Enamel hypoplasia ppt
- 1. 1 DEPARTMENT OF ORAL MEDICINE AND RADIOLOGY Guided by- Presented by- Dr. Vikram Khare Alankrita Sisodia Dr. Anshuman Jamdade Final year Dr. Hemant Shakya 2012-13 Dr. Satyapal yadav Dr. Neeraj Soni
- 2. 2
- 3. Definition Classification Etiology Clinical Features Radiographic features Management References 3
- 4. “An incomplete or defective formation of the organic enamel matrix of teeth.” 4
- 5. 5 1. Hereditary type enamel hypoplasia- This is an ectodermal disturbance that occurs during the embryonic development of the enamel. The mesodermal components are normal. Both the deciduous and permanent teeth are involved and only the enamel is affected.
- 6. The three types of hereditary type of enamel hypoplasia are the: • Hypoplastic type, where there is a defective formation of organic matrix. • Hypocalcification type, in which there is a defective mineralization of the matrix. • Hypomaturation type, where there is a defective maturation of the matrix 6
- 7. 2. Environmental type enamel hypoplasia- This is caused by the environmental factors that causes damage to the enamel cells. Either deciduous or permanent teeth are involved and sometimes a single tooth is involved. Here, both the enamel and the dentin are involved in varying degrees. Hypoplasia results only if the injury occurs during the time the teeth are developing or more specifically during the formative stage of enamel development. Once the enamel has calcified,no such defect can be produced. The environmental factors which produce enamel hypoplasia can include: 7
- 8. 8
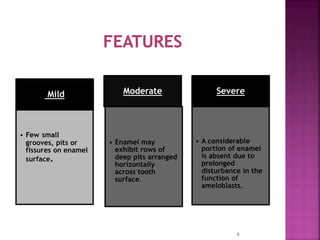
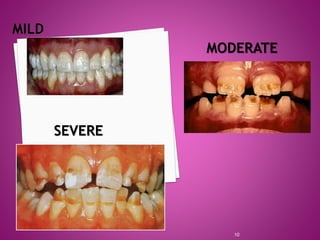
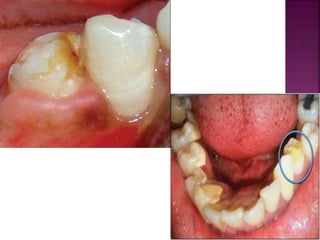
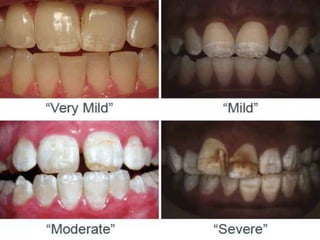
- 9. Mild • Few small grooves, pits or fissures on enamel surface. Moderate • Enamel may exhibit rows of deep pits arranged horizontally across tooth surface. Severe • A considerable portion of enamel is absent due to prolonged disturbance in the function of ameloblasts. 9
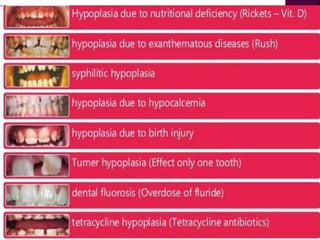
- 11. 1. HYPOPLASIA DUE TO NUTRITIONAL DEFICIENCY– Causes- It occurs due to deficiency of vit A,C,D,Calcium & Phosphorus. Age- 2/3rd of this occurs during infancy or early childhood. Site- Teeth formed within first year of birth are frequently affected. 11
- 12. Pathogenesis- Vit D deficiency causes rickketsial phenomenon due to lack of proper calcification of enamel matrix. Appearance- Horizontal pitting in rows on the teeth undergoing matrix formation at the time of dietary deficiency or during fever. Colour- Pitting picks up stains, hence discolouration occurs. 12
- 13. 2. HYPOPLASIA DUE TO EXANTHEMATOUS DISEASES- Causes- Includes measles, chicken pox and scarlet fever. Pathogenesis- Ameloblasts may be affected under increased body temperature . 13
- 14. 3. SYPHILITIC HYPOPLASIA Site- Involves maxillary and mandibular permanent incisors and first molar. Affected incisors are called as - “Hutchinson’s incisors” and molars are called as- “Mulberry molars”(Moon’s molar, Fournier’s molar) 14
- 15. Hutchinson’s Incisors- Upper central incisors are screwdriver shaped. Mesial and distal surfaces of crown are tapering and converging towards incisal edges rather than towards cervix of tooth. Incisal edge is also notched, the cause being absence of central tubercle or calcification centre. Mulberry molars- Crown of first molar in congenital syphilis is affected. Enamel of occlusal third appears to be arranged in an agglomerate mass or globule, rather than in well formed cusp and crown is narrower on occlusal surface than at cervical margin. 15
