quality assurance in nursing
- 3. Introduction of quality and quality assurance. Objectives of quality assurance. Approaches for quality assurance. General approach. Specific approach. Models used in evaluating quality assurance . Systematic model . ANA quality assurance model. Purposes of quality assurance model.
- 4. Research evidence. Conclusion
- 6. Quality is defined as the extent of resemblance between the purpose of health care and truly granted care. Actually, quality is interactive process between customer and provider.
- 8. Quality assurance is a judgement concerning the process of care, based on the extent to which that cares contributes to valued outcomes(Donabedian 1982)
- 9. Quality assurance is the defining of nursing practice through well written nursing standards and the use of those standards as a basis for evaluation on the improvement of client care.(Maker 1989)
- 10. To ensure the delivery of quality client care. To provide technical assistance in correcting systemic deficiencies. To refine existing methods for ensuring optional quality health care. To provide the best possible results.
- 11. Approaches General approach Specific approach
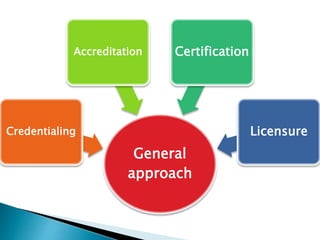
- 13. It involves large governing of official body evaluation of a person’s or agency’s ability to meet established criteria or standards at a given time.
- 15. It is the process through which a healthcare professional or agency is determined qualified to have certain medical privileges and have predetermined criteria.
- 17. It is the mandatory process by which a governmental agency grants time-limited permission to an individual to engage in a given occupation after verifying that he or she has met predetermined and standardized criteria. Examples: Licensed Estate nurse , Licensed Practice Nurse
- 18. CERTIFICATION
- 19. It is a Voluntary process by which a nongovernmental body grants a time- limited recognition to an individual after verifying that he or she has met predetermined and standardized criteria. Examples:Certified Meeting Planner, certified dialysis nurse trainer
- 21. It is a voluntary process by which a nongovernmental body grants a time- limited recognition to an organization after verifying that it has met predetermined and standardized criteria. Eg. Accredited healthcare facility
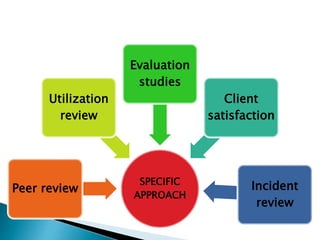
- 24. These are designed to monitor client specific aspects of care appropriate for certain levels of care. The audit has been the major tool used by peer review committee to ascertain quality of care.
- 25. Utilization review activities are directed towards assuring that care is actually needed and that the cost appropriate for the level of care provided.
- 27. Prospective: Assessment of the necessity of care before giving services. Concurrent :Review of care while the care is being given. Retrospective : Analysis after the care has being given.
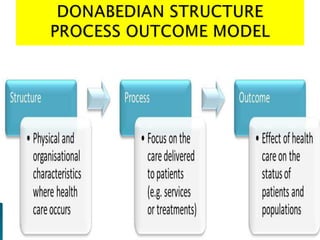
- 28. Three major models have been used to evaluate quality they are: Donabedian’s structure process outcome model The tracer model The sentinel model
- 30. Measure both process and outcome of care. Provides nurses with data to show the differences in outcomes as a result of nursing care standards.
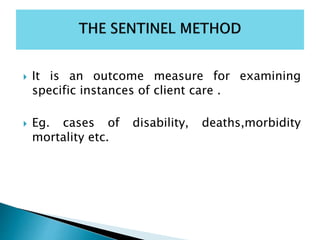
- 31. It is an outcome measure for examining specific instances of client care . Eg. cases of disability, deaths,morbidity mortality etc.
- 32. It can be assessed using person or telephone interviews and mailed questionnaire.
- 33. The critical incidents may be delayed attendance, incorrect medications, lack of cleanliness, lack of asespsis leading to infection, carelessness in carrying out nursing procedures.
