- enhanced T1-weighted MRI • B. Revealing a tumor in the conus medullaris; • C. Postoperative MRI revealing complete tumor excision Source: http://www.cancerjournal.net/viewimage.asp?img=JCanResTher_2013_9_1_60_110371_f3.jpg
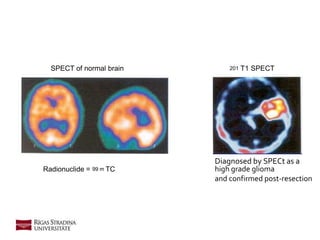
- 23. 23 Nuclear Medicine: SPECT • SPECT (Single positron emission computed tomography) • Gamma rays emitted during radionuclide decay that are detected by a gamma camera that rotates about the patients head. • The radionuclide must cross the blood-brain barrier. • The radionuclides used are: • 201 TI chloride • 99m Tc MIBI • 123 I alpha-methyl tyrosine • 111 In octreotide • Can be used in distinguishing between benign lesions, low-grade gliomas and high grade.
- 24. Radionuclide = 99 m TC SPECT of normal brain 201 T1 SPECT Diagnosed by SPECt as a high grade glioma and confirmed post-resection
- 25. 25 Nuclear Medicine: PET • Similar to SPECT but the radioisotopes used decay to produce positrons • These positrons quickly combine with adjacent electrons to produce two gamma rays that travel in opposite directions. Detection of these gamma rays allows the calculation of their exact point of origin, • Can evaluate different brain process depending on the radioisotope selected. • Radionuclides useful for PET analysis include: • Flourodeoxyglucose • C methionine • F alpha-methyl tyrosine
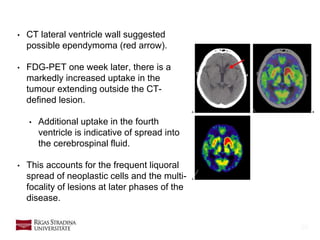
- 26. 26 • CT lateral ventricle wall suggested possible ependymoma (red arrow). • FDG-PET one week later, there is a markedly increased uptake in the tumour extending outside the CT- defined lesion. • Additional uptake in the fourth ventricle is indicative of spread into the cerebrospinal fluid. • This accounts for the frequent liquoral spread of neoplastic cells and the multi- focality of lesions at later phases of the disease.
- 27. 27 Treatment • Although total resection is optimal, it is only possible in approximately 30- 40% of cases because vital structures are frequently involved by the tumour. • Ependymomas arising above the tentorium, in the floor or roof of the fourth ventricle, or in the spinal canal are most amenable to complete resection. • Adjuvant treatment of histologically confirmed intracranial ependymoma remains an actively debated topic. • Currently, a reduced role exists for adjuvant therapy of spinal ependymoma after complete surgical resection. For patients who have postoperative residual tumor or early recurrence, radiation is considered on the basis of the individual patient's medical condition and neurological status. Source: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/277621-treatment
- 28. 28 Prognosis • 10-year overall survival rate for ependymoma can vary from 45-55%. • The current 5-year survival rate for patients with intracranial ependymomas is approximately 50%, • When rates from children and adults are combined. Stratification based on age reveals 5-year survival rates of 76% in adults and 14% in children. Source: Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery 7th edition
- 29. CASE REPORT
- 30. Patient data • Female, 39 years old • Complains about back pain for a half of year • There was MRI performed
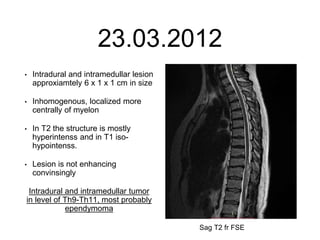
- 31. 23.03.2012 • Intradural and intramedullar lesion approxiamtely 6 x 1 x 1 cm in size • Inhomogenous, localized more centrally of myelon • In T2 the structure is mostly hyperintenss and in T1 iso- hypointenss. • Lesion is not enhancing convinsingly Intradural and intramedullar tumor in level of Th9-Th11, most probably ependymoma Sag T2 fr FSE
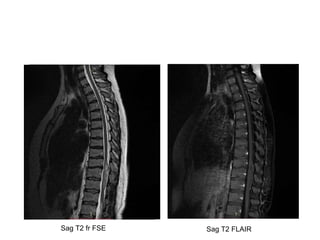
- 32. Sag T2 fr FSE Sag T2 FLAIR
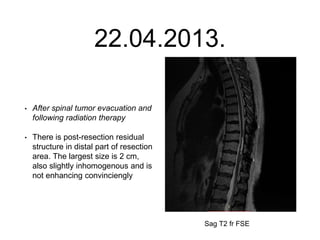
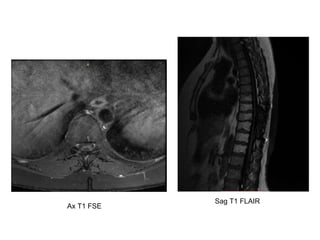
- 33. 22.04.2013. • After spinal tumor evacuation and following radiation therapy • There is post-resection residual structure in distal part of resection area. The largest size is 2 cm, also slightly inhomogenous and is not enhancing convinciengly Sag T2 fr FSE
- 34. Sag T1 FLAIR Ax T1 FSE
- 35. 35 Thank you!!!