Positron emission tomography
- 1. S.K.CHAUDHARY EDUCATIONAL TRUST’S SHANKARA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KUKAS, JAIPUR PRESENTED BY: ROHIT KUMAR B.TECH. 4TH YEAR 12ESIEC048 SESSION (2015-2016) POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY PRESENTED TO: MR. RAJESH KANWADIA (ASSISTANT PROF.) MS. SHWETA AGARWAL (ASSISTANT PROF.) E.C.E. DEPARTMENT 1
- 2. P.E.T. Positron Emission Tomography Presented by Ahmad Bdier
- 4. Presentation Outline What is PET? The Basic PET Process Basic Principle of PET 1) Positron Emission 2) Emission Detection A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is done to Clinical Applications of PET Advantages and Disadvantages of PET
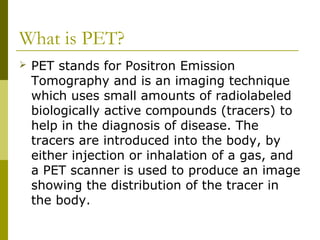
- 5. What is PET? PET stands for Positron Emission Tomography and is an imaging technique which uses small amounts of radiolabeled biologically active compounds (tracers) to help in the diagnosis of disease. The tracers are introduced into the body, by either injection or inhalation of a gas, and a PET scanner is used to produce an image showing the distribution of the tracer in the body.
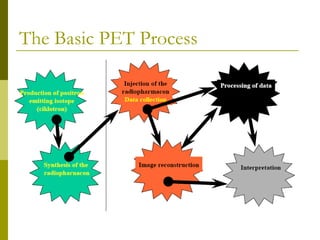
- 7. The Basic PET Process
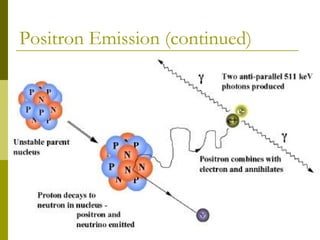
- 8. Basic Principle of PET (Positron Emission) Positron Emission occurs when the Proton rich isotope (Unstable Parent Nucleus) decays and a Proton decays to a Neutron, a Positron and a Neutrino. After traveling a short distance (3-5mm), the positron emitted encounters an electron from the surrounding environment. The two particles combine and "annihilate" each other, resulting in the emission of two gamma rays in opposite directions of 0.511 MeV each.
- 11. Positron Emission Electrons and a positron traveling after being emitted from the nucleus of the radioactive element.
- 12. Positron Emission The positron combines with electron forming positronium as an intermediate.
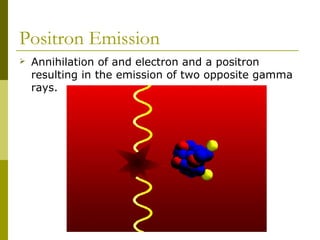
- 13. Positron Emission Annihilation of and electron and a positron resulting in the emission of two opposite gamma rays.
- 14. Positron Emission The image acquisition is based on the external detection the emitted Gamma-rays, and a valid annihilation event requires a coincidence within 12 nanoseconds between two detectors on opposite sides of the scanner. For accepted coincidences, lines of response connecting the coincidence detectors are drawn through the object and used in the image reconstruction. Any scanner requires that the radioisotope, in the field of view, does not redistribute during the scan.
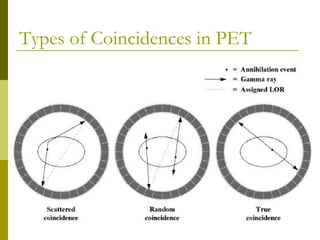
- 15. Types of Coincidences in PET
- 16. Basic Principle of PET (Emission Detection) As positron annihilation occurs, the tomograph detects the isotope's location and concentration.
- 17. Emission Detection Shown here in schematic form, the light photons are converted to electrical signals that are registered by the tomograph's electronics setup almost instantly.
- 18. Emission Detection The ring of squares represents one ring of detectors in a PET scanner, which may, for example, have fifteen such rings for simultaneous tomography of many transaxial slices
- 19. Emission Detection The tomograph's reconstruction software then takes the coincidence events measured at all angular and linear positions to reconstruct an image that depicts the localization and concentration of the radioisotope within a plane of the organ that was scanned.
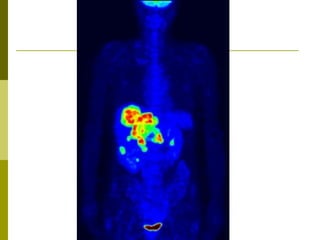
- 20. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is done to Study the brain's blood flow and metabolic activity. A PET scan can help a doctor find nervous system problems, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, transient ischemic attack (TIA), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Huntington's disease, stroke, and schizophrenia. Find changes in the brain that may cause epilepsy. Find some cancers, especially cancers of the breast, brain, lung, colon, or mouth. In its early stages cancer may show up more clearly on a PET scan than on a CT scan or an MRI. See how advanced a cancer is and whether it has spread to another area of the body (metastasized). It is often necessary to do both CT and PET scans to evaluate cancer.
- 21. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is done to Help a doctor choose the best treatment for cancer. PET scans may also be done to see whether surgery can be done to remove a tumor. Find poor blood flow to the heart, which may mean coronary artery disease. Find damaged heart tissue, especially after a heart attack. Help choose the best treatment, such as coronary artery bypass graft surgery, for a person with heart disease.
- 23. Advantages and Disadvantages of PET Advantages: PET imaging is unique in that it shows the chemical functioning of organs and tissues in vivo, while other imaging techniques – such as X-ray, CT and MRI – show structure. increased sensitivity and accurate attenuation correction provided by the PET imaging modality.
- 24. Disadvantages: • Allergic reactions to radiopharmaceuticals may occur but are rare. • Injection of the radiotracer may cause slight pain and redness which should rapidly resolve. • Expensive – due to cyclotrons needed to produce short lived radionuclides. • Low accecssbility. • Takes time.
- 25. Conclusion If we look to the clinical need instead of physical scanner parameters, then the image quality of heavy patients and the total scanning time stand out as a major challenge. While TOF scanners are just entering clinical use, it will be probably several years until they are widely available. It can be assumed that over the next few years the timing resolution will continue to improve. PET has taken a long time to move from a research tool to routine clinical use. At the same time, image quality has improved greatly.
- 26. Thank you