- 18. 4. HYPOPLASIA DUE TO HYPOCALCEMIA- Tetany induced by decreased level of calcium in blood : 6-8mg/100ml As calcium is required for normal tooth formation, there is defective enamel formation. Enamel hypoplasia is usually of pitting variety. 18
- 19. 5. HYPOPLASIA DUE TO BIRTH INJURY- Prenatal- Marked enamel hypoplasia affects enamel of maxillary primary incisors. It’s due to gastrointestinal tract or metabolic disturbances in the fetal life, during 2nd and 3rd trimester . Neonatal- A wide band or line of hypoplastic enamel affects the primary teeth of children associated with premature birth or low birth weight. Traumatic birth may affect amelogenesis. 19
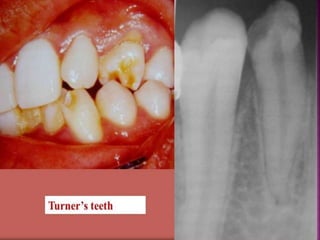
- 20. 6. TURNER’S HYPOPLASIA- Turner’s Tooth- Localized type of hypoplasia, it is caused by local infection or trauma and is called as “Turner’s Hypoplasia” and the tooth is called as Turner’s tooth. Pathogenesis- A. Local infection- If deciduous teeth become carious during the period when the crown of succeeding permanent tooth is formed, then bacterial infection involving periapical tissues may occur and this may disturb the ameloblastic layer of permanent tooth bud, resulting in hypoplastic crown. 20
- 21. B. Trauma- When deciduous teeth have been driven into alveolus and have disturbed the permanent bud while the permanent tooth bud is still being formed then resulting injury leads to yellowish or brownish stains of enamel usually on labial surface or as true hypoplastic pitting effect. Site- Most commonly affected teeth are permanent premolars as deciduous molars are most frequently affected carious tooth in primary dentition. lesion. 21
- 22. Appearance- Hypoplasia may be ranging from mild brownish discolouration of enamel to severe pitting and irregularity of crown. Cementum may also be stained yellowish-brown. 22
- 23. 23
- 24. 24
- 25. 7. HYPOPLASIA DUE TO DENTAL FLUOROSIS- Drinking water containing excess of 1 PPM (parts per million) of fluoride can affect the ameloblasts during the tooth formation stage and can cause formation of mottled enamel. Pathogenesis- A. Formative stage- Disturbance of ameloblasts during the formative stage of tooth development and higher levels of fluoride interfere with the calcification process of matrix. . 25
- 26. B. Matrix formation stage- There is diminished matrix production, change in matrix composition. C. Maturation stage- There is retention of amelogenin proteins in the enamel struture leading to formation of hypomineralized enamel.. 26
- 27. 27
- 28. Depending on the level of fluoride in water supply there is a wide range of severity in the appearance of mottled teeth varying from- 1. Questionable changes characterized by occasional white flecking or spotting of enamel. 2. Mild changes manifested by white opaque areas involving more of the surface area. 3. Moderate and severe change show pitting and brownish staining of the enamel surface and a corroded appearance of teeth and also a tendency for wear and fracture(Mottled enamel). 28
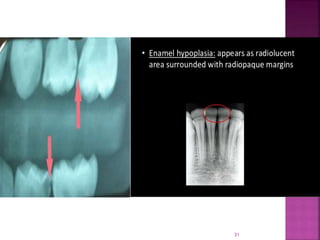
