PEB.pptx
- 1. PRE ENGINEERED BUILDING (PEB) 1 Unit : 03 Advanced Construction Methods Prepared by Mr. P .A. Nadgouda Assistant Professor D.Y.Patil College of Engineering & Technology Kolhapur
- 2. Contents • Introduction • PEB Concept • Why PEB • Components of PEB • Advantages of PEB • Difference between conventional steel building and PEB
- 3. Introduction Technological improvement over the year has contributed immensely to the enhancement of quality of life through various new products and services. One such revolution was the pre engineered buildings. Through its origin can be traced back to 1960’s its potential has been felt only during the recent years. This was mainly due to the development in technology, which helped in computerizing the design and design. 3
- 4. Introduction • Though initially only off the shelf products were available in these configurations aided by the technological development tailor made solutions are also made using this technology in very short durations. • A recent survey shows that about 60% of the non residential low rises building in USA are pre engineered buildings.
- 6. Introduction • The market potential of PEB’s : 1.2 million tones per annum. • The current pre engineered steel building manufacturing capacity : 0.35 million tones per annum. • The industry is growing at the compound rate of 25 to 30 %.
- 7. PEB concept • Pre engineered buildings are generally low rise buildings however the maximum eave height can go up to 25 to 30 meters. • Low rise buildings are ideal for offices, houses, showrooms, shop fronts etc CANOPY
- 8. PEB concept PEB is a steel structure built over a structural concept of primary members, secondary members and the cover sheeting connected to each other.
- 11. Why Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB's) • structural steel buildings gained acceptance in the USA during the early half of the 20th century. • Engineers were able to design steel buildings using standard published properties and load tables of hot rolled steel mill sections produced by most American steel mills. • Contractors preferred steel buildings to wood and concrete buildings because most quality requirements were handled by the fabricator leaving the contractor with the sole responsibility of erecting the steel structure.
- 12. Why Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB's) • Developers and Owners favored steel buildings because they were more economical, faster to construct and required less maintenance than reinforced concrete buildings which gave them a better return on investment. • PEB's use a pre-determined narrow range of raw material inventory to produce an infinite range of building geometries to satisfy virtually unlimited design requirements, functional considerations and aesthetic tastes.
- 13. Components of PEB • Built-up I – Sections (often tapered) which are used to produce the columns, rafters & beams of rigid frames, bearing frames, mezzanine structures, cranes runways, roof monitors, roof platforms, catwalks, fascias, parapets, canopies, roof extensions, etc.)
- 14. Components of PEB • Hot rolled I - Sections, channels, tubes and angles that are used in limited quantities in the PEB Steel Structure.
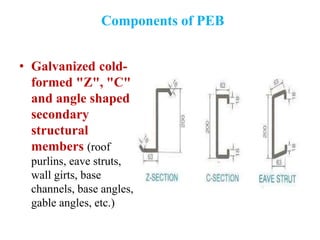
- 15. Components of PEB • Galvanized cold- formed "Z", "C" and angle shaped secondary structural members (roof purlins, eave struts, wall girts, base channels, base angles, gable angles, etc.)
- 16. Difference between conventional steel building and PEB Property PEB Conventional steel building STRUCTURE WEIGHT Pre engineered buildings are on the average 30% lighter because of the efficient use of steel. Primary framing members are tapered built up section. With the large depths in areas of higher stress. Primary steel members are selected hot rolled “T” sections. Which are, in many segments of the members heavier than what is actually required by design. Members have constant cross section regardless of the varying magnitude of the local stresses along the member length.
- 17. Difference between conventional steel building and PEB Property PEB Conventional steel building STRUCTURE WEIGHT Secondary members are light weight roll formed “Z” or “C” shaped members. Secondary members are selected from standard hot rolled sections which are much heavier
- 18. Difference between conventional steel building and PEB Property PEB Conventional steel building DESIGN Specialized computer analysis design programs optimize material required. Drafting is also computerized using standard detail that minimizes the use of project custom details. Substantial engineering and detailing work is required from the very basic is required by the consultant with fewer design aids
- 19. Applications of Pre Engineered Buildings (PEB) • WAREHOUSES • FACTORIES • WORKSHOPS • OFFICES • GAS STATIONS • VEHICLE PARKING SHEDS • SHOWROOMS • AIRCRAFT HANGARS • METRO STATIONS • SCHOOLS • RECREATIONAL • INDOOR STADIUM ROOFS • OUTDOOR STADIUM CANOPIES • BRIDGES • RAILWAY PLATFORM SHELTERS
- 20. 20 THANK YOU