Banking technology
- 1. TECHNOLOGY IN BANKING Prepared By: Akshay Nayyar Vinay Chaithanya Ashay Shah Ronak Maheshwari
- 2. Inter Bank Mobile Payment System Inter Bank Mobile Payment System (IMPS), an instant 24X7 mobile payment system launched in 2010 by NPCI, is an interbank electronic fund transfer service through mobile phones. IMPS facilitates customers to use mobile instruments as a channel for accessing their bank accounts and carry out interbank fund transfers in a secured manner with immediate confirmation features. At present there are 58 banks which are providing IMPS services.
- 3. online Banking Online banking is an electronic payment system that enables customers of a financial institution to conduct financial transactions on a website operated by the institution. Online banking is also referred as Internet banking, e-banking, virtual banking and by other terms.
- 4. Use of Advanced Analytics to drive customer experience and business With Big Data, banks have an opportunity to impact the success of their marketing efforts to both new and existing customers. The best way to successfully utilize this data involves transforming it into truly actionable insights by layering in analytics and combining it with other sources of data. Some of the additional capabilities that companies in the Financial Services are using advanced analytics for are: (i) Segmentation. (ii) Understanding Customer Preferences and with the help of analytics can also be used to find out customer preferences.
- 5. Convergence Banking and Financial institutions are looking towards converged infrastructure, which combines storage, networking and compute in one unit thereby reducing the complexities associated with heterogeneity within their environments.
- 6. Mobile banking: As per the survey in India we Indians have more cell phone than the population. As now having mobile phone is common, Mobile banking is a new way through which banks are now targeting more young group and people using mobile phones. Mobile banking is a financial transaction conducted by logging on the bank website by using a mobile phone or Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) to view balance account transaction, balance checks, payments etc. Today the mobile banking service is performed mainly via SMS or the internet.
- 7. Electronic bill presentment and payment This service facilitate payment such as electricity, telephone, insurance premium and many others by permitting customers to electronically settle payments of goods and services. Customers of bank and billing companies can make use of the phone or the internet to easily remit payment as well as accessing to their billing information. EBPP can provide considerable savings to traditional print and mail billing and payment remittance and causes significant reduction in the use of paper.
- 8. Electronic fund transfer (EFT) It refers to the transfer of money from one account to another either with the same financial institution or across multiple institutions. Customer can transfer fund in any bank using EFT. It provides greater security since there is no tangible cash involved and also offer continuous connection with the bank.
- 9. ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SERVICES - E CHEQUES A new technology is being developed in US for introduction of e-cheque, which will eventually replace the conventional paper cheque. So customers now able to pay through e-cheque.
- 10. REAL TIME GROSS SETTLEMENT (RTGS) Real Time Gross Settlement system, introduced in India since March 2004, is a Interlink Research Analysis system through which electronics instructions can be given by banks to transfer funds from their account to the account of another bank. The (RTGS) Real Time Gross Settlement system is maintained and operated by the RBI and provides a means of efficient and faster funds transfer among banks facilitating their financial operations. As the name suggests, funds transfer between banks takes place on a ‘Real Time’ basis. Therefore, money can reach the beneficiary instantaneously and the beneficiary’s bank has the responsibility to credit the beneficiary’s account within two hours.
- 11. Automatic Teller Machine (ATM) As it name suggest an Automatic Teller Machine acts as a teller in a bank by giving and ting money over the counter. It an electronic device that allows customers to have access to a financial institutions in a public place. It provide facilities of any time money. People having ATM card will able to withdraws and deposit money any time. ATM is run through identity such as card and password which help to identify customer.
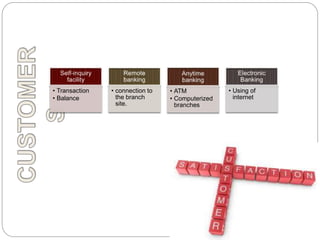
- 14. • Transaction • Balance • connection to the branch site. • ATM • Computerized branches • Using of internet
- 15. Immediate replies to the customers. Generation of various MIS reports and periodicals returns on due dates. Fast and up to date information, Speedy Decisions. Storage . Connected productivity benefits
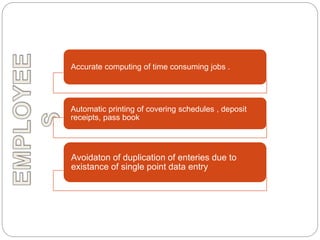
- 16. Accurate computing of time consuming jobs . Automatic printing of covering schedules , deposit receipts, pass book Avoidaton of duplication of enteries due to existance of single point data entry
- 17. Cost Risk of failure Penetration of IT in rural areas Challenge of Operations Transferring whole tradition banking to digitized. Upgrading the skill of work force spread across the country.