GHTF
- 1. Medical Devices and IVDs Global HarmonizationTask Force NAME : K . SriDivya ROLLNO: 6212095205 COURSE: M-Pharmacy BRANCH : Pharmaceutical Regulatory Affairs
- 2. INTRODUCTION: • GHTF was founded in the year 1993 by the government and industry representatives of Australia ,Canada , Japan ,US and the European Union. • GHTF is to encourage convergence at the global level in the evolution of Regulatory systems for medical devices in order to facilitate trade while preserving the right of participating members to address the protection of public health by Regulatory means to considered to be most suitable.
- 3. OBJECTIVES: • Medical devices like drugs are used world wide with the rapid growth in the global market . • For medical device there is need to harmonize national standards in order to minimize regulatory barriers ,facilitate trade & improve new technologies. • Harmonization also reduce the cost by implementing regulations for government and local industry.
- 4. GOALS: • The primary way in which GLOBAL HARMONIZATION TASK FORCE (GHTF) achieves its goal is through production of harmonized guidance documents suitable for implementation or adoption by members in Regulatory authorities ,as appropriate taking into account their existing legal framework , or by nations with developing programmes. • This guidance document is one of a series that together describe a global regulatory model for Medical Devices.
- 5. PURPOSE: • Its purpose is to assist manufacturer to allocate it’s In Vitro Diagnostic(IVD) medical device to an appropriate risk class using a set of harmonized principles. • The GHTF document has principles of conformity Assessment for IVD Medical devices that contains each of the four risk classes. • The link between development of documents on classification and conformity assessment is important to ensure a consistent approach across all countries adopting the global regulatory model recommended by GHTF. So that premarket approval for a particylar device acceptable globally.
- 6. SCOPE: • GHTF document applies to all products that fall within the definition of an IVD medical devices .An IVD medical device is defined as a device which, whether used alone or in combination ,is intended by the manufacturer for the in-vitro examination of specimens derived from human body or to provide information for diagnostic, monitoring or compatibility purposes materials . This includes reagents , calibrators, control materials ,soft ware ,and related instruments and apparatus.
- 7. USES OF IVD medical devices • Diagnosis , prevention ,monitoring , treatment , or alleviation of disease. • Investigation , replacement , modification , or support of the anatomy or of a physiological process, • Supporting or sustaining life, • Aids for persons with disabilities, • Disinfection of medical devices , • Providing information by means of in vitro examination of specimens derived from the human body.
- 8. Classification of IVD medical device based on following criteria: • The intended use and indications for use as specified by the manufacturer • The technical/ scientific/medical expertise of the intended user • The importance of the information to the diagnosis , taking into consideration the natural history of disease including signs and symptoms which may guide a physician • The impact of result to the individual or to public health.
- 9. Factors Influencing IVD Medical Device Classification 1) The duration of contact of the device with the body 2) The site of the body 3) Whether the device deliver medicine or energy to the patient 4) Intended actions on the human body 5) Whether the device comes in contact with injured skin 6) Whether for diagnosis or treatment 7) The ability to reuse or not 8) Combinations of device
- 10. General Classification system for IVD Medical Devices • General classification class Risk Level Examples A Low individual Risk and Low Public Health Risk Clinical chemistry analyser, prepared selective culture media B Moderate Individual Risk and Low Public Health Risk VitaminB12, Pregnancy self- testing, Anti- Nuclear Antibody, Urine test strips C High individual Risk and Moderate Public Health Risk Blood Glucose self Testing, HLA Typing, PSA Screening ,Rubella D High Individual Risk and High Public Health Risk HIV Blood donor screening, HIV Blood diagnostic