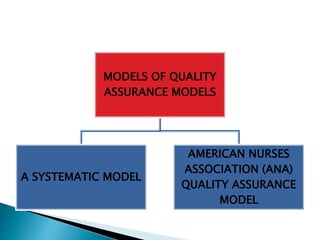
- 35. MODELS OF QUALITY ASSURANCE MODELS A SYSTEMATIC MODEL AMERICAN NURSES ASSOCIATION (ANA) QUALITY ASSURANCE MODEL
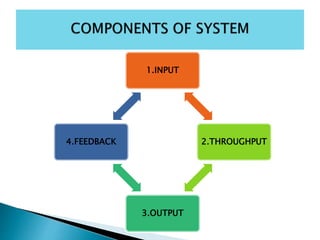
- 36. It is the system approach in which the task is broken down into manageable components based on defined objectives.
- 38. AMERICAN NURSES ASSOCIATION (ANA) QUALITY ASSURANCE MODEL
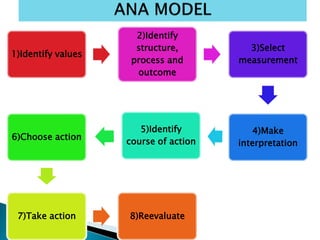
- 39. 1)Identify values 2)Identify structure, process and outcome 3)Select measurement 4)Make interpretation 5)Identify course of action 6)Choose action 7)Take action 8)Reevaluate
- 40. To ensure quality nursing care provided by nurses in order to meet the expectations of the receiver,management and regulatory body.
- 41. Title : “Donabedian's structure-process- outcome quality of care model: Validation in an integrated trauma system.” Journal :The journal of trauma and acute care surgery,2015. Authors :Moore l, lavoie A, Borgeois G, Lapointe J.
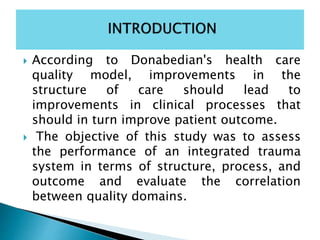
- 42. According to Donabedian's health care quality model, improvements in the structure of care should lead to improvements in clinical processes that should in turn improve patient outcome. The objective of this study was to assess the performance of an integrated trauma system in terms of structure, process, and outcome and evaluate the correlation between quality domains.
- 43. The study evalauated quality of care for patients treated in a Canadian provincial trauma system in 2005-2010 in 57 centers, n = 63,971) using quality indicators (QIs) developed and validated previously. Outcome performance was measured using risk- adjusted rates of mortality, complications, and readmission as well as hospital length of stay (LOS). Correlation was assessed with Pearson's correlation coefficients.
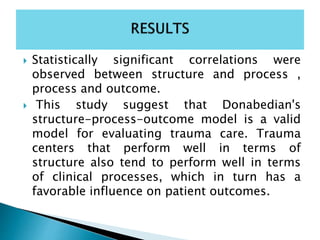
- 44. Statistically significant correlations were observed between structure and process , process and outcome. This study suggest that Donabedian's structure-process-outcome model is a valid model for evaluating trauma care. Trauma centers that perform well in terms of structure also tend to perform well in terms of clinical processes, which in turn has a favorable influence on patient outcomes.
- 45. Quality assurance is the monitoring of the activities of client care to determine the degree of excellence attained to the implementation of the activities.There are general and specific approach to assure quality.ANA quality assurance model and systematic models are the models of quality assurance.
- 46. Quality assurance is monitoring the activities of client care to determine the degree of excellence attained to the implementation of the activities and it is very essential to optional quality health care.
- 49. A) Peer review B)Accreditation C)Utilization review D)Evaluation studies B)Accreditation
- 50. 1)Donabedian’s structure process outcome model 2)The tracer model 3)The sentinel model.
- 51. Basher Shebeer.p, khan S.yaseen. A concise textbook of advanced nursing practice. 1st ed. Banglore: Emmess medical publishers; p.50- 55 Soni Samta. Textbook of advance nursing practice.1st ed. Newdelhi: jaypee brothers medical publishers; p.14-22.