Strategic change
- 2. Strategies change and evolve Management need to understand three considerations (1) The type of Change Required SCOPE OF CHANGE Nature of Realignment Transformation Change Incremental Adaptation Evolution Big Bang Reconstruction Revolution
- 3. (2) The wider context of Change In large part, cultural considerations Time available Capacity – resources, IS/IT, Management Effort Features to preserve Workforce readiness to change Organizational Diversity Power to effect change Capability Scope of change
- 4. (3) Force field analysis Restraining Forces Driving Forces Anxiety about job Fresh challenge in security job Change seems less Improved rewards stimulating Fear of loss of Increased job power, status discretion
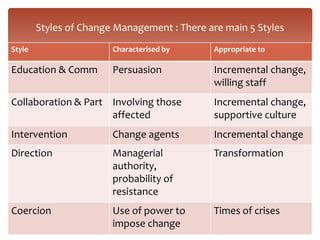
- 5. Styles of Change Management : There are main 5 Styles Style Characterised by Appropriate to Education & Comm Persuasion Incremental change, willing staff Collaboration & Part Involving those Incremental change, affected supportive culture Intervention Change agents Incremental change Direction Managerial Transformation authority, probability of resistance Coercion Use of power to Times of crises impose change
- 6. Change Management Roles Change Agents 1. Strategic leaders Five Approaches: Strategic Analysis (design focus) Human Assets (developmental focus) Expertise (as source of comp ad focus) Control (by procedure & monitoring) Change (as continuous process) 2. Middle Management 3. Outsiders
- 7. Change Management Levers Turn around strategy – when business in terminal decline CRISES STABALIZATION, MANAGEMENT CHANGES, COMMUNICATION WITH STAKEHOLDERS, ATTENTION TO TARGET MARKETS, CONCENTRATION OF EFFORT, FINANCIAL RESTRUCTURING, PRIORITIZATION
- 8. CHANGE MANAGEMENT LEVERS CHALLENGING THE PARADIGM CHANGING ROUTINES USE OF SYMBOLIC PROCESSES POWER AND POLITICS COMMUNICATION AND MONITORING TACTICS