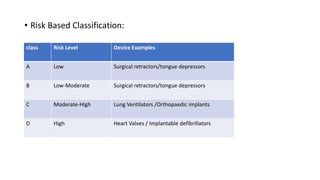
- 11. • Risk Based Classification: class Risk Level Device Examples A Low Surgical retractors/tongue depressors B Low-Moderate Surgical retractors/tongue depressors C Moderate-High Lung Ventilators /Orthopaedic implants D High Heart Valves / Implantable defibrillators
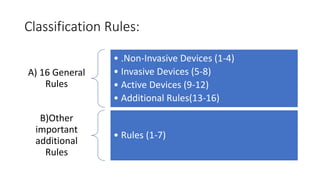
- 12. Classification Rules: A) 16 General Rules • .Non-Invasive Devices (1-4) • Invasive Devices (5-8) • Active Devices (9-12) • Additional Rules(13-16) B)Other important additional Rules • Rules (1-7)
- 13. 16 General rules • Rule-1 : in contact with injured skin and intended as a barrier • Rule -2: channel or store liquids /tissues/gases intended for infusion • Rule -3: Modify biological or body liquids intented for infusion • Rule -4 :Device or other than those where rules 1,2or3 apply • Rule-5: Invasive through body orifice • Rule -6: Surgically invasive – transient use • Rule -7: Surgically invasive – short term use • Rule -8 : Surgically invasive – long term use implants
- 14. • Rule -9: Active therapeutic devices intended to administer or exchange energy • Rule-10: Active diagnostic device • Rule -11:Active device to administer or remove medicinal products & other substance from the body • Rule- 12:Active devices other than those were in Rules 9,10or11 apply • Rule-13:Device incorporating medicinal product which has ancillary action • Rule-14: Device manufactured from or incorporating humans or animal tissue • Rule-15: Device intented specifically for sterilization of medicaldevices • Rule-16:Device used for Contaception
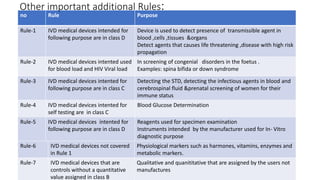
- 15. no Rule Purpose Rule-1 IVD medical devices intended for following purpose are in class D Device is used to detect presence of transmissible agent in blood ,cells ,tissues &organs Detect agents that causes life threatening ,disease with high risk propagation Rule-2 IVD medical devices intented used for blood load and HIV Viral load In screening of congenial disorders in the foetus . Examples: spina bifida or down syndrome Rule-3 IVD medical devices intented for following purpose are in class C Detecting the STD, detecting the infectious agents in blood and cerebrospinal fluid &prenatal screening of women for their immune status Rule-4 IVD medical devices intented for self testing are in class C Blood Glucose Determination Rule-5 IVD medical devices intented for following purpose are in class D Reagents used for specimen examination Instruments intended by the manufacturer used for In- Vitro diagnostic purpose Other important additional Rules: Rule-6 IVD medical devices not covered in Rule 1 Physiological markers such as harmones, vitamins, enzymes and metabolic markers. Rule-7 IVD medical devices that are controls without a quantitative value assigned in class B Qualitative and quanititative that are assigned by the users not manufactures
- 16. Conclusion: • By using an internationally recognized risk classification scheme for IVDs to determine routine regulatory oversight, regulatory authorities and conformity assessment bodies ensure that the level of assessment is proportionate to the degree of risk, taking into account the benefits offered by the IVD. Such an approach to IVD assessment takes into account the number and diversity of IVDs . • WHO recommends the adoption of this approach for WHO Member State regulating IVDs and those considering doing so. Because of its international acceptance , WHO undertakes PQ assessment activities according to the risk class as determined by applying the GHTF classification rules.
- 17. Reference • GHTF/SGI/N044:2008 Role of standards in the assessment of Medical Devices. • GHTF/SGI/N029:2005 Information Document Concerning the Definition of Term “Medical Devices”. • GHTF/SGI/N041:2005 Essential Principles of Safety and Performance of Medical Devices. • GHTF/SGI/N043:2005 Labelling for Medical Devices. • GHTF/SGI/N046:2008 Principles of conformity Assessment For In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) Medical Devices.
- 18. THANK YOU