- 29. 1. Mild form- If there is slight depression or pit in the mesial or distal borders of the crown, it is apparent on a radiograph. If there is depression on the lingual or labial surface it may present as a slightly increased darkness or goes unnoticed. 2. Moderate form- More extensive lesion appears as a series of rounded dark shadows crossing the tooth in straight lines. 3. Severe form- Very gross deformity produces a crown that is markedly shriveled at its incisal and occlusal surfaces, such teeth may be presented as small spikes of dental tissue arising from a short stunted base. 29
- 30. 30
- 31. 31
- 32. 8. TETRACYCLINE HYPOPLASIA- Pathogenesis- It may be incorporated in calcified enamel matrix by formation of a tetracyline calcium orthophosphate complex. Colour of teeth- Yellow to brown and varying degrees of hypocalcification exits. Prevention- Tetracyline should not be administered in pregnancy and to the children below 8 years of age. 32
- 33. 33
- 34. Treatment of enamel hypoplasia is always individualized and depends on the location and severity of then condition. The location of enamel hypoplasia also affects treatment options : > Anterior teeth - For sensitive teeth with no wear, SuperSeal (Phoenix Dental Inc.) or another desensitizing agent (such as potassium nitrate) as needed can be used. If there are esthetic concerns, composite or porcelain veneers may be bonded to the affected tooth. 34
- 35. > Posterior teeth – 1. For sensitive teeth with minimal wear, SuperSeal (Phoenix Dental Inc.) or another desensitizing agent (such as potassium nitrate) as needed can be used. 2. For mildly hypoplastic molars, place pit and fissure sealant on the occlusal surface. - at 6 month re-evaluation, if sealant is lost, go to step 3 3. Remove demineralized enamel and restore with composite. - at 6 month re-evaluation, if composite is lost, either replace using good isolation techniques or go to step 4 4. Perform minimal reduction of tooth and cement a stainless steel crown - evaluate clinically and radiographically as indicated 35
- 36. For permanent molars, stainless steel crowns are intended for temporary use only. These teeth should be restored with a permanent cast crown in the late teen years or early adulthood. Extremely malformed teeth should be extracted and implants can be placed. In deciduous dentition cases where the first primary molars are unrestorable or marginally restorable, extraction prior to the eruption of the premolars is a reasonable alternative. 36
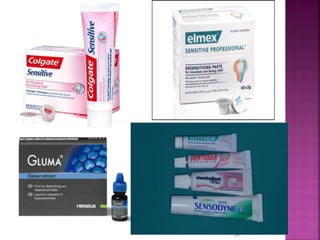
- 37. Other Treatment Options - Tooth whitening treatment can be done . Bleaching with 30% H202- It is enhanced by grinding or microabrasion of the surface layer. Can be done only in initial cases of hypoplasia. Microabrasion ,where pumice is used to abrade the discoloured area and reduce its appearance and make the teeth appear more even. 37 Desensitizing paste – Used to decrease sensitivity of teeth due to exposure of dentin.
- 38. Calcium sucrose phosphate gel- It involves cleaning of the affected teeth with pumice and glycerin and rinsing with water and applying 37% phosphoric acid for 1.5-2 minutes. This treatment is repeated , followed by application of 2% sodium fluoride for 4 minutes. Finally a thick layer of calcium sucrose gel is placed on the affected teeth . The patient is instructed not to eat anything or rinse for 30 minutes. It improves the colour of the teeth. 38
- 39. 39
- 40. Shafer’s textbook of oral pathology Burkitt’s textbook of oral medicine Pictures from the Internet 40
- 41. Thank you 41