Role of enzymes in metabolic reactions
- 2. are proteins that catalyze, or affect the rate, of chemical reactions without themselves being altered in the process. Specific enzymes catalyze each cellular reaction.
- 3. The main role of enzymes during metabolic reactions is to assist in transferring electrons from one molecule to another.
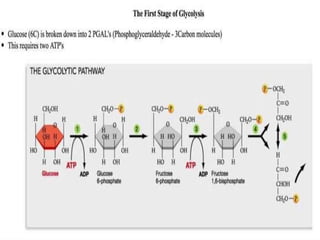
- 5. First step of the respiration takes place at cytoplasm. Consists of nine separate chemical reactions. The key players in glycolysis are the enzyme dehydrogenase and coenzyme called NAD+.
- 6. a series of reactions that constitute the first phase of most carbohydrate catabolism. Glycolysis breaks down glucose and forms pyruvate with the production of two molecules of ATP.
- 9. The second step of respiration reaction takes place inside a cell organelle called the mitochondria, which due to their role in ATP production are called “power factories” for the cell.
- 10. The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of enzyme-catalysed chemical reactions, which is of central importance in all living cells that use oxygen as part of cellular respiration. In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. The components and reactions of the citric acid cycle were established by seminal work from Albert Szent- Györgyi and Hans Krebs.
- 11. In aerobic organisms, the maerianne is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable energy. Other relevant reactions in the pathway include those in glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation before the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation after it. In addition, it provides precursors for many compounds including some amino acids and is therefore functional even in cells performing fermentation
- 13. Is a metabolic pathway which mitochondria use their structures, enzymes, released by oxidation to reform ATP. The final step of the respiration reaction also called the electron transport chain is where the energy payoff occurs for the cell.
- 14. The potential energy formed from this is stored and tapped by allowing protons to move back across the membrane, through a large enzyme ATP Synthesis. The enzyme uses the energy produced to generate ATP from ADP (adenosine diphosphate), in a phosphorylation reaction
- 17. Is the process by which plants use the sunlight as a form of energy by converting carbon dioxide. Only occurs in certain pigment-containing cell of producers. All producers contain pigments, which are essential for photosynthesis. The most common pigment in producers is chlorophyll.
- 19. During the first two stages of photosynthesis, enzymes break up the electrons from water molecules to yield oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. When it reaches the third stage, enzymes assist in the chemical reactions to produce three- carbon and six- carbon sugar.
- 21. The process of light- dependent uptake of molecular oxygen concomitant with release of carbon dioxide from organic compounds. occurs when the CO2 levels inside a leaf become low.
- 22. Photorespiration reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis for a couple of reasons.